- Securities User Guide
- Maintain a Security
- Process Security Instruments
18.5 Process Security Instruments
This topic describes the systematic instruction to process security instruments.
- On Home pae, specify SESTRONL in the text box, and click next arrow.
Securities Instrument Definition Summary screen is displayed.
Figure 18-8 Securities Instruments Definition Summary
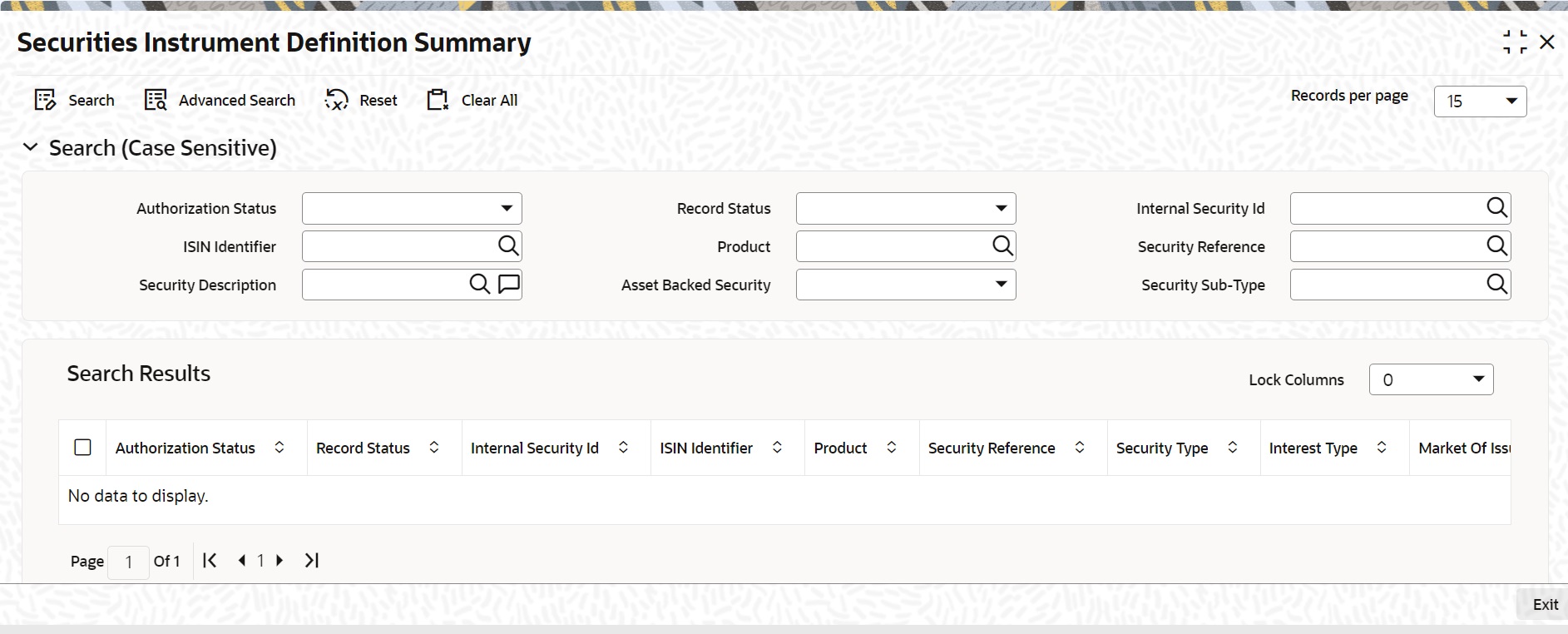
Description of "Figure 18-8 Securities Instruments Definition Summary" - On the Securities Instrument Definition Summary screen, specify the fields.
click the Search button to view all the pending functions. However, you can to filter your search based on any of the following criteria:
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- Internal Security Id
- ISIN Identifier
- Product
- Security Reference
- Security Description
When you click the Search button the records matching the specified search criteria are displayed. For each record fetched by the system based on your query criteria, the following details are displayed:
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- Internal Security Id
- ISIN Identifier
- Product
- Security Reference
- Security Type
- Interest Type
- Market Of Issue
- Issuer Code
- Registered/Bearer
- Form Type
- Quantity Quotation
- Price Quotation
- Interest Quotation
- Renounce able
- Security Currency
- Payment Currency
- Security Description
- Issue Date
- Start of Trading Date
- Redemption Date
- Maker Id
- Checker Id
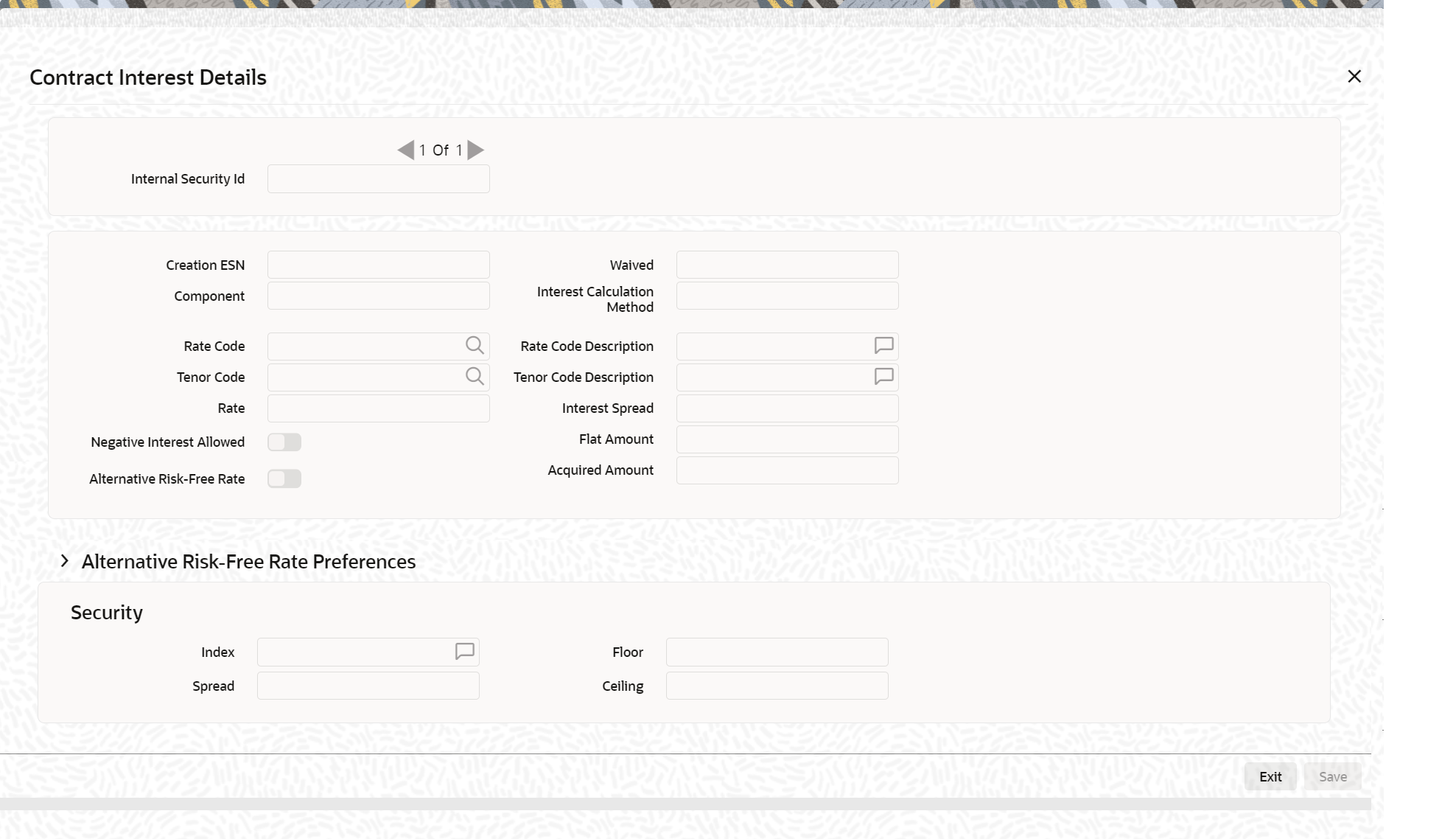
- On the Securities Instruments Definition Screen, click Interest.
Contract Interest Details screen is displayed.
- On Contract Interest Details screen, specify the fields.
For more information on fields, refer field description table.
Table 18-9 Contract Interest details - Field Description
Field Description Internal Security Id
Identify a security that you are maintaining, with a unique identifier. The identifier is referred to as the Security ID. Specify the security id.
Creation ESN
Event sequence number gets displayed by the system.
Component
Component gets displayed by the system.
Waiver
Check this box to indicate that interest on the contract should be waived.
Negative Interest Allowed
Check this box to allow negative interest for interest class. You can check this box only if interest class is maintained for Money Market, Corporate Deposit or Bills and Collections module and ‘Main Component’ flag is checked. If negative interest is allowed for an interest class, system will generate a negative interest component on saving the interest class. Negative Interest Class name is derived as Main Interest Class Code_N. If the length of main interest class code is more than 8, then the system truncates the interest class code to first eight characters and adds ‘_N”.
Rate Code
While processing a contract, you need to indicate this code to make the rate applicable to the contract. Specify a valid rate code to identify the rate you are defining. The adjoining option list displays all the valid rate code maintained in the system. You can select the appropriateone.
Tenor Code
Specify a valid tenor code to identify the tenor for which this rate code should be applicable. The adjoining option list displays all the valid tenor code maintained in the system. You can select the appropriate one.
Interest Spread
Specify the Interest spread.
Rate
Specify the interest rate.
Flat Amount
Specify the Flat amount.
Acquired Amount
Specify the acquired amount.
Interest Calculation Method
The method in which the number of days is to be calculated for interest, charge, commission or fee components and whether their application is tenor based is displayed here based on the specification you made at the product level. However, you can change it. The following are the options available in the drop-down list:
- 30(Euro)/360
- 30(US)/ 360
- Actual/360
- 30(Euro)/365
- 30(US)/365
- Actual/365
- 30(Euro)/Actual
- 30(US)/Actual
- Actual/Actual
- 30(Euro)/364
- 30(US)/ 364
- Actual/364
Alternative Risk-Free Rate Preferences
Select any one of the RFR calculation method check box from the below options:
- Lookback
- Payment Delay
- Lockout
- Interest Rollover
- Last Reset
- Last Recent
- Plain
- Weighted Average
The user can also select the combination of the below calculation method check box:- Lookback and Lockout
- Lookback and Payment Delay
- Lockout and Payment Delay
- Lookback, Lockout, and Payment Delay
Lookback
The user can select Lookback as RFR preference if the Rate Method is In-Arrears.
The observation period for the interest rate calculation starts and ends a certain number of days prior to the Interest period. As a result, you can choose the interest payment to be calculated prior to the end of the interest period.
Look Back Days
This field will only be relevant if 'Rate Method' is 'In-Arrears' or bearing and RFR method is Lookback.
Lockout
The user can select Lockout as RFR preference if the Rate Method is In-Arrears.
Lockout means that the RFR is frozen for a certain number of days prior to the end of an interest period (lockout period).
During this time, the RFR of lockout period days is applied for the remaining days of the interest period. As a result, the averaged RFR can be calculated a couple of days before the end of the Interest period.
Lockout Days
This field will only be relevant if 'Rate Method' is 'In-Arrears' or bearing and RFR method is Lockout.
Payment Delay
The user can select Payment Delay as RFR preference if the Rate Method is In-Arrears.
In this method, Interest payments are delayed by a certain number of days and are due a few days after the end of an interest period.Payment Delay Days
This field will only be relevant if 'Rate Method' is 'In-Arrears' or bearing and RFR method is Payment delay. Number of days by which the interest (or installment) payments are delayed by a certain number of days and are thus due a few days after the end of an interest period.
Interest Rollover
Select this check box to enable interest rollover as RFR preference.
Payments are set in advance and any missed interest relative to in arrears is rolled over into the next payment period.This option combines a first payment (installment payment) known at the beginning of the interest period with an adjustment payment known at the end.
Plain
The user can select Plain as RFR preference if Rate Method is In-Arrears or bearing. System uses averaged SOFR over current interest period, paid on first day of next interest period.
Index Value
Select the Index Value check box to use the RFR index rate.
The RFR Index measures the cumulative impact of compounding RFR on a unit of investment over time. Index Value supports below RFR preferences.
- Arrear Method
- Lookback
- Lockout
- Payment Delay
- Plain
- Advance Method
- Last Reset
- Last Recent
Note:
For more information on RFR Index value calculation, refer to the RFR Index Value calculation worksheet.Observation Shift
Select the Observation Shift check box to apply observation Shift to RFR calculation. The observation shift mechanism provides the rate to be calculated and weighted by reference to the Observation Period rather than the relevant interest period.
Observation Shift Currently supports below RFR Methods and combination.
- Lookback
- Lockout
- Lookback and Lockout combination
Note:
For more information on RFR Index value calculation, refer to the RFR Observation Shift calculation worksheet.Weighted Average
Select this check box to use weighted average calculation (WAC) as the RFR calculation method.
The WAC here represent the simple average calculation and not compounded. The averaged RFR in this convention is the simple arithmetic mean of the daily RFRs. OBTR supports WAC to calculate base rate (BR), Credit Adjustment Spread (CAS), and Customer Margin.
The WAC formula to calculate simple interest is:
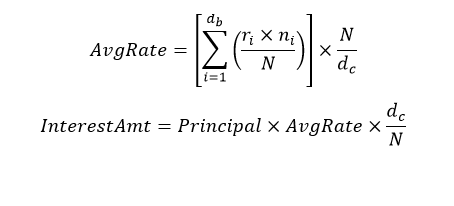
Here,
db: the number of business days for the interest calculation period
dc: the number of calendar days for the interest calculation period
ri: reference rate for the day number i within the interest calculation period
ni: the number of calendar days for which rate ri applied (on most days, ni will be 1, but on a Friday it will generally be 3, and it will also be larger than 1 on the business day before a holiday
N: the number of calendar days in one year (360 to 365)
For more information, refer to the RFR WAC sheet.
Spread Adjustment
Specify the Rate code spread adjustment.
Base Computation Method
Select the Base Computation Method from the drop-down list. The available options are:
- Simple
- Compounded
Spread/Margin Computation Method
Select the Spread\ Margin computation method from the drop-down list. The available options are:
- Simple
- Compounded
Spread Adj Computation Method
Select the Spread adjustment method is either as either Simple or compounded.
- Simple
- Compounded
Rate Compounding Method Select the Rate Compounding Method from the drop-down list. The available options are:
- CCR
- NCCR
This Rate Compounding method produces a rate for a period by applying the RFR compounding formula to the RFR rate and applying the compounded rate to the principal to calculate the interest due. Currently it’s applicable for MM & SR modules.Rate Compounding supports two methods:
1. Cumulative Compounded Rate (CCR)
Calculates the compounded rate at the end of the interest period and it is applied to the whole period. It allows calculation of interest for the whole period using a single compounded rate.
2. Non-Cumulative Compounded Rate (NCCR)
It is derived from Cumulative Compounded Rate i.e., Cumulative rate as of current day minus Cumulative rate as of prior Banking day. This generates a daily compounded rate which allows the calculation of a daily interest amount.Rate Compounding supports below RFR methods:
Arrear Method
- Lookback
- Lockout
- Payment Delay
- Plain
RFR Rounding Unit
Specify the Rounding Units value to round daily index value to the nearest whole number and use it for interest calculation. It is applicable only when RFR index value is used.
Index
Specify the index of the security.
Spread
Specify the spread component of the security.
Floor
Specify the lower limit of the security.
Ceiling
Specify the upper limit of the security.
During instrument creation and modification, user can change the RFR preferences in the interest call form.
During select and clear of the RFR flag, the respective Rate code mapping is done.
Existing Interest Spread field is used for RFR spread or margin value.
The Spread Adjustment is enabled for RFR component only.
Once an instrument is saved and authorized, the RFR preferences cannot be changed.
RFR instruments can be booked from non-RFR products and vice-versa.
Periodic revisions are not applied to RFR instruments.
RFR preferences defined at instrument level defaults to deal and cannot be modified.
To ensure that the rates are within the stipulated limits, Securities module supports Minimum and Maximum Rate pick up for RFR enabled contracts.
If the derived RFR rate for a contract considering the base rate and spread adjustment is less than the minimum rate, the minimum rate maintained is applied on the contract.
If the derived RFR rate for a contract considering the base rate and spread adjustment is greater than the maximum rate, the maximum rate is applied on the contract overriding the RFR rates.
Parent topic: Maintain a Security