10.2.2 Equivalence of the Static Spread and Margin
Static spread calculations are deterministic, therefore they are a special case of the equations in the previous section where, roughly speaking, all processes are equal to their expected value, and the margin p is substituted to the risk-adjusted margin m. The equivalent of �Equation 8–29 is then:
Equation 36
Figure 10-37 Equation 36
Description of the Transfer Pricing Option Cost Equation 36 follows:
Where f is the instantaneous forward rate. The equivalent of Equation 8–31 and Equation 8–33 is then:
Equation 37
Figure 10-38 Equation 37
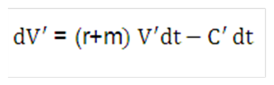
Description of the Transfer Pricing Option Cost Equation 37 follows:
Equation 38
Figure 10-39 Equation 38
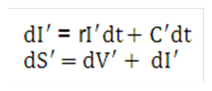
Description of the Transfer Pricing Option Cost Equation 38 follows:
Equation 39
Figure 10-40 Equation 39
Description of the Transfer Pricing Option Cost Equation 39 follows:
The solution of Equation 37 and Equation 39 is:
Equation 40
Figure 10-41 Equation 40
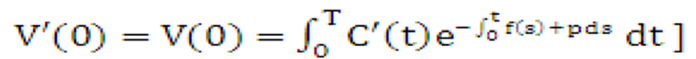
Description of the Transfer Pricing Option Cost Equation 40 follows:
Comparing Equation 40 and Equation 8:
Equation 41
Figure 10-42 Equation 41
Description of the Transfer Pricing Option Cost Equation 41 follows:
For example, the static spread is equal to the margin.