D Command-Line Options
This appendix describes some command-line options that can be useful when diagnosing problems with the Java HotSpot VM.
This appendix contains the following sections:
Java HotSpot VM Command-Line Options
Command-line options that are prefixed with -XX are specific to the Java HotSpot Virtual Machine. Many of these options are important for performance tuning and diagnostic purposes, and are therefore described in this appendix.
To know more about all possible -XX options, see the Java HotSpot VM Options.
You can dynamically set, unset, or change the value of certain Java VM flags for a specified Java process using the jinfo -flag command. See The jinfo Utility and the JConsole utility.
For a complete list of these flags, use the MBeans tab of the JConsole utility. See the list of values for the DiagnosticOptions attribute of the HotSpotDiagnostic MBean, which is in the com.sun.management domain. The following are the flags:
-
HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -
HeapDumpPath -
PrintGC -
PrintGCDetails -
PrintGCTimeStamps -
PrintClassHistogram -
PrintConcurrentLocks
The -XX:HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError Option
This option tells the Java HotSpot VM to generate a heap dump when an allocation from the Java heap or the permanent generation cannot be satisfied. There is no overhead in running with this option, so it can be useful for production systems where the java.lang.OutOfMemoryError takes a long time to appear.
You can also specify this option at runtime with the MBeans tab in the JConsole utility.
The following example shows the result of running out of memory with this flag set.
$ java -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -mn256m -mx512m ConsumeHeap
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
Dumping heap to java_pid2262.hprof ...
Heap dump file created [531535128 bytes in 14.691 secs]
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
at ConsumeHeap$BigObject.(ConsumeHeap.java:22)
at ConsumeHeap.main(ConsumeHeap.java:32)
The ConsumeHeap fills the Java heap and runs out of memory. When a java.lang.OutOfMemoryError is thrown, a heap dump file is created. In this case the file is 507 MB and is created with the name java_pid2262.hprof in the current directory.
By default, the heap dump is created in a file called java_pidpid.hprof in the working directory of the VM, as in the example above. You can specify an alternative file name or directory with the -XX:HeapDumpPath= option. For example -XX:HeapDumpPath=/disk2/dumps will cause the heap dump to be generated in the /disk2/dumps directory.
The -XX:OnError Option
When a fatal error occurs, the Java HotSpot VM can optionally execute a user-supplied script or command. The script or command is specified using the -XX:OnError=string command-line option, where string is a single command, or a list of commands separated by semicolons. Within this string, all occurrences of %p are replaced with the current PID, and all occurrences of %% are replaced by a single %. The following examples demonstrate how this option can be used when launching a Java application named MyApp with the java launcher.
-
java -XX:OnError="cat hs_err_pid%p.log | mail support@example.com" MyAppIn the example above, the contents of the fatal error log file are mailed to a support alias when a fatal error occurs.
-
java -XX:OnError="gdb - %p" MyAppOn Linux, the
gdbcommand launches the debugger. In the example above, thegdbdebugger is launched and attached to the current process when an unexpected error is encountered. -
java -XX:OnError="userdump.exe %p" MyAppOn Windows, the
userdump.exeutility creates a crash dump of the specified process. The utility does not ship with Windows and should be downloaded from the Microsoft website as a part of the Microsoft OEM Support Tools package.In the example, the
userdump.exeutility is executed to create a core dump of the current process in case of a fatal error.Note:
The example assumes that the path to the
userdump.exeutility is defined in thePATHvariable.
To know more about creating crash dumps on Windows, see Collect Crash Dumps on Windows.
The -XX:ShowMessageBoxOnError Option
When this option is set and a fatal error occurs, the HotSpot VM will display information about the fatal error and prompt the user to specify whether the native debugger is to be launched. In the case of the Linux operating system, the output and prompt are sent to the application console (standard input and standard output). In the case of Windows, a Windows message box pops up.
The following example shows a fatal error on a Linux system.
==============================================================================
Unexpected Error
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SIGSEGV (0xb) at pc=0x2000000001164db1, pid=10791, tid=1026
Do you want to debug the problem?
To debug, run 'gdb /proc/10791/exe 10791'; then switch to thread 1026
Enter 'yes' to launch gdb automatically (PATH must include gdb)
Otherwise, press RETURN to abort...
==============================================================================
In this case, a SIGSEGV error occurred, and the user is prompted to specify whether the gdb debugger is to be launched to attach to the process. If the user enters y or yes, thengdb will be launched (assuming it is set in the PATH variable).
On Windows a message box is displayed. If the user clicks Yes, the VM will attempt to start the default debugger. This debugger is configured by a registry setting which is described in Collect Crash Dumps on Windows. If Microsoft Visual Studio is installed, the default debugger is typically configured to be msdev.exe.
In the above example, the output includes the PID (pid=10791) and also the thread ID (tid=1026). If the debugger is launched, one of the initial steps in the debugger might be to select the thread and get its stack trace.
When the process is waiting for a response, it is possible to use other tools to get a crash dump or query the state of the process.
On Windows, a Dr. Watson crash dump can be obtained using the userdump or windbg programs. The windbg utility is included in Microsoft's Debugging Tools for Windows and is described in Collect Crash Dumps on Windows. In windbg, select the Attach to a Process menu option, which displays the list of processes and prompts for the PID. The HotSpot VM displays a message box, which includes the PID. After you selected the PID, the .dump /f command can be used to force a crash dump. Figure D-1 is an example crash dump created in a file named crash.dump.
Figure D-1 Example of a Crash Dump Created by windbg
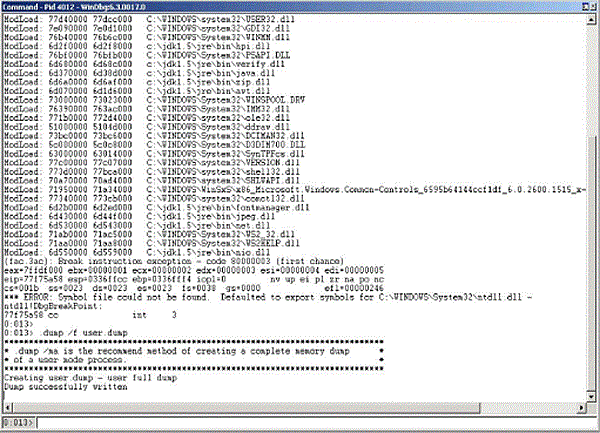
Description of "Figure D-1 Example of a Crash Dump Created by windbg"
In general, the -XX:+ShowMessageBoxOnError option is more useful in a development environment where the debugger tools are available. The -XX:OnError option is more suitable for production environments where a fixed sequence of commands or scripts are executed when a fatal error occurs.
Other -XX Options
Several other -XX command-line options can be useful when troubleshooting:
-
-XX:OnOutOfMemoryError=stringThis option can be used to specify a command or script to execute when a
java.lang.OutOfMemoryErroris thrown. -
-XX:ErrorFile=filenameThis option can be used to specify a location for the fatal error log file. See Location of Fatal Error Log.
-
-xx:HeapDumpPath=pathThis option can be used to specify a location for the heap dump. See The -XX:HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError Option.
-
-XX:MaxPermSize=sizeThis option can be used to specify the size of the permanent generation memory. See The java.lang.OutOfMemoryError Error.
-
-XX:+PrintCommandLineFlagsThis option can be used to print all the VM command-line flags. See Collect Data for a Bug Report.
-
-XX:+PrintConcurrentLocksThis option can be used to cause the Control+Break handler to print a list of concurrent locks owned by each thread.
-
-XX:+PrintClassHistogramThis option can be used to cause the Control+Break handler to print a heap histogram.
-
-XX:+PrintGCDetailsand-XX:+PrintGCTimeStampsThese options can be used to print detailed information about garbage collection. See The -verbose:gc Option.
-
-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC,-XX:+UseSerialGCand-XX:+UseParallelGCThese options can be used to specify the garbage collection policy to be used. See Working Around Crashes During Garbage Collection.
Other Command-Line Options
In addition to the -XX options, many other command-line options can provide troubleshooting information.
This section describes a few of these options.
The -Xcheck:jni Option
This option is useful when diagnosing problems with applications that use the Java Native Interface (JNI). Sometimes, bugs in the native code can cause the HotSpot VM to crash or behave incorrectly.
The -Xcheck:jni option is added to the command line that starts the application, as in the following example:
java -Xcheck:jni MyApp
The -Xcheck:jni option causes the VM to do additional validation of the use of JNI functions. This includes argument validation and other usage constraints as described below.
Note:
The option is not guaranteed to find all invalid arguments or diagnose logic bugs in the application code, but it can help diagnose a large number of such problems.When a significant usage error is detected, the VM prints a message to the application console or to standard output, prints the stack trace of the offending thread, and stops the VM.
The following example shows a null value was incorrectly passed to a JNI function that does not allow a null value.
FATAL ERROR in native method: Null object passed to JNI
at java.net.PlainSocketImpl.socketAccept(Native Method)
at java.net.PlainSocketImpl.accept(PlainSocketImpl.java:343)
- locked <0x450b9f70> (a java.net.PlainSocketImpl)
at java.net.ServerSocket.implAccept(ServerSocket.java:439)
at java.net.ServerSocket.accept(ServerSocket.java:410)
at org.apache.tomcat.service.PoolTcpEndpoint.acceptSocket
(PoolTcpEndpoint.java:286)
at org.apache.tomcat.service.TcpWorkerThread.runIt
(PoolTcpEndpoint.java:402)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.ThreadPool$ControlRunnable.run
(ThreadPool.java:498)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:536)
The following example shows an incorrect argument that was provided to a JNI function that expects a jfieldID argument.
FATAL ERROR in native method: Instance field not found in JNI get/set
field operations
at java.net.PlainSocketImpl.socketBind(Native Method)
at java.net.PlainSocketImpl.bind(PlainSocketImpl.java:359)
- locked <0xf082f290> (a java.net.PlainSocketImpl)
at java.net.ServerSocket.bind(ServerSocket.java:318)
at java.net.ServerSocket.<init>(ServerSocket.java:185)
at jvm003a.<init>(jvm003.java:190)
at jvm003a.<init>(jvm003.java:151)
at jvm003.run(jvm003.java:51)
at jvm003.main(jvm003.java:30)
- The thread doing the call is not attached to the JVM
- The thread doing the call is using the JNIEnv belonging to another thread
- A parameter validation check fails:
- A jfieldID, or jmethodID, is detected as being invalid. For example:
- Of the wrong type
- Associated with the wrong class
- A parameter of the wrong type is detected
- An invalid parameter value is detected. For example:
- NULL where not permitted
- An out-of-bounds array index, or frame capacity
- A non-UTF-8 string
- An invalid JNI reference
- An attempt to use a ReleaseXXX function on a parameter not produced by the corresponding GetXXX function
- A jfieldID, or jmethodID, is detected as being invalid. For example:
- A JNI call was made without checking for a pending exception from a previous JNI call, and the current call is not safe when an exception may be pending
- The number of JNI local references existing when a JNI function terminates exceeds the number guaranteed to be available. See the EnsureLocalcapacity function
- A class descriptor is in decorated format (Lname;) when it should not be
- A NULL parameter is allowed, but its use is questionable
- Calling other JNI functions in the scope of Get/ReleasePrimitiveArrayCritical or Get/ReleaseStringCritical
This non-fatal warning message is shown in the following example.
Warning: Calling other JNI functions in the scope of
Get/ReleasePrimitiveArrayCritical or Get/ReleaseStringCritical
A JNI critical region is created when native code uses the JNI functions GetPrimitiveArrayCritical or GetStringCritical to obtain a reference to an array or string in the Java heap. The reference is held until the native code calls the corresponding release function. The code between the get and release is called a JNI critical section, and during that time, the HotSpot VM cannot bring the VM to a state that allows garbage collection to occur. The general recommendation is not to use other JNI functions within a JNI critical section, and in particular any JNI function that could potentially cause a deadlock. The warning printed above by the -Xcheck:jni option is thus an indication of a potential issue; it does not always indicate an application bug.
The -verbose:class Option
This option enables logging of class loading and unloading.
The -verbose:gc Option
This option enables logging of garbage collection (GC) information. It can be combined with other HotSpot VM-specific options such as -XX:+PrintGCDetails and -XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps to get further information about GC. The information output includes the size of the generations before and after each GC, total size of the heap, the size of objects promoted, and the time taken.
More information about these options, along with detailed information about GC analysis and tuning are described in the GC Portal article.
The -verbose:gc option can be dynamically enabled at runtime using the management API or JVM TI. See Custom Diagnostic Tools.
The JConsole monitoring and management tool can also enable or disable the option when the tool is attached to a management VM. See JConsole.
The -verbose:jni Option
This option enables the logging of JNI. When a JNI or native method is resolved, the HotSpot VM prints a trace message to the application console (standard output). It also prints a trace message when a native method is registered using the JNI RegisterNative function. The -verbose:jni option can be useful when diagnosing issues with applications that use native libraries.