Life Cycle of TOU Data Sets
The following diagram shows the possible lifecycle of a TOU data set.
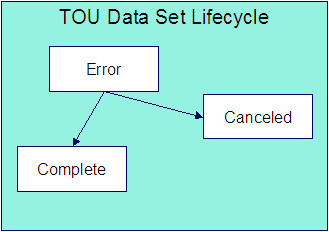
Error A creation algorithm may set this status for a data set if it detects an error condition. Data sets in this status are also written to the TOU Data Exception table. Refer to How To Correct a TOU Data Set in Error.
Canceled A user can cancel an Error data set if the data set should not be used for further processing. Refer to TOU Data Maintenance for more information. Additionally, algorithms may be designed to cancel data sets in certain situations.
Complete Only complete data sets are used by rate application and derivation algorithms. Data creation algorithms may create a data set in Complete status or change the status of a data set to Complete if no error conditions are detected. Data sets created online are set to Complete.
A user can only change the status of a data set to Canceled. All other state transitions are done by an algorithm. For more information about data creation algorithms, refer to Setting Up Classic TOU Map Types.
Creation algorithms may be written to automatically delete any Error data sets and start over in an attempt to produce a Complete data set. This is similar to the billing process, which deletes error bill segments and tries from the beginning to produce an error free segment. Another alternative is to Cancel any data sets in Error rather than deleting them.
