- Over the Counter Options User Guide
- Define Attributes Specific to OT Products
- Maintain Products in Options Module
3.1 Maintain Products in Options Module
This topic describes the systematic instruction to maintain OT products.
You can create OT products in the OT Product Definition screen, processed from the Application Browser. In this screen, you can enter basic information relating to a product such as the Product Code, the Description, and so on.
- On Home page, type OTDPRMNT in the text box, and then click next arrow.The Options Product Definition screen is displayed.
- On the Options Product Definition screen, click New.
- On the Options Product Definition screen, specify the fields.
The first attribute you define for a product is its Type. Once you have made this basic classification, then you can tailor the product to suit your requirements. Therefore, before specifying the attributes of a product, you have to indicate whether the product is an Interest Rate option product or whether it is a Currency option product.
Since you define products for convenience, all OT deals involving the product inherit the attributes defined for the product. Yet, you have room for flexibility. You can change the inherited attributes of a specific option to suit your requirements at the time of processing it.
For any product you create in Oracle Banking Treasury Management, you can define generic attributes, such as branch, currency, customer restrictions, interest details, tax details, and so on, by clicking on the appropriate icon in the horizontal array of icons in this screen. For an OT product, in addition to these generic attributes, you can specifically define other attributes. These attributes are discussed in detail in this topic.
You can define the attributes specific to an OT product in the OT Product Definition Main screen and the OT Product Preferences screen. In these screens, you can specify the product type and set the product preferences respectively.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-1 Options Product Definition - Field Description
Field Description Product Type Specify the product type. The product type identifies the basic nature of a product. An options product that you create can either be an Interest Rate option or a Currency option. You have to specify the product preferences depending on the product type.
- On the Options Product Definition screen, under Exchange Rate Variance, specify the fields.
For a special customer, or in special cases, you can use an exchange rate (a special rate) that is greater than the exchange rate maintained for a currency pair. The variance is referred to as the Exchange Rate Variance.
When creating a product, you can express an Exchange Rate Variance Limit in terms of a percentage. This variance limit would apply to all contracts associated with the derivatives product.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-2 Options Product Definition - Field Description
Field Description The Override Limit Specify the override limit. If the variance between the default rate and the rate input varies by a percentage that is between the Override Limit and the Rate Stop Limit, you can save the deal (involving the product) by providing an override.
The Rate Stop Limit Specify the Rate Stop Limit. If the variance between the default rate and the rate input varies by a percentage greater than or equal to the Rate Stop Limit, you cannot save the deal.
Rate Code While settling charges for cross currency settlements, you can choose to debit the customer by applying the mid rate or by using the buy/sell spread over the mid-rate.
Rate Type Specify the Rate Type which should be picked up for exchange rate conversions involving settlement of charges for cross currency deals. You can maintain any one of the following as the Rate Type:
- Swaprate
- Spot
- Money
- Bills
- Standard
For further information on the generic attributes that you can define for a product, refer the following Oracle Banking Treasury Management User Manuals under Modularity:
- Product Definition
- Settlements
- On Options Product Definition, click Preferences.
The Product Preferences screen is displayed.
Preferences are the options available for defining the attributes of a product. The instruments categorized under a product can inherit the preferences that are defined for it.
Preferences screen gets displayed based on the product type. In case of an Interest rate Option product, the screen is classified into three sections:
- Main – wherein you specify the common preferences applicable to both IRO
- Interest Rate Option – wherein you can specify the attributes specific to an Interest Rate option
- Interest Rate Option Schedules – wherein you can define schedule for the IRO
In case of a currency option product, the screen has only two tabs:
- Main - wherein you specify the common preferences applicable to Currency options.
Currency Option - wherein you can specify the attributes specific to the currency options.
Each of the preferences is documented in detail in the subsequent topics.
- On the Product Preferences screen, under Main tab, specify the fields.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-3 Product Preferences - Field Description
Field Description Deal Type Specify whether the product caters to options wherein your bank is buying or selling options. You will be allowed to change this preference for a particular option.
Contract Type Specify whether the product is meant for Trade deals (Speculation on interest rate or spot rate movement) or Hedge deals (Protection against risk due to interest rate or spot rate movement). You will be allowed to change this preference while processing a specific deal.
Brokerage Allowed Select this preference, which indicates that option deals involving this product can involve brokerage.
- On the Product Preferences screen, under Main tab, specify the common details.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-4 Product Preferences - Common Details - Field Description
Field Description Expiration Style Specify any one of the following methods for contract expiration:
- European - exercise possible only on maturity date
- American - exercise possible between any pre-specified date and the maturity date
- Bermudan - exercise possible only on some pre-specified dates before the maturity date and the maturity date itself
Note:
As per swift 2023 standards, expiration style is applicable only for Plain Vanilla.Tenor (Days) Specify the periodicity of the Options deal involving the product. The periodicity is indicated in terms of days and can be changed while processing a specific contract.
Apart from Swaptions, for all other Interest Rate options, expiration is allowed only on the maturity date (European), since the settlement is always done on the Maturity Date if the option is in the- money.
For Swaptions, the expiration style can be American or Bermudan or European. Manually enter an Interest Rate swap in case of a deliverable Swaption (by specifying the details of the Interest Rate Swap in the DV Contract Online screen) and manually exercise the Swaption by entering the settlement amount (Cash settled Swaption)/Swap Value (Physically settled Swaption).
The following expiration styles are allowed for Currency Options:
Table 3-5 Expiration Styles
Field Expiration Style Plain Vanilla American, Bermudan, and European Binary NA Digital NA No Touch NA Note:
As per swift 2023 standards, expiration style is applicable only for Plain Vanilla. - On the Product Preferences screen, under Main tab, specify the Amortization Details.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-6 Product Preferences - Amortization Details - Field Description
Field Description Amortization Inception Gain Required Check this box if you want the inception gain (if any) to be amortized. At the time of inception, Gain is distributed throughout the contract - from Effective Date to Maturity Date. Amortization of Termination gain Required Specify whether you want to amortize the deferred Termination Gain if an option deal involving the product is terminated prematurely. At the time of termination, Gain is distributed throughout the period of the contract from Termination Date to Maturity Date. This feature is applicable only for hedge deals. In case of termination gain, the amortization will happen from the Date of Termination till the Maturity Date of the contract. Whereas; in case of inception gain, the amortization will happen from the Effective Date till the Maturity Date of the contract. Amortization Level Specify at which level you want the system to perform amortization. It is performed either at the Product or the Contract level. At the product level, accounting entries involving all products are netted, and a single entry is posted for all deals involving the product.
Amortization Frequency Specify the frequency of amortization. The options available are Weekly, Monthly, Quarterly, Half Yearly, and Yearly.
Amortization Start Weekday / Start Day / Start Month In case of a Weekly frequency, Specify the day of the week on which amortization should start. If the frequency is fortnightly or monthly, you have to specify the date on which the amortization starts. Similarly, when the frequency is Half-yearly or Yearly, you have to select the month of the year in which the amortization should start.
Note:
If you choose to amortize inception gain, the same is amortized over a period from the value date of the option contract till its maturity/termination irrespective of the date of payment of the premium.Processing Impact The system processes contracts involving the product based on the preferences you set. Accordingly, the following activities are performed during processing:
- Amortization is done only for deferred gains (Inception Gain, Time Value in case of hedge deals, and termination gains). There is no amortization of Inception and termination loss. These are recognized as Expenses when incurred.
- Amortization of Time Value in case of hedge deals is based on the Revaluation parameters (level, frequency, and so on) since it is the revaluation of the contract.
- The following fields are not defaulted to the contracts involving the product:
- Amortize Inception Gain
- Amortize termination gain
- Revaluation required
- Moreover, you are not allowed to modify your preferences for these options if a contract involving the product are still active.
- If a day which is not present in a month has been selected as the Amortization Start Day or Termination Start Day, the Start Day is taken as the last day of the current month. For instance, if you have selected 31 as the Amortization Start Day, with the frequency as Monthly, and the processing month is February, the processing is done on the 28th of the month. Else it is done on the 29th if it is a leap year.
- On the Product Preferences screen, under Main tab, specify the Holiday Details.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-7 Product Preferences - Holiday Details - Field Description
Field Description Holiday Treatment Specify the holiday treatment. In Oracle Banking Treasury Management, a Maturity Date falling due on a holiday is treated in any of the following ways: - Ignore the holiday - In which case the holiday will be ignored and the Maturity Date will be retained as per the frequency
- Choose to follow the Local holiday - The contract Maturity Date is defaulted on the Next Working Day or the Previous Working Day, as per your specifications in the Branch Holiday Maintenance screen
- Choose to follow the Currency holiday - The movement of the Maturity Date is based on the holiday calendars maintained for the currency specified in the Holiday Currency field
- Choose to follow the Financial Center holidays - The movement of the Maturity Date is based on the holiday calender maintained for the financial center specified in the Holiday Financial center field.
Holiday Currency Select the holiday treatment as Currency. If you have chosen the holiday treatment as Currency, indicate the currency code in this field. Resultantly, the movement of the Maturity Date is based on the holidays maintenance for the currency code that you identify in the Holiday Currency field. Financial Center Specify that the holiday treatment needs to be governed by the Financial Center. In such a case, the movement of the Maturity Date is based on the holidays' maintenance for the financial institution (Clearing House) that you identify in the Financial Center field. If you choose either the currency holiday or the holiday calendar maintained for the financial center, you need to specify the currencies or financial institutions for deals involving in the product. When Maturity Date falls due on a holiday, then the system computes the next maturity date. This is based on the combination of holiday calendars maintained for all the currencies or financial institutions that you have specified for the contract. Therefore, the next maturity date for a contract is a working day in all the calendars involved in the contract.
Holiday Movement
Specify the movement of the maturity date.
Occasionally the preferred holiday treatment, the branch holiday, the currency holiday, or the holiday governed by the financial center fall on a holiday.
Whether it is to be moved forward to the next working day or whether it should be moved back to the previous working day.
Local Holiday: Select this check box, to execute the Local Holiday calendar validation of the dates and movement of schedules.
Currency Holiday: Select this check box, to execute the Currency Holiday Calendar validation of the dates and movement of schedules.
Financial Center: Select this check box, to execute the Financial Center Holiday Calendar validation of the dates and movement of schedules.
Moving the Maturity Date across Months If you choose to move the Maturity Date falling due on a holiday either forward or backward, such that it falls due on a working day, and it crosses over into another month, the maturity date is moved into the next month only if you so indicate. If not, the maturity date will be kept in the same month. - On the Product Preferences screen, under Main tab, specify the Revaluation Details.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-8 Product Preferences - Revaluation Details - Field Description
Field Description Revaluation Required Select Revaluation Required check box for a contract involving the product needs to be revalued. External Revaluation Required Select External Revaluation Required check box for the contract level revaluation level (Revaluation done externally). The External Revaluation Required flag is amendable.
External revaluation is done for trade deals only.
Note:
The event and the accounting entries maintained for the product to trigger external revaluation is operational controlled.Revaluation Frequency and Revaluation methods are not considered for External revaluation.
Note:
You can choose either the option Revaluation Required or External Revaluation Required at a time. You cannot choose both at the same time.Revaluation Level Enable this preference to specify the level at which revaluation is to be performed. At the product level, revaluation entries are netted and passed for all deals involving the product.
Revaluation Frequency Select the frequency at which revaluation is to be performed from the adjoining drop-down list. The list displays the following values:
- Daily
- Monthly
- Quarterly
- Half yearly
- Yearly
Revaluation Start Weekday / Start Day / Start Month Specify the date on which the revaluation needs to be done during the month. For example, if you specify the date as ‘30’, the revaluation will be carried out on that day of the month, depending on the frequency.
If you want to fix the revaluation date for the last working day of the month, you have to specify the date as 31 and indicate the frequency. If you indicate the frequency as monthly, the revaluation will be done at the end of every month, which is on 31st for months with 31 days, on 30th for months with 30 days and on 28th or 29th, as the case can be, for February.
If you specify the frequency as quarterly and fix the revaluation date as 31, the revaluation will be done on the last day of the month at the end of every quarter. It works similarly for half-yearly and yearly revaluation frequency.
If you set the revaluation frequency as quarterly, half-yearly, or yearly, you have to specify the month in which the first revaluation has to begin, besides the date on which the revaluation needs to done.
Processing Impact For Hedge deals amortization of Time Value is performed only if the Revaluation Required option is enabled.
If the Amortize Inception Gain option is not enabled, Inception Gain if any are treated as income directly on the inception of the options deal. Also, termination gain for hedge deals amortizes, only if the Amortize Termination Gain option is enabled for the product, else any termination gain treats as income on termination and will not be amortized.
- On the Product Preferences screen, under Main tab, specify the Liquidation Details.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-9 Product Preferences - Liquidation Details - Field Description
Field Description Numerator Method Select the method that is used to calculate the number of days between the schedule start and end dates for calculating the settlement amount from the adjoining drop-down list. The list displays the following values:
- 30-US
- 30-ISDA
- 30-PSA
- Actual
- Actual-Japanese
Denominator Method Select the method that is used to calculate the number of days in a year for the calculation of the settlement amount from the drop-down list. The list displays the following values:
- Actual
- 365
- 360
Denominator Basis Specify whether the difference between the Strike Rate and the Reference Rate is to be taken for the whole year or for the schedule period during Settlement Amount calculation. The basis can either be Per Period or Per Annum.
- On the Product Preferences screen, under the Main tab, select the Rekey filed.
Select the Rekey check box to specify the values of certain fields should be entered when an Option contract is invoked for authorization - as a cross-checking mechanism.
While defining the product you have to indicate the fields whose values you need to enter before a contract is authorized. Thus it becomes mandatory for you to enter the values of rekey fields for all contracts linked to the product.
You can specify any or all of the following as rekey fields:
- Contract Currency
- Option Premium
- Counter Currency (applicable only for Currency options)
- Maturity Date
- Premium Currency
- Value Date
If no rekey fields is defined, the system displays the details of the contract immediately when the authorizer calls the contract for authorization.
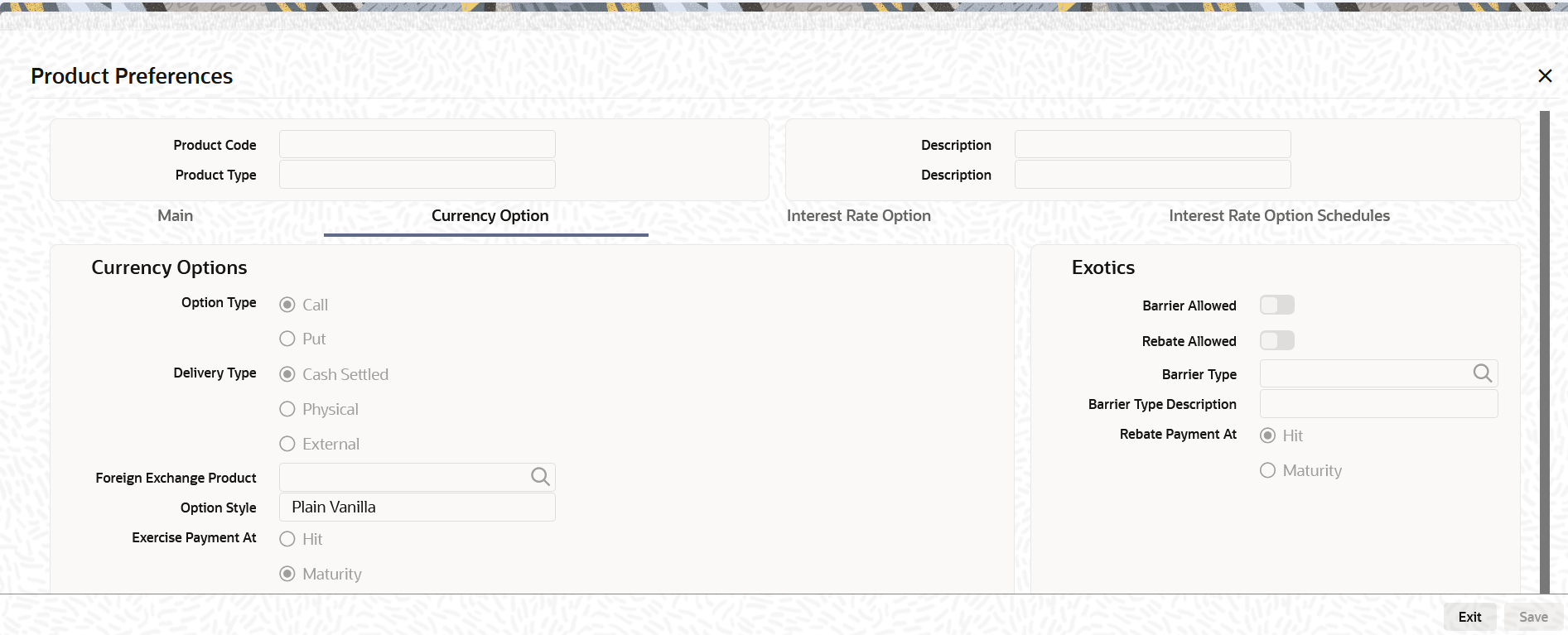
- On the Product Preference screen, click the Currency Option tab.
The Currency Option section is displayed.
Since currency option preferences are specific to currency options, the Currency Option tab displays only if you have indicated that you would like to define products meant for Currency Options.
- On the Product Preferences screen, under Currency Option tab specify the currency options.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-10 Product Preferences - Currency Option - Field Description
Field Description Option Type Specify whether the currency option that you define is a Call option or a Put option.
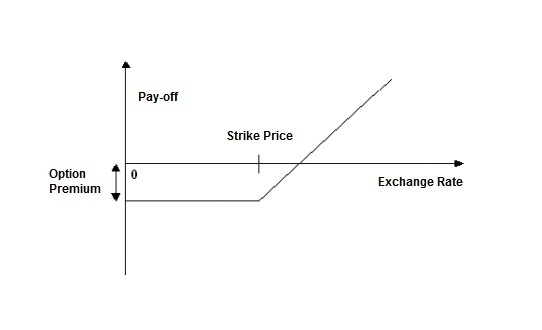
- A call option gives the buyer the right to buy a specified quantity of a certain currency (contract currency) against another (counter currency) at a specified exchange rate on or before a pre-specified future date. If on the specified future date, the market exchange rate is lower than the rate specified in the call option, the buyer will not exercise the right and, instead, buy the contract currency at the more favorable market rate.
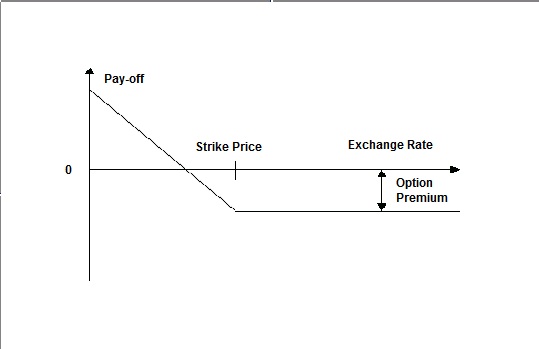
- A put option gives the buyer the right to sell a specified quantity of a certain currency (contract currency) against another (counter currency) at a specified exchange rate on or before a pre-specified future date. If on the specified future date, the market exchange rate is higher than the rate specified in the put option, the buyer will not exercise the right and, instead, sell the contract currency at the more favorable market rate.
Currency Options, thus, protect the buyer against adverse exchange rate movements, while giving the buyer the benefit of favorable exchange rate movements.
Delivery Type Specify the delivery type. Options involved in a product can either be allowed to get into future FX deals (Physical) or you can opt for a net cash agreement on exercise (Cash Settled) or could be external (through uploads). If you choose Physical as the delivery type, you have to identify the Spot FX product which is to be used to upload an FX contract. If you choose the Cash Settled option, you have to indicate whether the option style is any one of the following:
- Plain Vanilla - This is a contract that provides the buyer the right but not the obligation to buy or sell the underlying currency at a predetermined rate. The expiration style can be American, European, or Bermudan. This is a standard currency option. It becomes a non-standard option if exercised with a barrier.
- Binary - This is an agreement, under which a fixed amount is paid by the option writer to the option holder if a specific condition is met at any time during the exercise period. The payment of the fixed amount can be either at the time when the specific condition is met before or on maturity date for a manual exercise or on the expiration date for auto Exerci se/expiry.
- Digital - This is an agreement under which a fixed amount is paid by the option writer to the option holder if a specific condition is met on the expiration date.
- No Touch – This is an agreement under which a fixed amount is paid by the option writer to the option holder unless a specific condition is met on the expiration date.
Note:
As per Swift 2023 standards, expiration style is applicable only for Plain Vanilla and the Digital and No Touch option will be same as Binary.Foreign Exchange Product Select the FX product. If you have chosen the delivery type is Physical, it is necessary to provide the details of the FX product.
Option Style Select the option style from the drop-down menu which displays the following values:
- Plain Vanilla
- Binary
- Digital
- No Touch
If Digital and No touch options are selected as the option style, the processing is same as Binary.
The buyer’s pay-off for a call option is graphed as follows:
Figure 3-5 Call Option
The buyer’s pay-off for a put option is graphed as follows:
Figure 3-6 Put Option
- On the Product Preferences screen, under Currency Option tab specify the details.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-11 Product Preferences- Currency Options - Exotics -Field Description
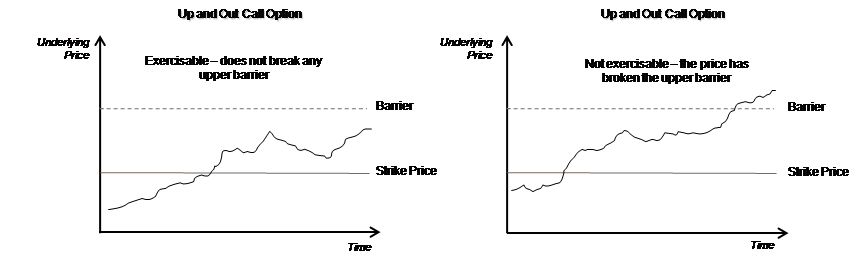
Field Description Barrier Allowed Specify whether a barrier can be used for knock-in or knock-out of an option. A barrier is a predetermined underlying asset price at which the deal ceases to exist (gets knocked out) or comes into existence (gets knocked in). If you enable this preference, you will have to identify the barrier type. The options available are:
- Single Knock In - A deal comes into existence if a pre-specified asset price is met between the start and end of the barrier window
- Single knock Out - A deal ceases to exist (Knocked-out) if a pre-specified asset price is met between the start and end of the barrier window. A pre-determined rebate amount is paid in this case
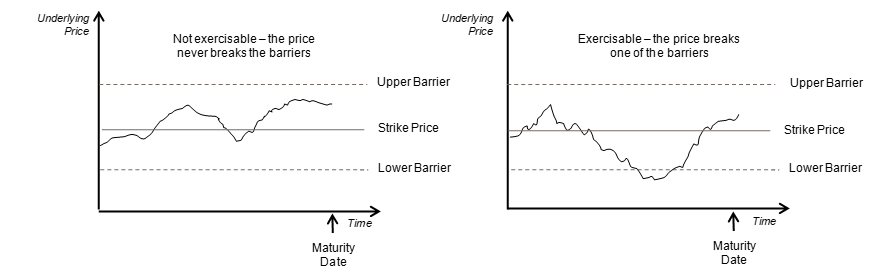
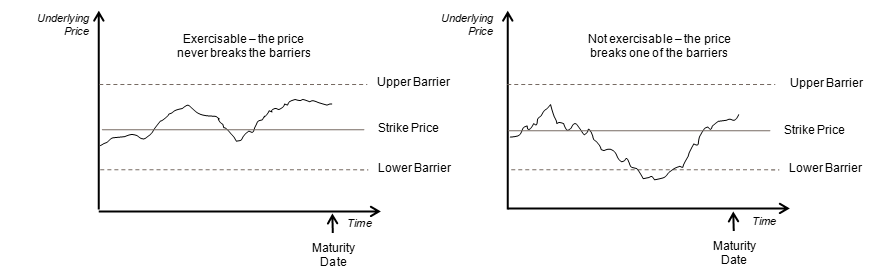
- Double Knock In - A deal comes into existence if any of the two pre-specified underlying asset prices are met between the start and end of the barrier window
- Double Knock Out - A deal ceases to exist if any of the two pre-specified underlying asset prices are met between the start and end of the barrier window. A pre-determined rebate amount is paid in this case
As per SWIFT 2023 standards, new barrier events are introduced in place of Single Knock In and Single Knock Out as mentioned below:- Below are the Single knock In barrier events:
- Up and in Knock in (UIKI) - If spot rate is greater than barrier price, then Knock in will be triggered
- Down and in Knock in (DIKI) - If spot rate is lower than barrier price, then Knock in will be triggered
- Below are the Single Knock Out barrier events:
- Up and Out Knock Out (UOKO) - If spot rate is greater than barrier price, then Knock out will be triggered
- Down and Out Knock Out (DOKO) - If spot rate is lower than barrier price, then Knock out will be triggered
Refer to Annexure B for examples on the various type of exotic currency options.
Rebate Allowed Select the Rebate Allowed check box for a rebate, that is paid if a contract involving the product gets knocked-out. Rebate is usually given for contracts that are knocked-out before maturity due to a single or double knock-out barrier hit. Banks want to give a rebate on the option premium to a certain percentage of the premium, in case of a knock-out. The amount which is given as rebate can credits to the counterparty’s account, either at Hit or at contract maturity which is determined by the field Payment At.
Barrier Type Select the barrier type from the drop-down menu. Oracle Banking Treasury Management allows you to select any one of the following:
- SKOT- Single Knock Out (SKOT)
- DKOT - Double Knock Out (DKOT)
- SKIN - Single Knock In (SKIN)
- DKIN - Double Knock In (DKIN)
As per swift 2023 standard, the below new barrier types are introduced in place of single knock in and knock out:
- DIKI - Down and In Knock-in
- DOKO - Down and Out Knock-out
- UIKI - Up and In Knock-in
- UOKO - Up and Out Knock-out
- DKIN- Double Knock-in
- DKOT- Double Knock-out
Rebate Payment At Select Hit or Maturity to specify when the Rebate amount has to be paid. Rebate payment for a knock-out option can be made either at Hit or at Maturity. When an option gets knocked-out it is considered as Hit.
Rebate payment for an option which has not knocked-in can be made at Maturity only.
Exercise Payment At Select Hit or Maturity to specify when the exercise amount has to be settled.Note:
For an vanilla option, with expiry style as European the exercise payment must be at maturity.Although you have set these as preferences at the product level, for a specific Currency Option you are allowed to change the following details:
- Option Type
- Delivery Type
- Option Style.
- Barrier Type
- Payment At
SWIFT 2023 Barrier EventsBarrier events occur as described below. In order for the barrier events to occur, the barrier spot rate needs to breach (for example, be greater than or less than, as applicable, as described in the relevant barrier event) the relevant barrier level(s) at any barrier event determination time on any barrier event determination date. However, if the Barrier Event Equal Modifier is specified as "Y", then the words "or equal to" will be deemed to be removed from relevant barrier event definition.
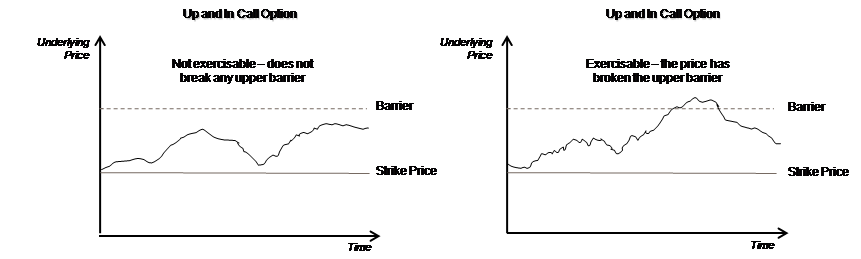
- Up and In Knock-in Event: An event that occurs when the spot rate is greater than or equal to the barrier level. If the event has occurred, the buyer of the option shall have the right to exercise it. If the event has not occurred, the option shall expire worthless.
- Down and In Knock-in Event: An event that occurs when the spot rate is less than or equal to the barrier level. If the event has occurred, the buyer of the option shall have the right to exercise it. If the event has not occurred, the option shall expire worthless.
- Up and Out Knock-out Event: An event that occurs when the spot rate is greater than or equal to the barrier level. If the event has occurred, the option shall expire worthless. If the event has not occurred, the buyer of the option shall have the right to exercise it.
- Down and Out Knock-out Event: An event that occurs when the spot rate is less than or equal to the barrier level. If the event has occurred, the option shall expire worthless. If the event has not occurred, the buyer of the option shall have the right to exercise it.
- Double Knock-in Event: An event that occurs when the spot rate is either (i) greater than or equal to the upper barrier level or (ii) less than or equal to the lower barrier level. If the event has occurred, the buyer of the option shall have the right to exercise it. If the event has not occurred, the option shall expire worthless.
- Double Knock-out Event: An event that occurs when the spot rate is either (i) greater than or equal to the upper barrier level or (ii) less than or equal to the lower barrier level. If the event has occurred, the option shall expire worthless. If the event has not occurred, the buyer of the option shall have the right to exercise it.
Knock-in Barrier TypesA deal comes into existence, if a pre-specified asset price is met between the start and end of the barrier window. The two scenarios are:- down and in
- up and in
Down and In (D&I): A form of a knock-in Option whose payoff is determined by the price of the underlying asset sinking to the lower barrier price level.
Example: consider a one-month down and in Put Option on a stock that is trading at $10.00, with a strike price of $9.50 and a barrier of $9.00. If the price of the stock falls below $9.00 before the one-month expiration of the Option contract, the Put Option is activated and the buyer has the right to sell the stock at the strike price of $9.50. On the other hand, if the stock does not fall below the $9.00 barrier, the Put Option is not activated and will expire worthless.
Up and In (U&I): An Option that can only be exercised when the price of the underlying asset reaches a set barrier level. This is a type of a knock-in barrier Option.Example: consider a one-month up and in Call Option on a stock that is trading at $9.50, with a strike price of $9.00 and a barrier of $10.00. If the price of the stock climbs above $10.00 before the one-month expiration of the Option contract, the Call Option is activated and the buyer has the right to buy the stock at the strike price of $9.00. On the other hand, if the stock does not climb above the $10.00 barrier, the Call Option is not activated and will expire worthless.
Knock-out Barrier TypesA deal comes into existence, if a pre specified asset price is met between the start and end of the barrier window. A pre-determined rebate amount is paid in this case. The two scenarios are down and out & up and out
- down and out
- up and out
Down and Out (D&O): A type of knock-out barrier Option that ceases to exist when the price of the underlying security hits a specific barrier price level. If the price of the underlying does not reach the barrier level, the investor has the right to exercise their European Call or Put Option at the exercise price specified in the contract.
Example: Consider a one-month down and out Put Option with a strike price of $9.00 with knock-out barrier at $8.00 when the underlying asset is trading at $8.50. The underlying asset diminishes steadily but slowly and closes at $7.50 upon expiration of the Option. Even though the underlying asset is trading lower than the Option's strike price of $9.00, the Barrier Options becomes immediately worthless as the knock-out barrier price of $8.00 is reached.
Up and Out (U&O): A type of Option that ceases to exist when the price of its underlying asset has reached a pre-specified price level.Example: Consider a one-month up and out Call Option with a strike price of $8.00 with knock-out barrier at $9.00 when the underlying asset is trading at $7.00. The underlying asset gains steadily but slowly and closes at $9.50 upon expiration of the Option. Even though the underlying asset is trading higher than the Option's strike price of $8.00, the Barrier Options becomes immediately worthless as the knock-out barrier price of $9.00 is reached.
Double Knock In Barrier Type
Double Knock-In means that if the Spot Exchange Rate on a Barrier Event Determination Date is either:- greater than or equal to the Upper Barrier Level or
- less than or equal to the Lower Barrier Level
If the above conditions are applied, the option will knock- in and exercisable.
If the price is not breached, then option will expire.
For example, if the current GBP/USD rate is 1.15, and a trader believes this rate will breach over the next 15 days, the trader could use a double knock in option with barriers at 1.10 and 1.20. If the underlying asset reaches the barrier at any time during the option's life, the knock-in option is brought into active existence and will remain that way until expiration.
Double Knock-Out Barrier Type
Double Knock-Out means that if the Spot Exchange Rate on a Barrier Event Determination Date is either:
- greater than or equal to the Upper Barrier Level or
- less than or equal to the Lower Barrier Level, then Automatic Termination shall apply to the Transaction upon such occurrence; otherwise, if it is not breached, the option will be exercisable.
For example, if the current GBP/USD rate is 1.15, and a trader believes this rate will stay static over the next 15 days, the trader could use a double knock out option with barriers at 1.10 and 1.20. The investor can profit if the rate does not move beyond either of the two barriers.
- On the Product Preference screen, click the Interest Option tab.
The Interest Option section displays.
Interest Rate preferences are specific to interest rate options. You can access the Interest Rate tab only if you are defining interest rate products.
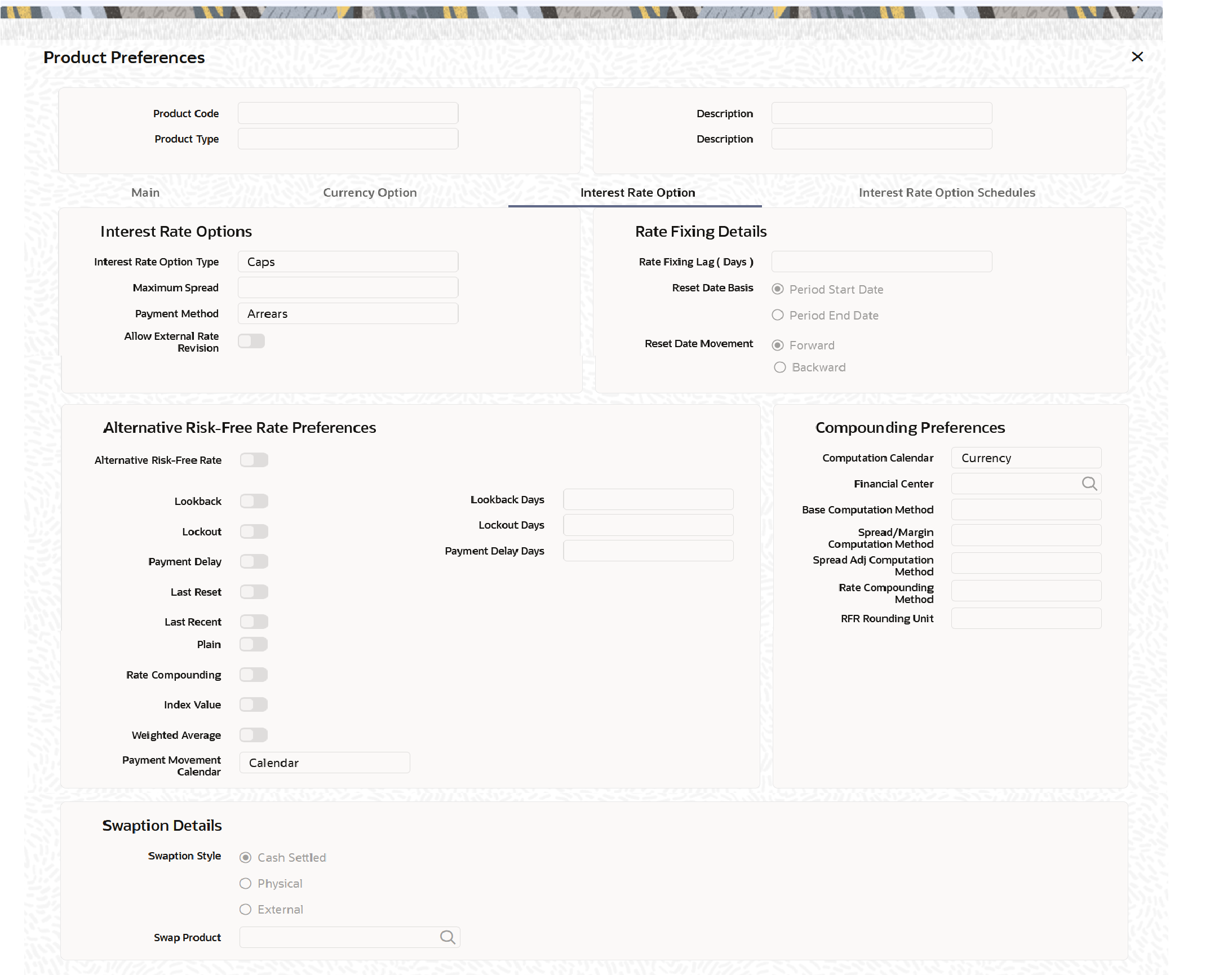
- On the Product Preferences screen, under Interest Option tab, specify the Interest Rate Option Schedules Preferences.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-12 Product Preferences - Interest Option - Field Description
Field Description Interest Rate Options Type Indicate whether the Interest Rate option product is meant to cater to any one of the following types: - Caps
- Collars
- Corridors
- Floors
- Swaptions
Maximum Spread Specify the maximum spread over and above the Reference Rate. You can specify the spread in terms of a percentage. Payment Method Select the payment method. To make the payment at the beginning of a schedule, select Advance. To do the settlement at the maturity of a schedule, select Arrears. Allow External Rate Revision Select Allow External Rate Revision check box to indicate that for the contracts linked to this product, you can allow rate revision based on the rates uploaded from an external system. Alternative Risk Free Rate Select this checkbox to identify if the product is enabled for RFR. Alternative Risk Free Rate Preferences Select any one of the following RFR calculation method check box from the below options: - Lookback
- Lockout
- Payment Delay
- Last Reset
- Last Recent
- Plain
- Rate Compounding
- Index Value
- Weighted Average
The user can also select the combination of the below method:
- Lookback and Lockout
- Lookback, Lockout, and Payment Delay
Lookback The user can select Lookback as RFR preference if the Rate Method is In-Arrears.
The observation period for the interest rate calculation starts and ends a certain number of days prior to the Interest period. As a result, you can choose the interest payment to be calculated prior to the end of the interest period.
Lookback Days Enter the number of days by which the system look back to derive the relevant RFR.
This field is applicable when the Rate Method is In-Arrears or Bearing and RFR method is Lookback.
Lockout The user can select Lockout as RFR preference if the Rate Method is In-Arrears.
Lockout means that the RFR is frozen for a certain number of days prior to the end of an interest period (lockout period).
During this time, the RFR of lockout period days is applied for the remaining days of the interest period. As a result, the averaged RFR can be calculated a couple of days before the end of the Interest period.
Lockout Days This field is relevant when the Rate Method is In-Arrears or Bearing and RFR method is Lockout.
Enter the number of Lockout period days.
Payment Delay The user can select Payment Delay as RFR preference if the Rate Method is In-Arrears.
In this method, Interest payments are delayed by a certain number of days and are therefore due a few days after the end of an interest period.
Payment Delay Days This field is applicable only if Rate Method is In-Arrears or Bearing and RFR method is Payment delay.
Enter the Number of days by which the interest payments are delayed by a certain number of days and are thus due a few days after the end of an interest period.
Last Reset This field is applicable when the Rate Method is In-Advance. In this option, interest payments are determined on the basis of the averaged RFR of the previous period.
Last Recent This field is applicable when the Rate Method is In-Advance. In this option, a single RFR or an averaged RFR for a short number of days, are applied for the entire interest period.
Plain This field is applicable only if Rate Method is In-Arrears or Bearing. System uses the averaged SOFR over current interest period, paid on first day of next interest period.
Index Value Select the Index Value check box to use the RFR index rate.
The RFR Index measures the cumulative impact of compounding RFR on a unit of investment over time. Index Value supports below RFR preferences:
Arrear Method
- Lookback
- Lockout
- Payment Delay
- Plain
Advance Method
- Last Reset
- Last Recent
For more information on Index value, refer to the attached RFR Index Value calculation worksheet,
Weighted Average Select this check box to use weighted average calculation (WAC) as the RFR calculation method.
The WAC here represent the simple average calculation and not compounded. The averaged RFR in this convention is the simple arithmetic mean of the daily RFRs. OBTR supports WAC to calculate base rate (BR), Credit Adjustment Spread (CAS), and Customer Margin.
The WAC formula to calculate simple interest is:Here,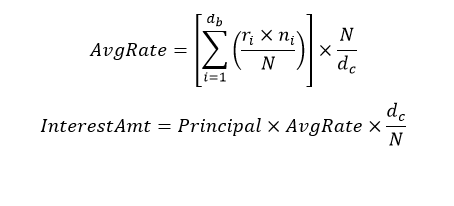
db: the number of business days for the interest calculation period
dc: the number of calendar days for the interest calculation period
ri: reference rate for the day number i within the interest calculation period
ni: the number of calendar days for which rate ri applied (on most days, ni will be 1, but on a Friday it will generally be 3, and it will also be larger than 1 on the business day before a holiday
N: the number of calendar days in one year (360 to 365)
For more information, refer to the RFR WAC sheet.
Payment Movement Calendar Select the payment movement calendar. The list displays the following values:- Calendar
- Business
Computation Calendar Select the Computation Calendar from the drop-down list, when RFR is selected for interest calculation. The available options are:- Currency
- Financial Calendar
Financial Center This field is mandatory if the Financial Center is selected as a computation calendar. Select the code of the financial center from the displayed list of values.
Rate Compounding Method Select the Rate Compounding Method from the drop-down list. The available options are:- CCR
- NCCR
- Cumulative Compounded Rate (CCR): Calculates the compounded rate at the end of the interest period and it is applied to the whole period. It allows calculation of interest for the whole period using a single compounded rate.
- Non-Cumulative Compounded Rate (NCCR): It is derived from Cumulative Compounded Rate i.e., Cumulative rate as of current day minus Cumulative rate as of prior Banking day. This generates a daily compounded rate which allows the calculation of a daily interest amount. Rate Compounding supports below RFR preferences:
- Arrear Method
- Lookback
- Lockout
- Payment Movement
- Plain
Rate Compounding User can select the rate compounding to be applied for each calculation period. When enabled, system opts for rate compounding instead of amount compounding, the amount difference comes into effect only if any pre-payment is done.Note:
For more information on RFR Rate Compounding, refer to the RFR Rate Compounding calculation worksheet.RFR Rounding Unit Specify the value in the RFR Rounding Unit field to round daily index and rate compounding to the nearest whole number and use it for interest calculation.Note:
The rate compounding rounding units value can be specified up to 9 decimals.At the product during creation and unlock after authorization, user can change below preferences:
- Check and Uncheck of alternate RFR
- RFR method
- Lookback Days
- Lockout days
- Payment Delay Days
During check and uncheck of RFR flag, respective Rate code mapping is done.
Rate Fix Lag (days) is considered along with the reference rate consideration as part of respective RFR methods.
If the payment method is chosen as arrears then user can only select one of the below RFR calculation methods:
- Lookback
- Lockout
- Plain
- Payment Delay
If the payment method is chosen as advance then user can only select one of the advance RFR calculation methods Last reset and last recent.
Cap - A cap is a series of call interest rate options with multiple exercise dates. A cap gives the buyer the right to enter into strips of notional future borrowings at a pre-agreed rate (strike rate), thus protecting him against interest rates moving above this pre-agreed rate.
Floor - A floor is a series of put interest rate options with multiple exercise dates. A floor gives the buyer the right to enter into strips of notional future lending at a pre-agreed rate (strike rate), thus protecting him against interest rates moving below this pre-agreed rate.
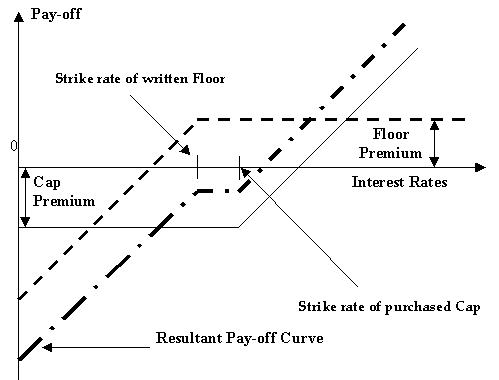
Collar - A collar is a combination of a purchased cap and a written floor. This enables the buyer to lock into an interest rate band.
For example, a floating-rate borrower buys a cap to protect him/herself against a rise in interest rates above the strike rate. The price of this protection is the premium user pays for the cap. The cap, of course, allows the user's to go on enjoying the benefits if the market (reference) interest rates remain below the strike rate – in such events, the user does not exercise the cap and uses market rates to apply to her borrowings. However, if the user has a view that market rates are not likely to fall below a certain rate (which is below the cap strike rate), then the user can choose to forgo part of the benefits of low market rates in return for a reduction in the premium that user pays for the cap.
The user achieves this by simultaneously writing a floor, the strike rate of which is lower than the strike rate of the cap that the user has purchased. The user is of the view that market interest rates are unlikely to go below the strike rate of the floor and, therefore, the floor has little probability of being exercised by the counterparty. The premium that the user receives on the floor partially offsets her premium outgo on the cap.
The above set of deals is bundled in a collar. Suppose Bank A buys a collar from Bank B. This means that Bank A has purchased a cap from Bank B and written a floor favoring Bank B. The following outcomes are possible, depending on various interest rate scenarios:
Table 3-13 Interest Rate Scenario - Outcome
Interest rate scenario Outcome Market interest rate is more than the cap strike rate Bank B pays to Bank A for the difference between market rate and cap strike rate. Market interest rate lies between the floor strike rate and the cap strike rate or is equal to either of them No payment is exchanged. Market interest rate is less than the floor strike rate Bank A pays to Bank B for the difference between the floor strike rate and the market rate. The pay-off for the buyer of a collar is shown in the diagram below:
Figure 3-14 Pay-off
Corridor - A corridor ((also called Bull Spreads)) or a bull spread is a combination of a cap purchased at a certain strike rate and another (otherwise equivalent) cap written at a higher strike rate. Like a collar, a corridor is also a premium mitigation strategy.
An entity with floating-rate borrowings buys a cap to protect itself against interest rates rising above the strike rate of the cap. However, it also feels that there is a limit to the possible rise in interest rates. Therefore, it is willing to sacrifice part of its gains arising from high market interest rates, that is opportunity gains arising from having purchased the cap, in return for a reduction in the premium that it pays for the cap. It achieves this by selling a cap with a strike rate higher than that of the original cap, the premium income on the sold (written) cap partially offsetting the premium outgo on the purchased cap.
The above sets of deals are bundled in a corridor. Suppose Bank A buys a corridor from Bank B. This means that Bank A has purchased a cap 1 from Bank B and written a cup 2 favoring Bank B. The strike rate of cap 1 is lower than cap 2.
The following outcomes are possible, depending on various interest rate scenarios:
Table 3-14 Interest Rate Scenario - Outcome
Interest rate scenario Outcome Market interest rate is equal to or more than the strike rate of cap 2.
Bank B pays Bank A for the difference between the strike rates of cap 1 and cap 2.
Market interest rate lies between the strike rates of cap 1 and cap 2.
Bank B pays Bank A for the difference between market interest rate and cap 1 strike rate.
Market interest rate is equal to or less than the strike rate of cap 1.
No payment is exchanged.
The pay-off for the buyer of a corridor is shown in the following figure:
Figure 3-15 Pay-off

Swaption - A swaption is an option on a swap. It gives the buyer, on payment of an advance fee, the right, but not the obligation, to enter into an interest rate swap at a specified future date, at a particular fixed rate and for a specified term.
Refer to the Derivatives manual for details on Interest Rate Swaps (IRS).
The terms of a swaption that the buyer and the seller agree on are:
- The strike rate
- The length of the swaption period (which usually ends on the starting date of the swap if the swaption is exercised)
- The notional amount for the underlying swap
- The frequency of settlement under the underlying swap
- Other terms of the underlying swap
- On the Product Preferences screen, under Interest Option tab, specify the Rate Fixing Details.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-15 Product Preferences - Rate Fixing - Field Description
Field Description Rate Fixing Lag (Days) Specify the number of days before or after the schedule maturity or schedule start date for the reference rate reset to be done. Reset Date Basis Specify whether the reference reset lag is with reference to the Period Start Date (schedule begin date) or the Period End Date (schedule maturity date). Reset Date Movement Fix the reset date lag for the reference rate before (Backward) or after the period start or begin date (Forward).
- On the Product Preferences screen, under Interest Option tab, specify the Swaption Details.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-16 Product Preferences - Swaption Details - Field Description
Field Description Swaption Style Indicate whether the product is meant for actual interest rate swaps (Physical) or for cash settled swaps or for external swaps (if this product is to be used for uploaded contracts).
For physically settled Swaptions, there will be an underlying derivatives swap deal which will get initiated once the Swaption contract is exercised.
For cash settled Swaptions, the swap value of the contract needs to be calculated outside the system and the same needs to be entered during manual exercise of the Swaption deal.
Swap Product Specify the swap product. This is applicable in case of actual interest rate swaps. You can identify the swap product which is used to default the details of the Derivatives contract. Processing Impact The processing impacts are given below. - While specifying the common preferences if you have selected Hedge as the Contract Type, you will not be allowed to specify Collar as the IRO Type.
- If you have chosen Advance as the Payment Method, then you have to necessarily specify Backward as the Reset Date Movement and Period Start Date as the Reset Date Basis.
- You will not be allowed to upload Derivative contracts for physically settled swaptions. To save an interest rate swap, you will have to invoke the Derivatives Online screen from the Contract Online screen.
- On the Product Preference screen, click the Interests and Rate Option Schedules tab.
The Interests and Rate Option Schedules section displays.
Figure 3-16 Interests and Rate Option Schedules Tab
Description of "Figure 3-16 Interests and Rate Option Schedules Tab"The Settlement Amount (SETTLE_AMT), which is the component for which the schedule is to be defined, is displayed in this screen. You are not allowed to change it.
- On the Product Preferences screen, under Interests and Rate Option Schedules tab, specify the details.
For more information on the fields, refer to the below Field Description table.
Table 3-17 Product Preferences - Interests and Rate Option Schedules - Field Description
Field Description Start Reference Specify the start reference date. This can either be the Value Date or the Calendar Date. If you specify Value Date as the Start Reference, the settlement schedule is calculated using the frequency and frequency units with respect to the contract value date. If the start reference is Calendar date, the settlement schedule is calculated based on the frequency, frequency units, Start Day, start weekday, and start month (whichever is applicable).
Frequency Specify the frequency. The Frequency of the schedule can either be Daily, Weekly, Monthly, Quarterly, Half Yearly or Yearly. Frequency Units Specify the frequency units. The number of frequency units after which a schedule should repeat. For example, a monthly frequency with a frequency unit of 2 is effectively a bi-monthly schedule. Start Weekday Specify the Start Weekday only if the Frequency is Weekly. Select any day from Sunday to Saturday. This is the day of the Week on which a schedule should start. Start Day Select any day of the month from the 1st to the 31st. Indicate the Start Day if the Frequency selected is Daily or Weekly. This is the day on which a schedule should start.
Start Month Specify the Start Month only in case of Quarterly, Half-yearly and Yearly frequencies. This is the month from which a schedule should start. Adhere to Month End This indicates whether a schedule should adhere to month ends if the maturity date is a day less than the month-end date. For example, a quarterly schedule starting on 31st January will have schedule maturity on 30th April, 30th July, and 30th October if you have failed to enable this option. But if you enable this option, the scheduled maturity will be performed on the 30th of April, 31st of July and 31st of October. Note:
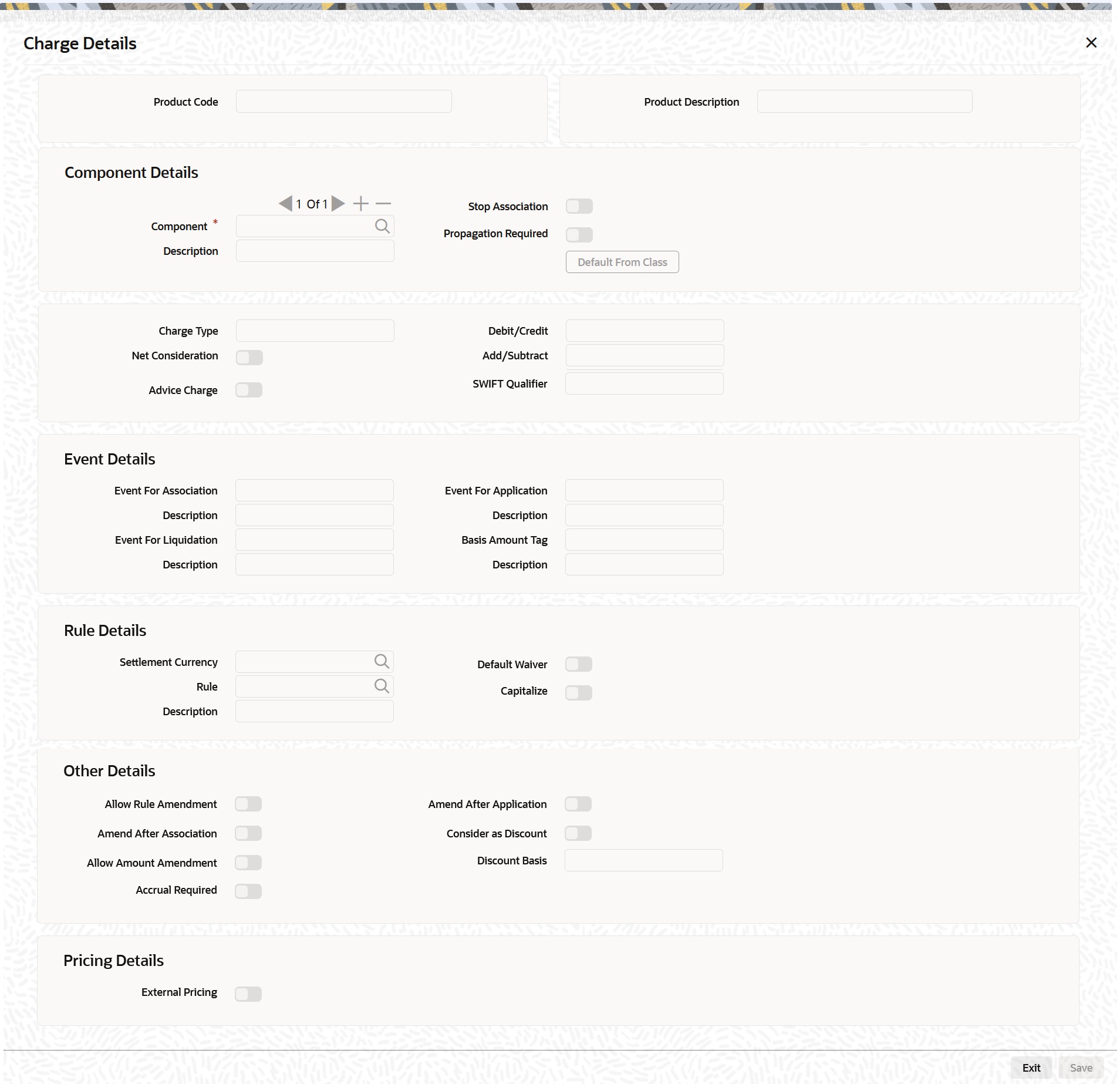
It is mandatory to visit the Schedules screen and add an empty row. The system defaults SETTLE_AMT as a component in that. - On Options Product Definition, click Charges Details.
The Charges Details screen is displayed.
A charge class is a specific type of component that you can build with certain attributes. You can build a charge class, for instance, with the attributes of a specific type of charge component, such as Charge for Manual Exercise. You can specify the different charge components for a product, in the Product Charge Definition screen, by associating the product with the different charge classes you have built.
In Charge Detail screen, you can define the charges for the product that you are creating.
To associate a charge class to a product that you are defining, choose the Default From Class button. A list of the classes that you have defined specifically for the OT Interest Rate/ Currency options module is displayed. Choose the class (or classes) that you like to associate with the product.
Charges for the portfolios maintained under the product is calculated on the basis of the associated charge classes.
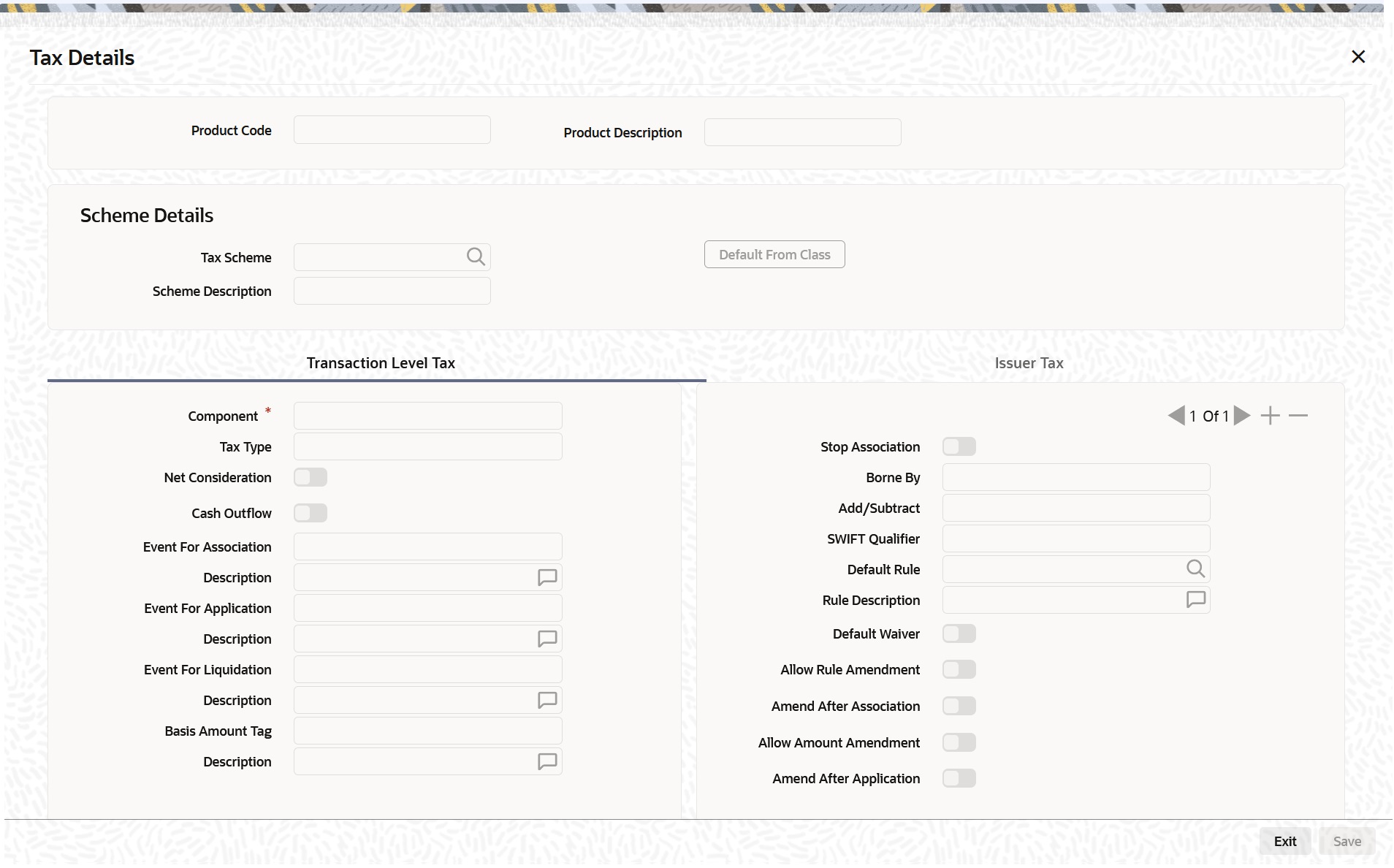
- On Options Product Definition, click Tax.
The Tax Details screen is displayed.
A tax Class is a specific type of component that you can build with certain attributes. You can build a tax class, for instance, with the attributes of a specific type of tax, such as Options tax. You can group several tax classes into a Tax Scheme Class. You can specify the taxes for a product, in the Product Tax Definition screen, by associating the product with a tax scheme class you have built. Note that you cannot define a tax component specific to a product.
To associate a tax scheme class with a product that you are defining, choose the Default From Class button. A list of the tax scheme classes that you have defined specifically for the OT Interest Rate/Currency options module will be displayed. Choose the class that you like to associate with the product.
Taxes for the portfolios maintained under the product is calculated on the basis of the associated tax scheme classes.
- On the Product Definition screen, click ISDA.
ISDA Confirmation Preferences is displayed.
Figure 3-19 ISDA Confirmation Preferences
Description of the illustration otdprmnt_cvs_isda.jpg - On the ISDA confirmation preferences screen, Click Default ISDA Events, to populate the list of ISDA events applicable for the module.
- Select the check box next to the Description based on the requirement.
- Click Ok to save the details or Exit to close the screen.
Parent topic: Define Attributes Specific to OT Products