5.3.3.4.2 Create Forecast All Business Rule
To create a new Forecast All Business Rule, follow these steps:
- Click Add icon from the top of the Forecast All Business Rule
Summary page.
Figure 5-187 Forecast All Business Rule Page
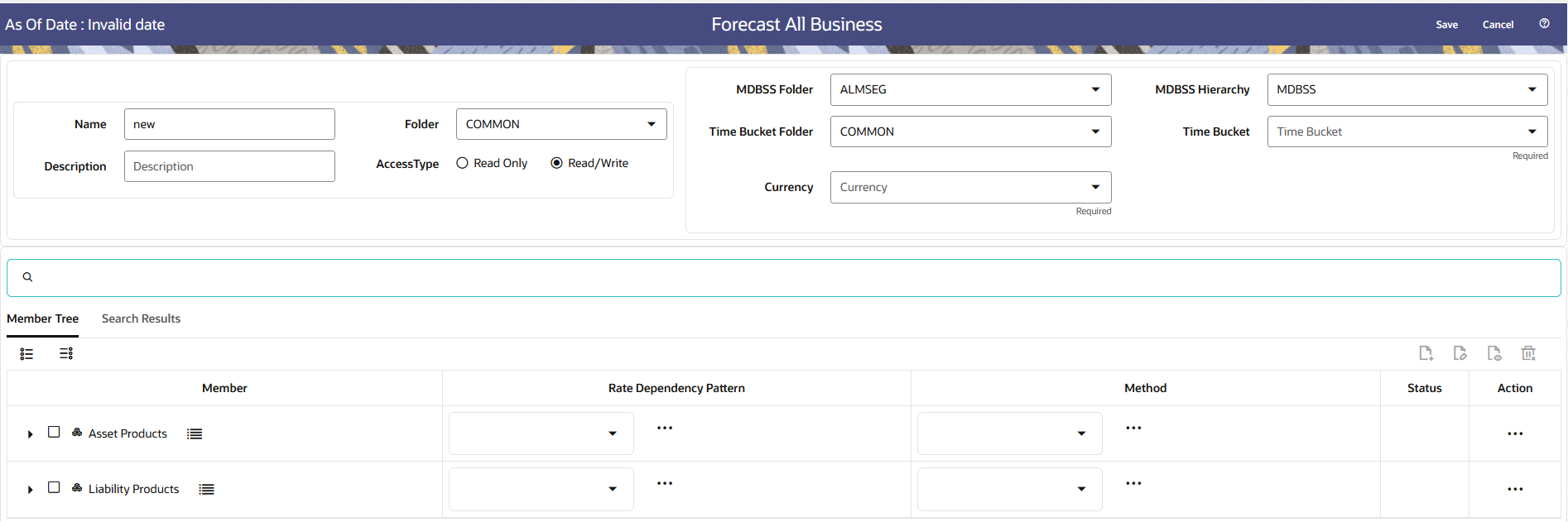
- Enter the following Details.
Table 5-46 Create Forecast All Business Rule
Fields Description Name Enter the name of the Forecast All Business Rule. Description Enter the description of the Forecast All Business Rule. This is an optional field. Folder Select the Folder where the Forecast All Business Rule needs to be saved. Access Type Select the Access Type as Read-Only or Read/Write. MDBSS Folder and MDBSS Hierarchy Select the MDBSS folder and MDBSS hierarchy Time Bucket Folder and Time Bucket Select the Time Bucket folder and Time Bucket Currency Select the currency for Forecast All Business Rule Note:
If any member is a currency in the MDBSS hierarchy (for example, INR) and selected currency is different (for example, USD), then the member and its children nodes can not be defined.
- Select MDBSS node(s) from Member Tree tab of Assumption Browser.
Assumption Browser has two tabs: Member Tree and Search Results.
- Member Tree: Member Tree tab shows the hierarchical
structure and allows you to define rules by selecting the node members from
the browser. Select Node and Click Menu icon next to it to view the
available options.
Figure 5-188 Member Tree Selection
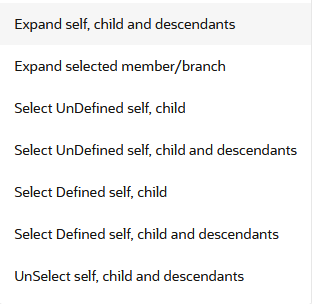
Status of node is also displayed in Member Tree section, for example Selected, and so on. To select member hierarchy, following options are available:
- Expand self, child and descendants: Allows to expand the selected node itself along with its child and descendants.
- Expand selected member/branch: Allows to expand the selected node
- Select UnSelect self, child: Allows to unselect the selected node itself along with its child
- Select UnSelect self, child and descendants: Allows to unselect the selected node itself along with its child and descendants.
- Select Defined self, child: Allows to select the selected node itself along with its child.
- Select Defined self, child and descendants: Allows to select the selected node itself along with its child and descendants.
- UnSelect self, child and descendants: Allows to unselect the selected node itself along with its child and descendants.
You can perform the following tasks on the selected node(s):
- Add
- Edit
- View
- Delete
- Copy
Use Show Numeric Code Values (Left) icon to view the code value left to the Node name.
Use Show Numeric Code Values (Right) icon to view the code value right to the Node name.
- Search Results: You can also search the members based on
the filters. This section shows the searched node(s).
To search a member, follow these steps:
- Navigate to Search Results tab of Assumption Browser section.
- Enter the Member ID, Name, Status, or Is Leaf in Search
Criteria.
Figure 5-189 Searching Member
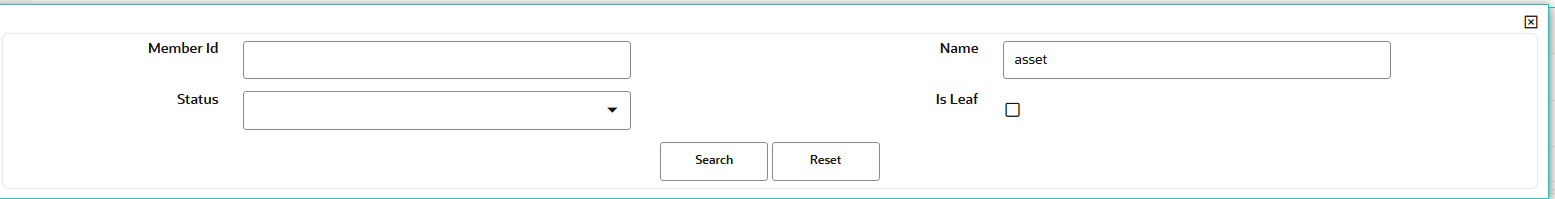
- Click Search. The searched member(s) will be
displayed in Search Results section of Assumption
Browser.
Figure 5-190 Search Results
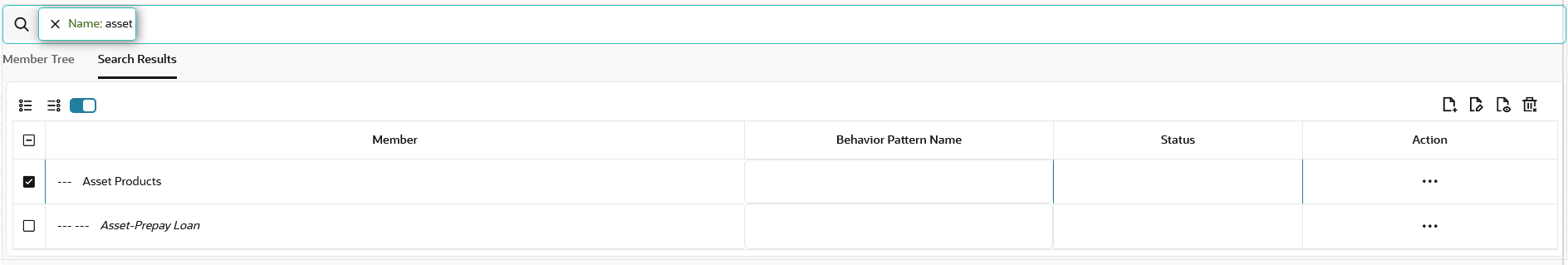
You can perform the following tasks on the searched node(s):
- Add
- Edit
- View
- Delete
- Copy
Use Show Numeric Code Values (Left) icon to view the code value left to the Node name.
Use Show Numeric Code Values (Right) icon to view the code value right to the Node name.
- Member Tree: Member Tree tab shows the hierarchical
structure and allows you to define rules by selecting the node members from
the browser. Select Node and Click Menu icon next to it to view the
available options.
- Select the predefined Rate Dependency Pattern from Rate
Dependency Pattern drop-down. Else, click corresponding
Action button to create new Rate Dependency Pattern, edit Rate Dependency
Pattern, or view Rate Dependency Pattern. There are four rate-volume options to
choose from:
- No Relationship
If you want new business amounts to stay constant regardless to the interest rate environments, select this option.
- Rate-Level Dependent The Rate-Level dependent relationship allows you to change new business behavior for different values of a single indicator interest rate. The indicator interest rate, referred to as the Base Interest Rate, is defined by an Interest Rate Code, a term selection, and a rate lag.
- Interest Rate Code: The Interest Rate Code identifies the reference yield curve or rate index whose forecasted value determines the new business amount. You can select the Interest Rate Code from all available interest rate codes for the selected currency, as defined within Rate Management. The list of Interest Rate Codes includes only codes with a reference currency equivalent to the currency selected in the Floating Tree Bar.
- Term Selection: If the selected Interest Rate Code is a yield curve, you must also select a term. Your term choices depend on the definition of the Interest Rate Code within Rate Management. Note that the selection automatically defaults to the shortest available term.
- Rate Lag: If you want the base interest rate calculation to perform a look back function, you can input a rate lag. The new business assumption lookup uses the forecasted interest rates as of a date within the current modeling bucket less the rate lag. If the timing of new business is End of Bucket, the lookup function uses the last day of the modeling bucket less the rate lag. For all other cases, the mid-point of the bucket less the rate lag is used.
- Rate-Spread Dependent
With the Rate-Spread dependent relationship, you can input new business assumptions for different spreads between two indicator interest rates, or a spread between two term points on the same yield curve. You define the first indicator interest rate, the Base Interest Rate, as described previously. The second indicator interest rate, the Alternate Interest Rate, also requires definition of an Interest Rate Code, a term selection, and a rate lag.
The rate spread equals the Alternate Interest Rate minus the Base Interest Rate.
- Economic Indicator Dependent With the Economic Indicator Dependent relationship, you can input new business assumptions related to defined economic indices (as defined in Rate Management), where the change in the index will drive a different outcome of new business. For example, you can forecast a higher GDP and tie the new business assumptions to that particular forecast.
- Rate Tiers: The Rate Tiers tab will become available to edit when one of the following three rate volume relationships have been selected (Rate Level, Rate Spread, and Economic Indicator). Once you have selected a rate-volume relationship and defined your base and alternate interest rates, you must define rate tiers. Rate tiers provide the lookup values for which different new business assumptions can be input.
- Lookup Method: The lookup method determines
which new business assumption is selected from the input values
when the forecasted interest rate falls between two rate tiers.
There are two methods to choose from:
Interpolate: Specify Interpolation as the lookup method if you want the application to interpolate add-on rate values for applicable reference terms falling between node points specified in the Adjustments rule, using straight line interpolation between the term points.
Range: If you select Range, Oracle ALM selects the new business assumption as the closest assumption associated with the rate tier which is less than or equal to the forecasted interest rate.
- No Relationship
- Select Forecast Balance method from Method drop-down.
- Click Add from Assumption Browser section.
- Click Save.