Variance Report
A variance report is created for each bucket in each cycle of the inventory count. After the final count cycle sheet has been submitted, or once all inventory bucket statuses are complete, the system posts inventory and creates the final variance report for all buckets.
-
To view a variance report, select the View Variance Reports menu option. See Figure 5-33.
-
Select a variance report from the list:
Figure 5-37 Variance Reports LIst
-
Select Print report to execute the report and send the results to a printer.
-
Select Save report to save this report with the current data or save only the report parameters to run this specific report with these parameters again. If you save the report, assign a name to it so it can be viewed whenever needed. Xstore suggests a name, but you may type in the Save Report As field and change it.
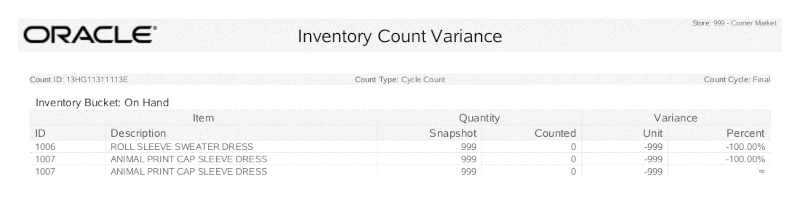
Variance Reports include the following header information:
-
Count #: The auto-generated count identifier associated with the Inventory Count document.
-
Count Type: The type of count: Physical Count, Cycle Count, Supply Count
-
Count Cycle: Indicates the number of times the bucket was counted to obtain these results.
-
Inventory Bucket Section: Used for Physical Inventory counts; defines the store layout area for the count.
For each Item ID with a variance in the inventory bucket, the following information is shown:
-
Item ID: The item identifier.
-
Description: The item description.
-
Snapshot quantity: The quantity recorded when the count was initialized.
-
Counted quantity: The count value submitted by the associate after counting the items.
-
Unit variance: The difference between the snapshot value and the submitted count value.
-
% variance: The difference between the snapshot value and the submitted count value, as a percentage.
Variance Percentage Calculation Formula: If snapshot quantity = 0 then infinity,
else,
If snapshot quantity < 0 then (-1 * (unit variance / snapshot quantity)) * 100, else,
(unit variance / snapshot quantity) * 100
Please note that rather large variance percentages (well over 100%) are correct if you have a small snapshot quantity and a large unit variance.
Figure 5-38 Count Cycle Variance Report Example
-