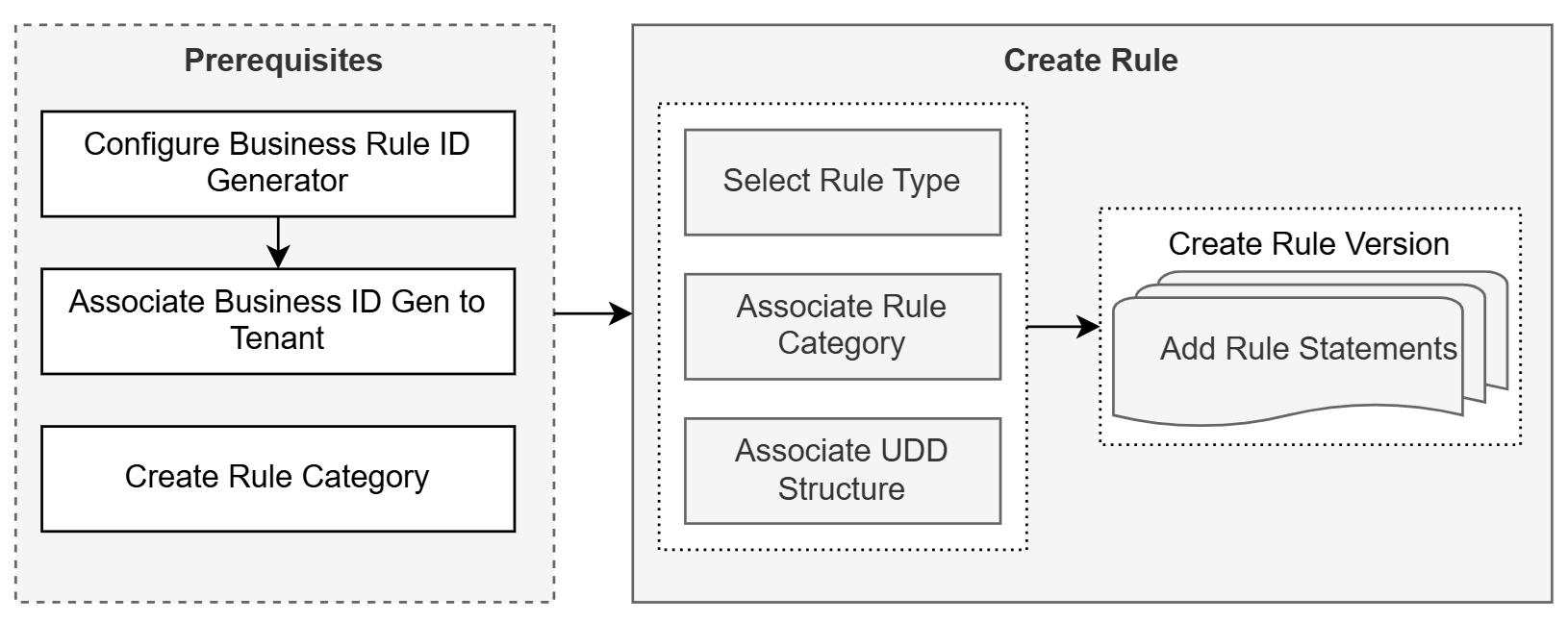
Configuring a Rule
Introduction
- Configuring Business Rule ID Generator
- Associating Business ID Generator to Tenant
- Creating a Rule Category
- Creating a Rule
Creating a Rule Category
Each Rule belongs to a Rule Category. The Rule Category decides the Operations Company for which the Rule is applicable. See Creating a Rule Category.
Creating a Rule
A Rule is a collection of one or more Rule Versions. Each Rule Version contains a set of Rule Statements that define the conditions and their result. See Creating a Rule.
Components of a Rule
- Rule Type: You can segregate Rule configurations based on the business service that consumes them. This is done using the Rule Type. Currently, there are two Rule Types available for selection while creating rules:
- Communication: Rules of type Communication are consumed by features like Communication generation and distribution. These rules enable you to define conditions for managing the Communications sent through Communication Distribution.
- Digital Asset: Rules of type Digital Asset are consumed by Digital Asset feature. These rules enable you to define conditions for storage of assets using the Digital Assets feature.
- Rule Category: Every Rule created in Communication Cloud Service maps to a Rule Category. This enables you to group rules based on the Operations Company for which it is applicable. See Creating a Rule Category for more information.
- User Defined Data Structure: While creating a rule, you can define the operands of a condition using fields of User Defined Data Structures. To facilitate this, you can associate User Defined Data Structures to a Rule configuration, and the User Defined Data fields within the associated User Defined Data Structures are available for configuring the conditions within the Rule Statement. See Creating a User Defined Data for more information.
Note:
You can associate multiple User Defined Data Structures to a Rule, in which case, the common fields that belong to all these User Defined Data Structures are available for use while creating Rule Statements. - Rule Version: You can create multiple versions of a Rule with different active dates. Every Rule Version holds two or more Rule Statements.
- Rule Statement: A Rule Statement is a collection of Conditions and their Result that constitutes the Rule. You can add two or more Rule Statements to a Rule Version and specify the order in which they are to be processed. Once a Rule Statement returns True, subsequent Rule Statements are not executed. You can configure more than one Conditions within a Rule Statement and connect them using a logical operator. The last Rule Statement within a Rule Version should have only Result, and no Condition.
- Condition: You can create a Rule Statement using one or more Conditions. A condition is a combination of two operands, Condition On and Condition For, connected by an Operator. You can select either User Defined Data Field or Rule as the operands.
- Result: Every Rule Statement should have a Result. The Result Type available is Boolean. That is, the result of a rule can be either True or False.
Note:
While creating a Rule from the context of Digital Asset feature, you can configure Result Type as Digital Asset, and select a Digital Asset Detail as the value.
Understanding Rule Statement
A Rule Statement helps you define the conditions of a rule and its possible outcome. You can configure two or more Rule Statements within a Rule Version, that are applied sequentially until one of them returns a result. That is, once a Rule Statement returns a result, the subsequent Rule Statements are not executed.
Condition
A Condition comprises of three parts:
- Condition On: Condition On denotes the type of left-hand side operand in a Condition. It can be either a User Defined Data Field, or a Rule. Once you select the Condition On, you can select its value within the Condition.
Condition On Description User Defined Data Select User Defined Data as Condition On operand to create a condition using User Defined Data fields as operands. All User Defined Data fields within the User Defined Data Structure associated to the Rule configuration are available for selection as the Value of Condition On operand. Note:
If there are multiple User Defined Data Structures associated to a Rule configuration, then the fields that are common to all the associated User Defined Data Structures are available for selection.Rule Select Rule as Condition On operand to create a Nested Rule with which you can configure a complex business logic. You can select an existing Rule as the Value of Condition On operand. Note:
While creating Nested Rules, ensure that you select Rules of same Rule Type. - Operator: Operators are used to connect the Condition On and Condition For operands to form a Condition. You can select the Operator from a predefined list that varies based on the value of the Condition On operand. If the Condition On operand is Rule, then only two operators are available for selection: == and !=.
- Condition For: Condition For denotes the type of right-hand side operand in a Condition. The values available for Condition For varies based on the Condition On operand and the Operator you have selected. Once you select the Condition For, you can either select or enter its value within the condition.
Note:
Within a condition, both the operands (Condition On and Condition For) must be of the same data type.- AND: Both Conditions must be true.
- OR: One of the Conditions must be true.
Rule Result
All Rule configurations include a Result Type of Boolean, with a possible Result Value of either True or False.
Rules that are created from the context of Digital Asset configurations would have a Result Type of Digital Asset and the Result Value is the name of the Digital Asset Detail.
Configuring a Rule Statement
While configuring Rule Statements, ensure that every Rule Version includes at least two Rule Statements, the first one with one or more Conditions and a Result, and the last one with only a Result.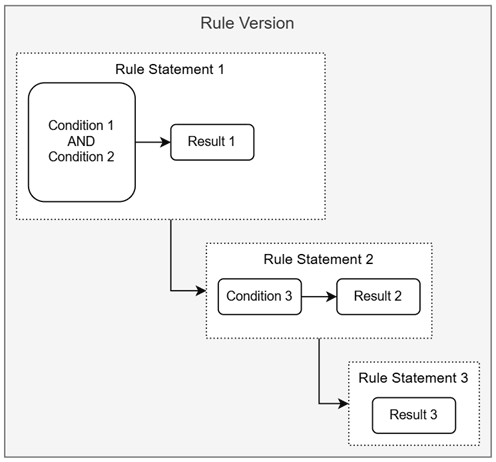
Rule Statement Examples
Refer the following business scenarios to learn more about configuring rule statements:
- Create Rule Statement 1 that includes the Condition:
Age<21and Result:True. - Create Rule Statement 2 that includes only Result:
False.
- Create Rule Statement 1 that includes two Conditions:
State=TexasandSmoker=True, and Result:True. - Create Rule Statement 2 that includes two Conditions:
State≠TexasandSmoker=True, and Result:False. - Create Rule Statement 3 that includes one Condition:
Rule 1and Result:True. - Create Rule Statement 4 that includes only Result:
False.
Related Topics