1.20.3.1 Define Interest Rate Curve Forecast
The IRCs for all active currencies (and Reporting Currencies, a subset of the Active Currencies) are listed under Interest Rate Curve Section. The options under Interest Rate Code Forecast Method provide multiple ways to model the effects on Portfolio Cash Flows due to Interest Rate changes.
Note:
For Cash Flow Engine Cloud, see the following notes:
- Only one scenario is applicable.
- IRRBB scenario type in not supported.
- Only Flat and Direct Input methods are applicable.
Figure 1-79 Interest Rate Curve Forecast Rates
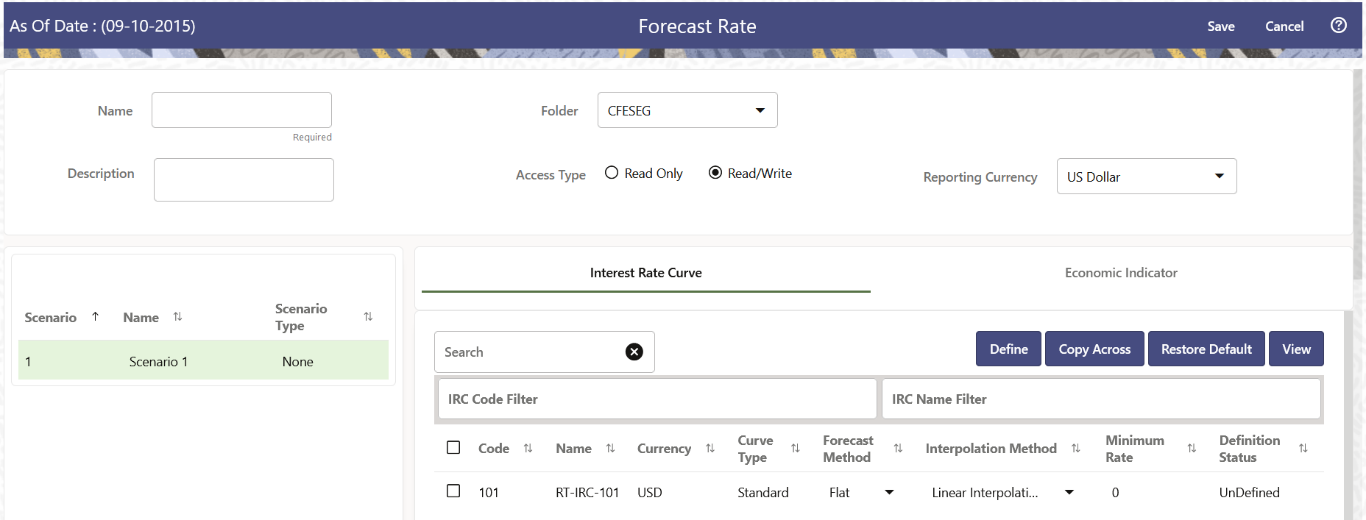
You can define Interest Rate Forecast for the following methods:
Table 1-52 Forecast Rate rule – Methods and Descriptions
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Flat | Forecast no change in the Interest Rate for all dates beginning with the As-of Date. |
| Direct Input | Type Interest Rates directly for any modeling period or Interest Rate term. |
| Structured Change | Forecast exchange rates as an incremental change from the previous period. Forecast rate changes in terms of absolute or percent change, for any modeling period or interest rate term, such as: +100 basis points on Day 1 -200 basis points over the first 6 months Yield curve rotation (short point decreasing, long point increasing) |
| Implied Forward | Forecast interest rates based on the yield-curve interest rates in effect at the as-of date and consistent with the modeling bucket definitions. |
| Yield Curve Twist | Flatten or steepen the yield curve around a specific point on the curve. |
For more information, see the Cash Flow Engine Reference Guide.
The following Interpolation Methods are available.
Table 1-53 Forecast Rate Rule – Interpolation Methods and Descriptions
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Linear Interpolation | Linear interpolation uses Linear Yield Curve smoothing. Linear Yield Curves are continuous but not smooth; at each knot point, there is a kink in the yield curve. You may not want to use a Linear Yield Curve with a model that assumes the existence of a continuous Forward Rate Curve, due to the nonlinear and discontinuous knot points of a Linear Yield Curve. |
| Cubic Spline of Yields |
A cubic spline is a series of third-degree polynomials that have the form:
y = a + bx + cx2 + dx3 These polynomials are used to connect the dots formed by observable data. The polynomials are constrained so they fit together smoothly at each knot point (the observable data point.) This means that the slope and the rate of change in the slope with respect to time to maturity have to be equal for each polynomial at the knot point where they join. If this is not true, there is a kink in the yield curve and they are continuous but not differentiable. Two more constraints make the Cubic Spline Curve unique. The first restricts the zero-maturity yield to equal the 1-day interest rate. The second restricts the yield curve at the longest maturity to be either straight (y"=0) or flat (y'=0). |
| Quartic Spline |
Quartic interpolation requires a minimum of 4 knot points. The quartic interpolation equation can be represented as:
Y = a + bX + cX2 + dX3 + eX4 The end knot points satisfy equations for one curve and all intermediate points satisfy two curves. Therefore, in a scenario with a minimum number of knot points, there are 6 equations. For n number of knot points, the number of equations is 2n-2. If n is the number of points to be interpolated, the order of the matrix to be formed is 5*(n-1) x 5*(n-1). The matrix is formed according to the following logic: The second derivative at the endpoints and the first derivative of the last point is Zero. At the points other than the endpoints, the value of the first derivatives, second derivatives, and the third derivatives of the function are equal. |
In looking up the Forecast Rates, the Cash Flow Engine (where necessary) performs an interpolation between yield curve term points. For example, in determining a three-month rate from a yield curve that contains only a one-month rate and a six-month rate, the Cash Flow Engine performs an interpolation to determine the implied three-month rate. The Interpolation method used is defined by the selected interpolation method for the Interest Rate Curve.
You can generate the forecast rates for 360 calendar months starting from As-of-Date.
Following options are available for Interest Rate Curve Forecast Rule:
Define
-
Flat Method
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Flat.
- Select the Interpolation method.
- Input Minimum Rate, if required.
- Click Define.
The status of the Interest Rate Code is changed to Defined.
- Direct Input
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Direct Input.
- Select the Interpolation Method.
- Input Minimum Rate, if required.
- Click Define.
The Direct Input window is displayed:
- Enter data and click Apply.
- The status of the Interest Rate Code is changed to Defined.
- Structured Change
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Structured Change .
- Select the Interpolation Method.
- Input Minimum Rate, if required.
- Click Define.
The Structured Change window is displayed:
- Select the Shock Type as Rate or Percent. Shock Type as Rate designates to absolute rate change and Shock Type as Percent designates to percent rate change.
- Enter a shock amount to apply to the IRC in absolute rate or percentage change. Click Apply
- Enter data and click Save.
- The status of the Interest Rate Code is changed to Defined.
- Implied Forward
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Implied Forward.
- Select the Interpolation Method.
- Input Minimum Rate, if required.
- Click Define.
The Implied Forward window is displayed:
- Select the Shock Type as Rate or Percent. Shock Type as Rate designates to absolute rate change and Shock Type as Percent designates to percent rate change.
- Enter a shock amount to apply to the IRC in absolute rate or percentage change. If no change is required to the base curve, leave at 0.0, and click Apply.
- The status of the Interest Rate Code is changed to Defined.
- Yield Curve Twist
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Yield Curve Twist.
- Select the Interpolation Method.
- Input Minimum Rate, if required.
- Click Define.
The Yield Curve Twist window is displayed:
- Select the tenors using the Short Point, Mid Point, and Long Point.
- For each of these tenor points, add the required shock amounts for each tenor. At runtime and display time, the rate changes are added to the as-of-date rates to create a future scenario. No conversion is applied before the rate is passed to the Cash Flow Engine.
- Click Apply.
The status of the Interest Rate Code is changed to Defined.
Copy Across
This allows you to copy Forecast Method and related details from one IRC to another.
For example, if you have 10 IRCs enabled in the application and you must input only one set of assumptions, then copy those assumptions across all enabled IRCs, instead of having to input 10 full sets, thereby saving a significant amount of input time.
- Flat Method
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Flat.
- Click Copy Across.
- Click Apply Copy Across.
- You can click Cancel Copy Across to cancel the Copy Across function.
Note:
You must select a defined IRC. For more information, see the Define section of Interest Rate Curve.- Structured Change
- Select Interest Rate Code using the corresponding checkbox and
select Forecast Method as Structured Change..
Note:
You must select a defined IRC. For more information, see the Define Section of Interest Rate Curve. - Click Copy Across.
- Click Apply Copy Across.
- You can click Cancel Copy Across to cancel the Copy Across function.
- Select Interest Rate Code using the corresponding checkbox and
select Forecast Method as Structured Change..
- Implied Forward
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast
Method as Implied Forward.
Note:
You must select a defined IRC. For more information, see the Define section of Interest Rate Curve. - Click Copy Across.
- Click Apply Copy Across.
- You can click Cancel Copy Across to cancel the Copy Across function.
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast
Method as Implied Forward.
Restore Default
Use this action to reset previously entered details to Undefined status.
- Flat Method
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Flat.
- Click Restore Default.
- The status of the Interest Rate Code is changed to Undefined.
- Direct Input
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Direct Input.
- Click Restore Default.
- The status of the Interest Rate Code is changed to Undefined.
- Structured Change
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Structured Change.
- Click Restore Default.
- The status of the Interest Rate Code is changed to Undefined.
- Implied Forward
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Implied Forward.
- Click Restore Default.
- The status of the Interest Rate Code is changed to Undefined.
- Yield Curve Twist
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Yield Curve Twist.
- Click Restore Default.
- The status of the Interest Rate Code is changed to Undefined.
View
After defining Forecast Method and other parameters for an IRC you can view the forecasted interest rates by clicking this button.
- Flat Method
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Flat.
- Click View to see the output table.
- Direct Input
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Direct Input.
- Click View to see the Output Table.
- Structured Change
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Structured Change.
- Click View to see the Output Table.
- Yield Curve Twist
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Yield Curve Twist.
- Click View to see the Output Table.
- Implied Forward
- Select Interest Rate Code using corresponding checkbox and select Forecast Method as Implied Forward.
- Click View to see the Output Table.