21 Process Orchestration and Monitoring
This chapter describes the basic workflow that triggers batch processes from Process Orchestration and Monitoring (POAM), including monitoring and error handling.
Batch Administration
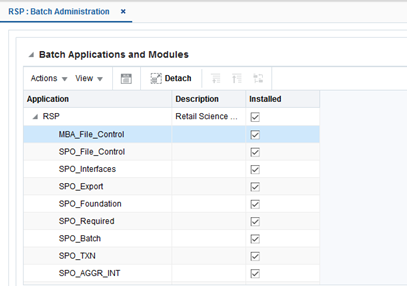
Using the Batch Administration functionality, shown in Figure 21-1, the user can enable and disable application-specific batch processes as a whole or enable and disable individual batch processes at the job level. Any modifications made will become effective with the next scheduler day load (except batch throttling configurations). The execution of application batch processes can be controlled by selecting or deselecting the check box.
To access Batch Administration, from the Tasks list, select Batch Administration.
Batch Monitoring
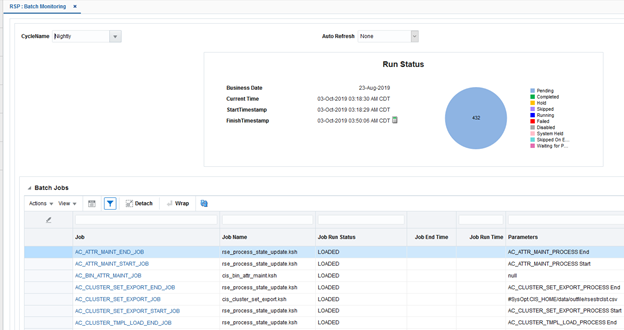
Using Batch Monitoring, shown in Figure 21-2, the user can monitor the current status of different batch processes at cycle level including nightly, ad hoc, and hourly. This screen displays a pie chart section that provides a summary view of the current cycle execution. A job can have 12 different job statuses: Loaded, Pending, Completed, Error, Held, Skipped, Running, Long Running, Disabled, System Held, Skipped on Error, and Waiting.
To access Batch Monitoring, from the Tasks List, select Batch Monitoring.
Monitoring a Batch Cycle
To create a new scheduler day.
-
Access Batch Monitoring.
-
Select the schedule tile for the application for which you want to create a new scheduler day.
-
Click Create Schedule. A popup window appears with the following: Do you want to create a new <application name> schedule for <POM business data>?
-
Click Yes to confirm. A new scheduler day will be created.
-
From the Monitoring Cycle list box, select the Nightly/Ad hoc/Hourly cycle. Note that the individual nightly batch job with its run status is loaded.
-
A pie chart displays the summary view of the current cycle execution.
Triggering Process from POAM
Running a Nightly Batch Process
To run a nightly batch process via the POM UI, complete the following steps:
-
Log into POAM using a valid username and password.
-
Navigate to Batch Monitoring.
-
Select the Nightly tab located below the schedule tiles.
-
From the Auto Refresh drop-down list, select 30 sec.
-
Click the Scheduler Tasks link.
-
In AIF applications Nightly Scheduler Task, select a Task ID, and select Actions > Edit. Alternatively, you can select the Pencil icon.
-
In Edit Task Nightly, do the following:
-
Set Enabled to true.
-
Set the Schedule Date.
-
Set the Schedule Time.
-
Click Ok.
-
-
The nightly batch will kick-off at the specified date and time.
Alternatively, running a nightly batch process can be done via Postman, by executing the following:
-
From Postman, do the following:
-
Post the url and the process to be started in the following format, replacing POAM_URL with the correct value.
POAM_URL/ProcessServices/services/private/executionEngine/schedules/RSP/execution
For example:
http://<pom-server-url>.us.oracle.com/ ProcessServices/services/private/executionEngine/schedules/RSP/execution.
-
In the Authorization section, provide the correct user name and password for the environment.
-
In the body, provide details for Cycle name, Flow name, and Request type. For example:
{ "cycleName" : "Nightly", "flowName" : "Nightly", "requestType" : "External Request" } -
Click Post. The body indicates that the execution has started. The process begins executing in POAM.
-
Monitoring the Process Executions
After triggering the process from Postman, the user can view the progress of the batch execution and the state of the batch process (either pass or fail) in the POAM UI. In the POAM UI, open the Batch Monitoring screen and select Nightly. Refresh the scheduler day you created. The batch schedule status can be viewed in the displayed graph; if Auto Refresh is set, then the graph is automatically updated.
Note the following:
-
The nightly batch schedule, once executed successfully, opens the next day automatically.
-
If any batch failures have occurred, the next day will not open automatically. In such cases, the failure must be resolved, the existing scheduler day must be closed, and the new scheduler day must be opened manually.
-
AIF Data and AIF Apps schedules must always be on same business dates. Triggering AIF DATA will automatically start the AIF application batch processes (once AIF Data completes, it starts the AIF Apps schedule.)
Error Handling
A batch process can fail because of the following:
-
An actual batch process failure.
-
A failure as a result of the loss of communication between POAM JOS components.
-
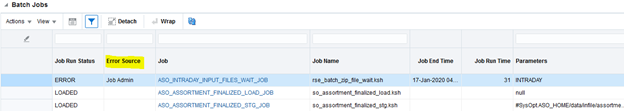
'The Error Source column lists the source of error. If the source is POAM, it is generally a connection issue.
If the source of the error is Job Admin, it can be either a connection failure or an actual job failure. This can be determined by examining the logs for JOS JOB ADMIN.
JOS JOB ADMIN
-
.Log into JOS JOB ADMIN using a valid user name and password.
-
Navigate to System Logs.
-
Against the job name, there is a link to download the log. Also, clicking on the job name brings up a screen that also has a link to download the logs.
Skipping a Failed Job
If any job has failed for a known reason, the user can bypass it. In this way, the schedule releases the dependency and can continue executing other jobs.
To skip a failed job, complete the following steps:
-
Navigate to POAM > Batch Monitoring.
-
Select the job row that you want to skip.
-
Click Skip or Release Skip from More Actions.
-
Add any appropriate comments.
-
The status of the job will change to SKIPPED if the action is SKIP or to LOADED if the action is Release Skip.
-
Note that a job that already has a status of Skipped can only be released.