Concepts
Application Modularity
The Oracle Health Insurance product comprises several applications, each with its own database schema to maintain modularity and isolation between the applications. This design helps in scaling, security, and independent management of the applications. In order to ensure full compatibility between these applications, they share a common base. The licensed applications are installed and upgraded together; each application has the same version number.
Database Users and Roles
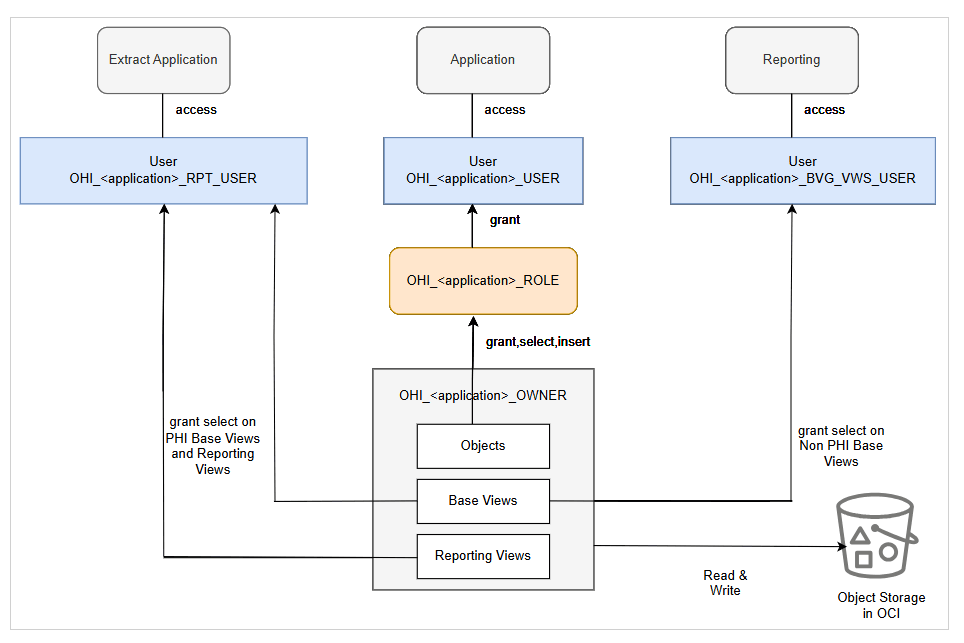
In order to support the modularity, each application has a separate database schema. Below is the description of each schemas that is used to control the way different database users can access the database objects owned by the OHI_<application>_OWNER.
-
Schema OHI_<application>_OWNERcontains the application objects like tables and also the generated base views. This schema is only meant to store objects, not to be accessed directly. -
Schema OHI_<application>_USERis used by the applications to connect to the application objects. This schema cannot access the base views. -
Schema OHI_<application>_BVG_VWS_USERcan be used by reporting tools to access the base views without PHI data. However, if the system property ohi.baseview.exclude.pii is enabled, this user can access base views that include PHI data. This user cannot access the other application objects for security reasons. -
Schema OHI_<application>_RPT_USERis used by the Data Transfer integration point and Operational Reporting user interface pages. This user has access to both reporting views and base views that include PHI data. For auditing and compliance purposes, all PHI data retrieved from these views is logged. The results of the extracts and the PHI retrieval logs are written to OCI Object Storage using the DBMS_CLOUD package in SaaS environment. For On-Prem customers, the results are stored in file system in the database.
The following diagram shows the schemas and their relationships:
Base Views
The Oracle Health Insurance applications present their data model through base views. The base views provide an abstraction over the technical table structure, offering several advantages, such as:
-
Combine fields from base and translation tables for simplified querying.
-
Include both fixed and dynamic fields, making them adaptable to changing data structures.
-
Extensibility structures like dynamic field and dynamic record definition lead to additional views.
Base views may or may not contain PHI data. Generating the base views with PHI data can be controlled using the Base View Integration Point.
For more details about the types and the structure of the base views, see Overview.
Reporting Views
The Oracle Health Insurance applications provide reporting views which are a set of database views specifically designed to support real-time or near-real-time reporting on day-to-day operational data. These views provide an organized, read-only representation of transactional data to ensure that business users, analysts, or reporting tools can access the latest information without directly impacting the underlying transactional systems. Operational reporting views contain PHI data.
User Profiles
Create the user profiles non_phi_user_profile and phi_user_profile to limit the resources utilized by OHI_<application>_BVG_VWS_USER and OHI_<application>_RPT_USER.
To create the user profiles, use the following command:
create profile non_phi_user_profile limit sessions_per_user 10 cpu_per_session unlimited; create profile phi_user_profile limit sessions_per_user 20 cpu_per_session unlimited;
To assign the user profiles to OHI_<application>_BVG_VWS_USER and OHI_<application>_RPT_USER, use the following command:
alter user ohi_<app>_bvg_vws_user profile non_phi_user_profile; alter user ohi_<app>_rpt_extract_user profile phi_user_profile;
Access Restrictions
Operational Reports
These are hand-crafted views that are exposed through the user interface and the associated download function. Target users are application end users, who view the same data as they view anywhere else in the application. Therefore, all types of access restrictions are implemented in these views.