8 Troubleshooting
Implementing the Oracle Hospitality Integration Platform (OHIP) Streaming API can present challenges. This chapter provides guidance on common issues and their resolutions to ensure a smooth integration process.
Troubleshooting for Automation
The below flowchart illustrates how errors occur and how to rectify them. This is explained in the text that follows the image.
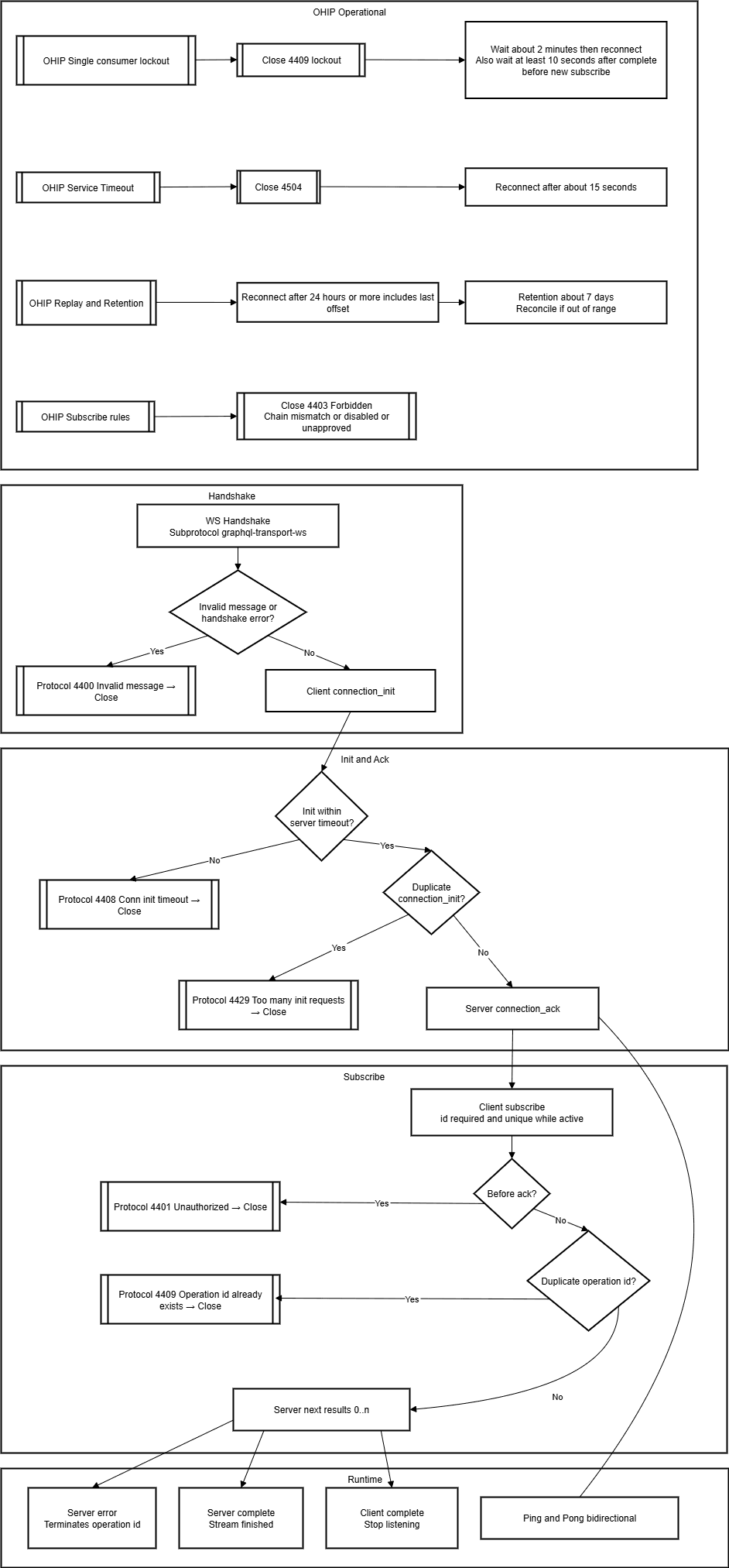
Upon failure or unexpected behavior:
- Check error codes in received WebSocket close frames or control messages (for example, 4401, 4403, 4409, 4504).
- Parse and log all errors; classify as transient (retryable) or permanent (requires human intervention).
- After error 4409, set a timer and attempt reconnect after the minimum lockout time.
- Always log offset at successful processing and on any disconnect.
Common Pitfalls for Polling Users
Multiple Connections: You might be used to having several threads or apps polling at the same time. With OHIP streaming, only one client per app key/chain is allowed to maintain the sequencing of events. Extra clients will be rejected (error 4409).
Disconnections: Unlike polling (where losing a single request is not critical), you must handle reconnections.
Not Receiving Events from the Streaming API
Resolution:
- Confirm that the OPERA environment is listed and marked as "Streaming Enabled" on the Environments tab of the Developer Portal.
- Ensure you have valid credentials to obtain the OAuth token.
- Verify that the OAuth token is current using the
exp. - Ensure your application's streaming configuration is both requested and approved.
- Ensure you stay connected. If you leave over 24 hours between connecting, you must
include in the
subscriberequest the last offset you received (see Replaying Events). - Verify you are not unexpectedly using the
hotelIdfilter in the subscribe message.
If you are not receiving all new reservations, it is possible the customer has an external CRS setup. Request the customer to set up a "publisher" on your external system (the external system code appears on the Application, Events, and Subscribed tab in the developer portal) following this process (see the "Managing External System Publishers" heading under the Configuring Business Events topic in the OPERA Cloud User Guide).
WebSocket Connection Closes Unexpectedly
Resolution:
- Send a "ping" message every 15 seconds to keep the connection open.
- The server will close the connection if it does not receive a
pongwithin 180 seconds; ensure your client responds to serverpings withpongand continues to sendpings every 15 seconds. In Performance Considerations, see "Maintain a Healthy Connection and Token Lifecycle." - If using Postman, note that it cannot send "ping" messages on an open WebSocket, leading to automatic closure.
- Wait at least 10000ms between closing and reopening the WebSocket to avoid 4409 errors.
Receiving a 4409 Error
This indicates "Too Many Requests."
Resolution:
- Ensure that only one client or process consumes events from a given gateway using a specific application key and chain code.
- Send the "Complete" message before disconnecting from the WebSocket.
- Wait two minutes after receiving error 4409 for the lock to auto-unlock, and then reconnect.
Receiving a 4401 Error
This indicates "Unauthorized - Invalid credentials."
Resolution:
- Verify that you are sending the correct application key.
- Verify that you are sending the SHA256 hash of the application key.
- Ensure the application is subscribed to consume events and that the subscription is approved.
- Check that the OAuth token is valid and current.
Receiving a 4403 Error
This indicates "Forbidden - You are not authorized to access the resource."
Resolution:
- Ensure that the chain code in the subscription message matches the chain code being accessed.
- Confirm that streaming is enabled for the environment you are accessing.
Receiving a 4504 Error
This indicates a "Service Timeout" and occurs when the OCI Streaming Service is down for more than 30 seconds.
Resolution:
- Try reconnecting after 15 seconds.
- If the problem persists, contact Oracle Customer Support.
Getting Overwhelmed with Events
Resolution:
- Implement a buffering mechanism to process events before writing to the back-end database, preventing potential overload.
- Ensure that your consuming architecture can scale to handle the volume of events.
Handling Duplicate Events
In rare scenarios, the same event can be sent twice, identified by identical primaryKey and offset.
Resolution:
- Process the first event that arrives and disregard duplicates.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can address common issues encountered when implementing the OHIP Streaming API, ensuring a more reliable and efficient integration.
Not Receiving the Expected Data
If you are not receiving the pieces of data you expected, check the subscribe message to ensure it includes the expected field.
The hotelId will always be null for chain-level entities, such as profiles, which tend to be shared across all hotels in the chain.
Verify this page lists the expected data values for the event(s) to which you are subscribed. See the "Business Events - Activity" heading in the Configuring Business Events topic in the OPERA Cloud User Guide.
Receiving Unexpected Events
Keep in mind that a single action, such as checking a guest in, can trigger multiple business event notifications because that single action modifies multiple resources.
For integration partners developing against the sandbox, keep in mind that the actions taken by other partners in the sandbox will generate events.
- If you are seeing "echo" events produced by your own REST write operations and you wish
to suppress them, include
x-externalSystem: externalSystemCodeon those write calls. The value appears in the Developer Portal on your Application Events Subscribed tab as "Application's external system code."
Error code matrix
Common close codes and operational responses.
- 1000 Normal Close
- Meaning: Normal closure after client sent complete and server drained final messages.
- Action: None.
- 4401 Unauthorized
- Meaning: Invalid or expired OAuth token, or missing/invalid hashed app key.
- Action: Fetch a new OAuth token; verify app key hash; reconnect (include saved offset if more than 24 hours since last connect). In Performance Considerations, see "Maintain a Healthy Connection and Token Lifecycle."
- 4403 Forbidden
- Meaning: Chain/environment not authorized or not enabled for streaming.
- Action: Verify
chainCodeinsubscribe; ensure environment streaming is enabled and subscriptions approved.
- 4406 Subprotocol not acceptable
- Meaning: WebSocket upgrade did not include graphql-transport-ws.
- Action: Set header
Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: graphql-transport-ws.
- 4408 Connection initialization timeout
- Meaning:
connection_initnot received within server timeout. - Action: Send
connection_initwithin 5 seconds of connect.
- Meaning:
- 4409 Too Many Requests (single-consumer lock)
- Meaning: Another active subscriber holds the lock for (appKey, chainCode, gateway).
- Action: Wait about 2 minutes plus jitter, then retry; use status check/failover pattern (in Scaling Recommendations, see "Implement a Connection Status Check").
- 4504 Service Timeout
- Meaning: Downstream streaming service interruption (more than 30s).
- Action: Back off ~15s and reconnect; preserve offset.
See also operational patterns and backoff strategies:
- In Performance Considerations, see "Maintain a Healthy Connection and Token Lifecycle."
- In Scaling Recommendations, see "Implement a Connection Status Check."