Note:
- This tutorial requires access to Oracle Cloud. To sign up for a free account, see Get started with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tier.
- It uses example values for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure credentials, tenancy, and compartments. When completing your lab, substitute these values with ones specific to your cloud environment.
Configure HTTP Virtual Service on NSX Advanced Load Balancer in Oracle Cloud VMware Solution SDDC for Internal Users
Introduction
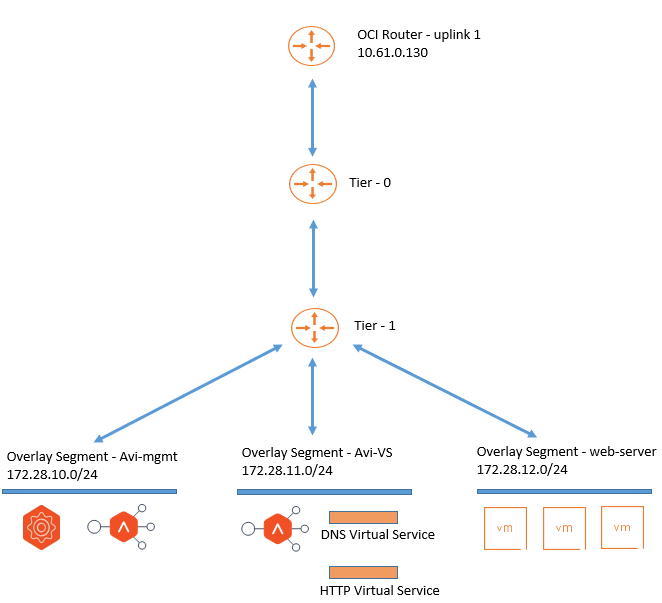
In this series, we have covered the deployment and configuration of NSX Advanced Load Balancer (formerly known as Avi Networks) controllers, along with the set up of a DNS virtual service.
This is the fourth tutorial and focuses on the deployment of an HTTP virtual service on the NSX Advanced Load Balancer (NSX ALB) within the Oracle Cloud VMware Solution Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC).
Objectives
- Administrators will be able to deploy and access HTTP virtual service via domain name for internal users.
Prerequisites
-
NSX ALB (Avi) controller has been deployed and configured on the Oracle Cloud VMware Solution SDDC, see Tutorial 1: Deploy VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer on Oracle Cloud VMware Solution SDDC and Tutorial 2: Configure VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer on Oracle Cloud VMware Solution.
-
DNS virtual service to be set up as it is required for name resolution, see Tutorial 3: Configure DNS Virtual Service on NSX Advanced Load Balancer in Oracle Cloud VMware Solution SDDC.
Task 1: Verify a Web Server Accessibility
We have deployed three Nginx web servers connected to Oracle Cloud VMware Solution NSX-T overlay web segment. The servers are reachable directly via their IP address.
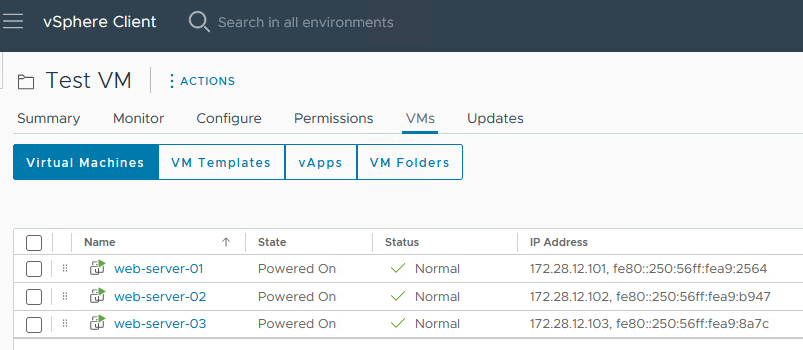
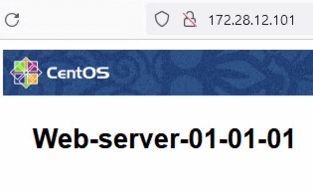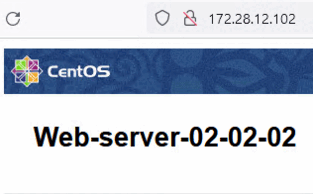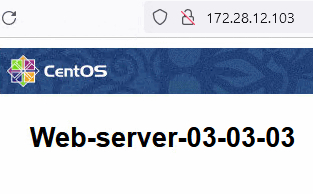
Task 2: Deploy HTTP Virtual Service
For the web servers, we will deploy HTTP virtual service. After deploying the HTTP virtual service, web servers will be accessible in a round robin method.
-
Log in to the NSX ALB (Avi) controller portal, navigate to Applications, Virtual Services, Create Virtual Service and click Advanced Setup.
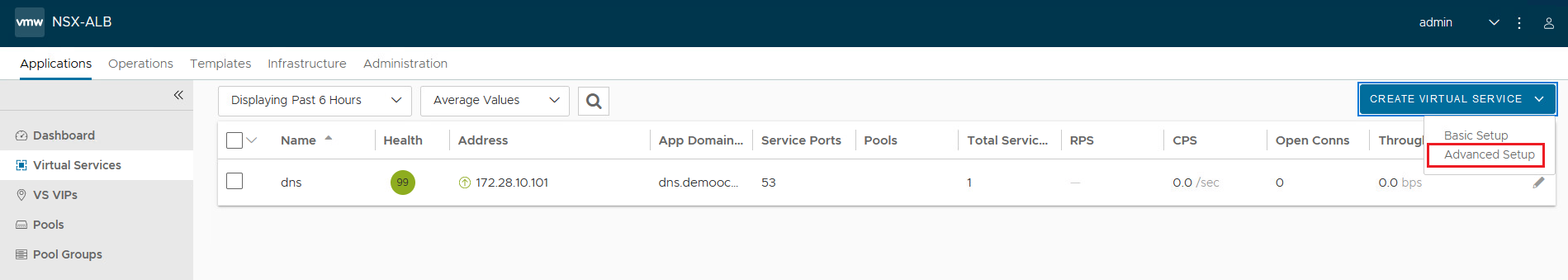
-
In the Select Cloud window, select NSX-T as Cloud connector and click Next.
-
Enter the Virtual Service Name and select the Application Profile as
System-HTTP. -
Click on the VS VIP drop-down list, Create VS VIP and select Tier1 Logical Router as
Tier-1.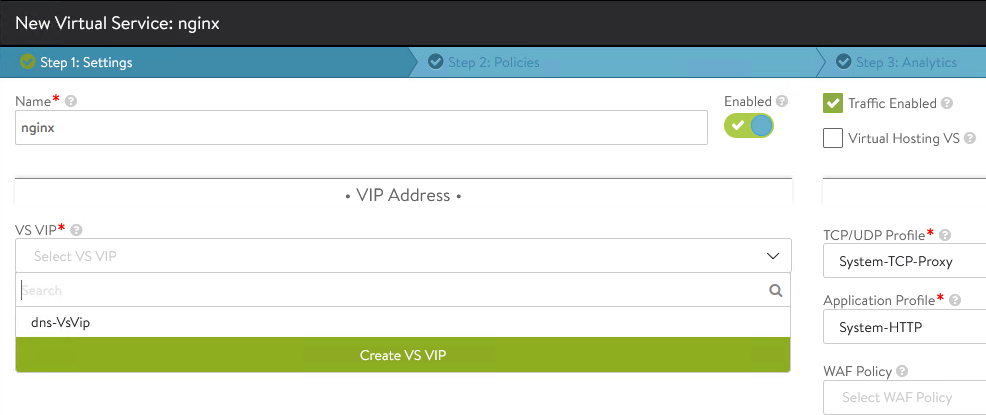
-
In the VIP window, click Add. Keep the default options and enter
avi-vsas VIP Address Allocation Network, the associated CIDR block as IPv4 Subnet and then click Save.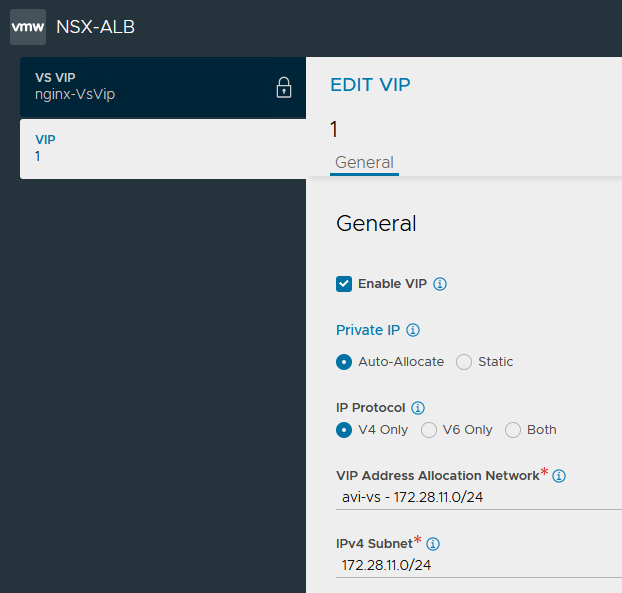
-
In the DNS section, click Add and keep the default configurations and then click Save. We are publishing HTTP virtual service with the Application Domain name
nginx. Click Save again on the VS-VIP window.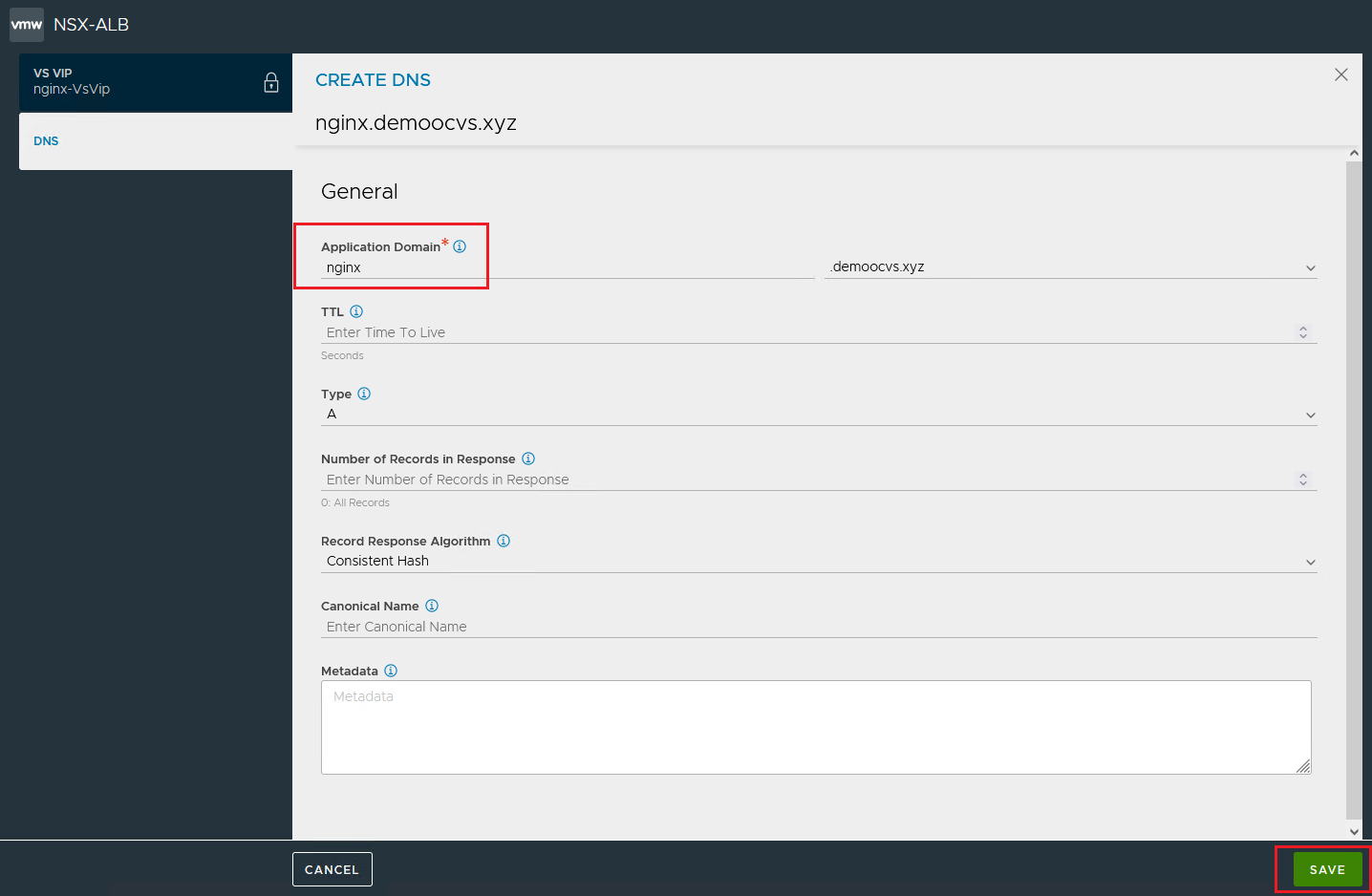
-
In the Pool section, click on the Pool drop-down list and then Create Pool.
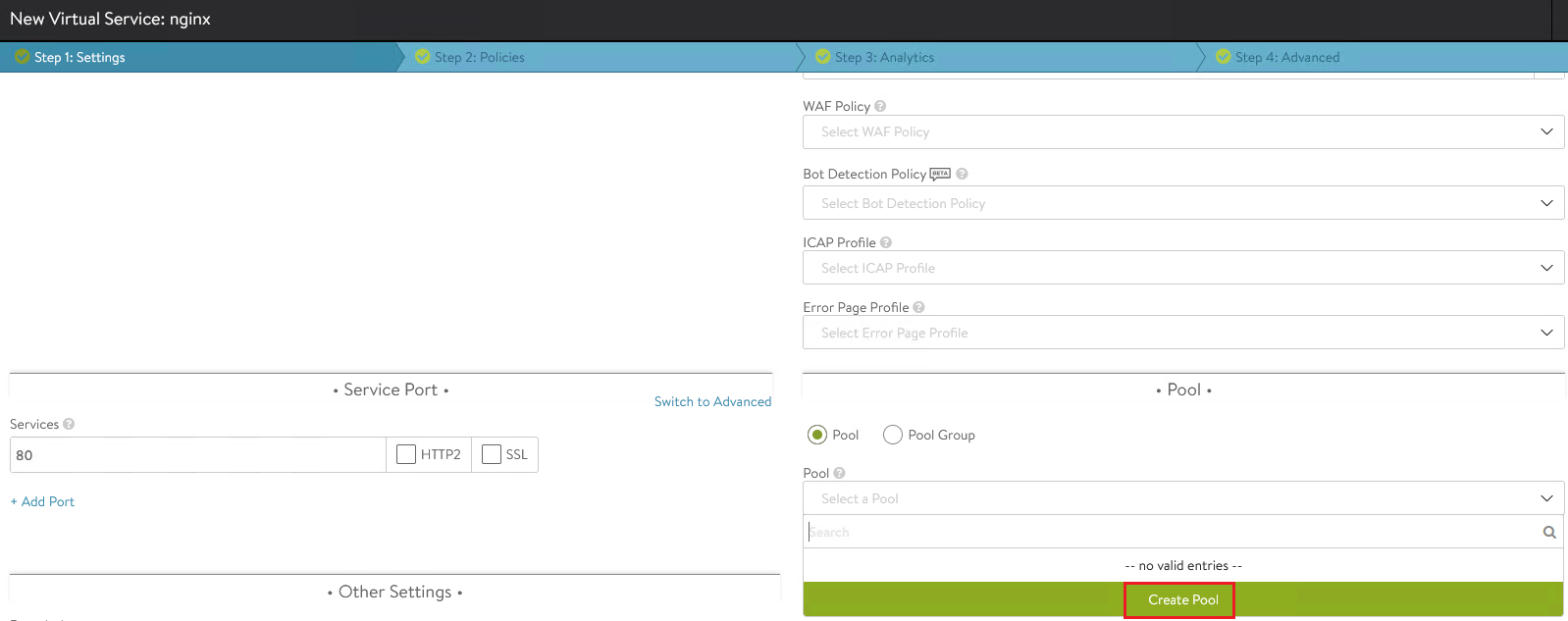
-
Keep other details as default and select the Load Balance Algorithm as
Round Robin.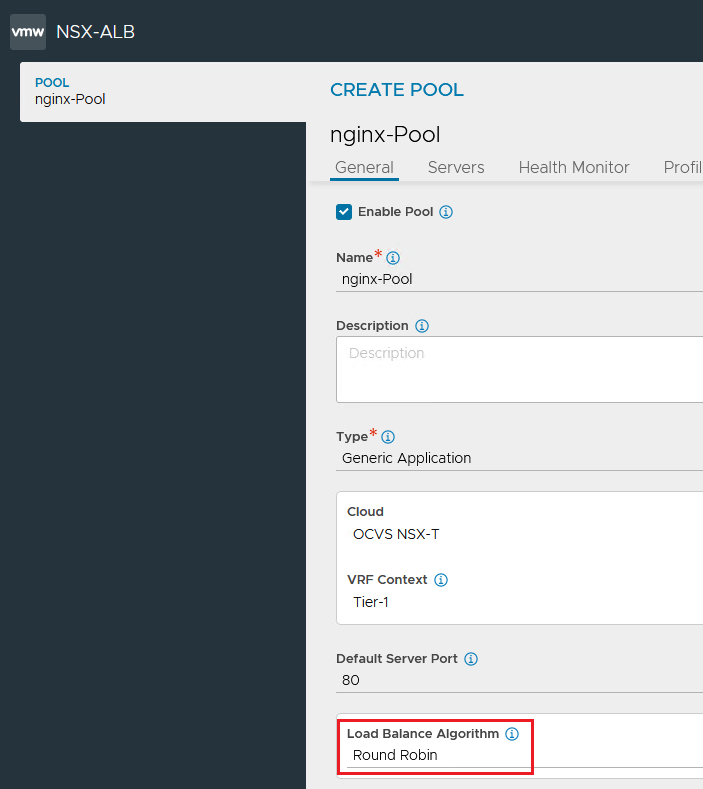
-
Select Tier1 Logical Router as
Tier-1. Scroll down and add the backend nginx web servers via IP address.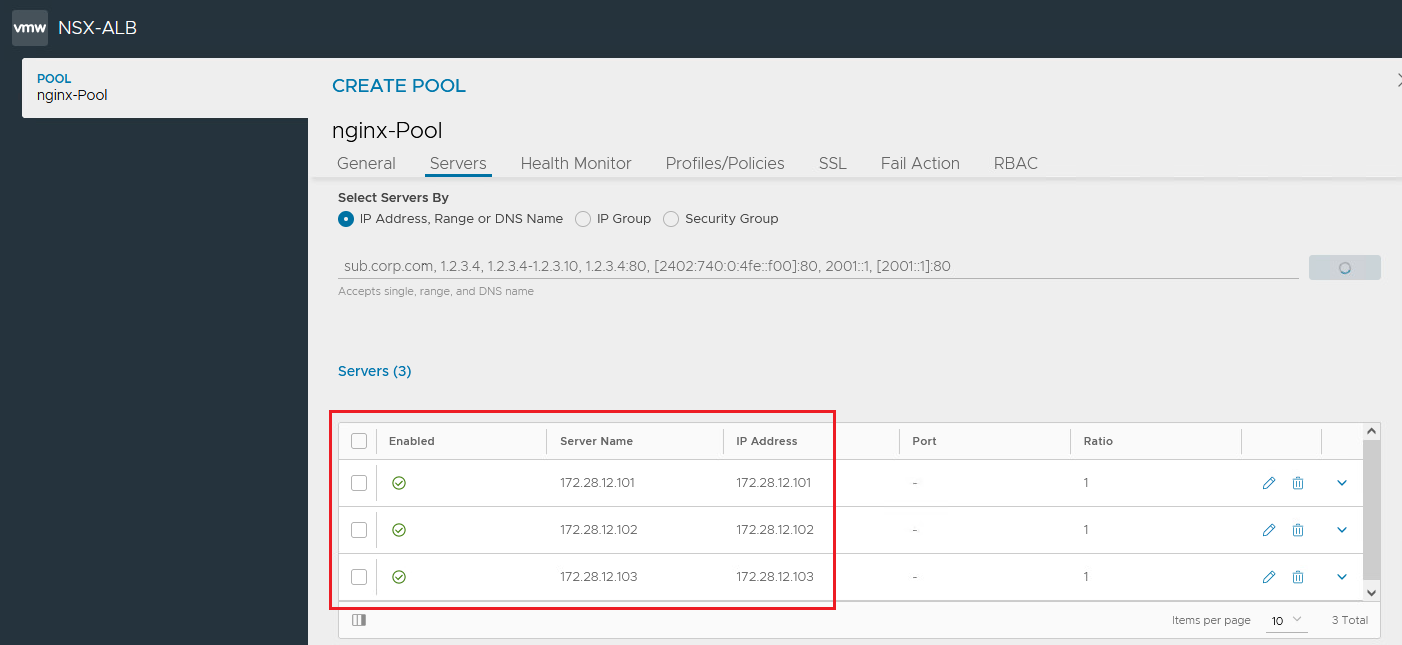
-
In Health Monitor section, click Add and select Name as
System-HTTP. Click Save and then Next.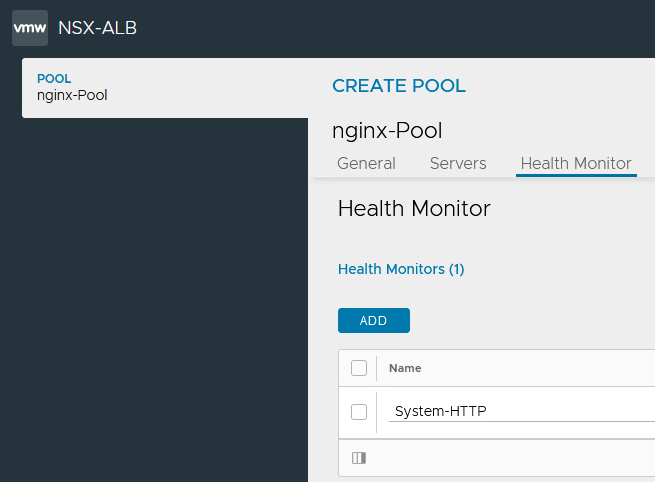
-
In the Analytics section, select Log all headers and update non-significant log duration to
0to keep all the non-significant logs and then click Next to finish the wizard.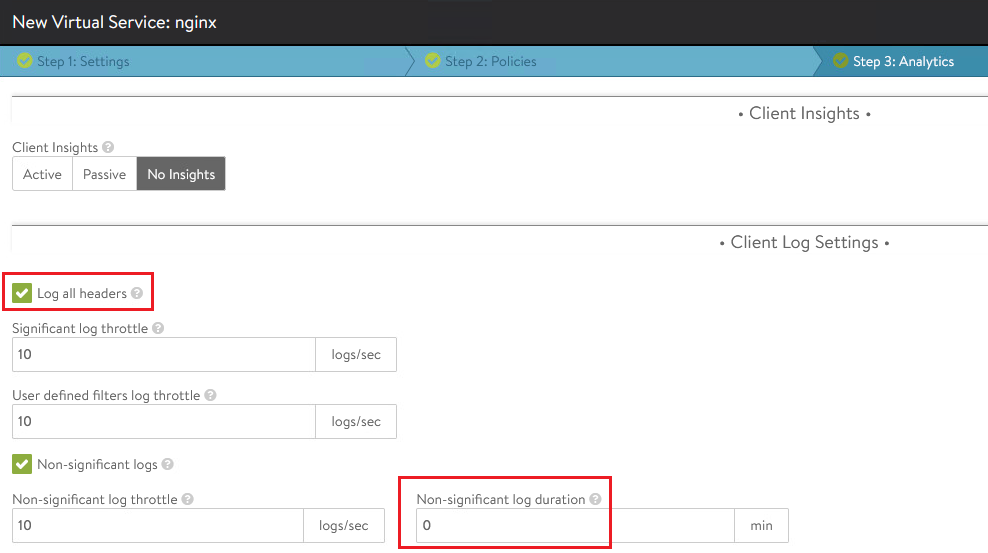
After this nginx virtual service should report healthy status.
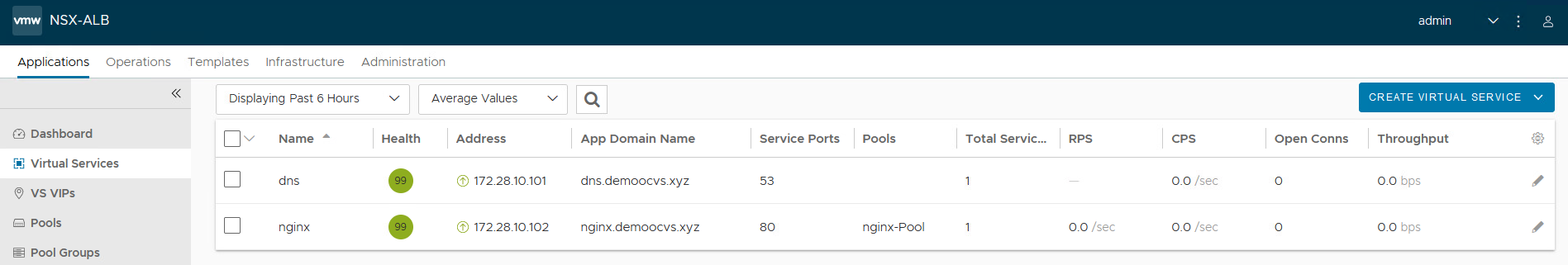
Task 3: Verify DNS Records
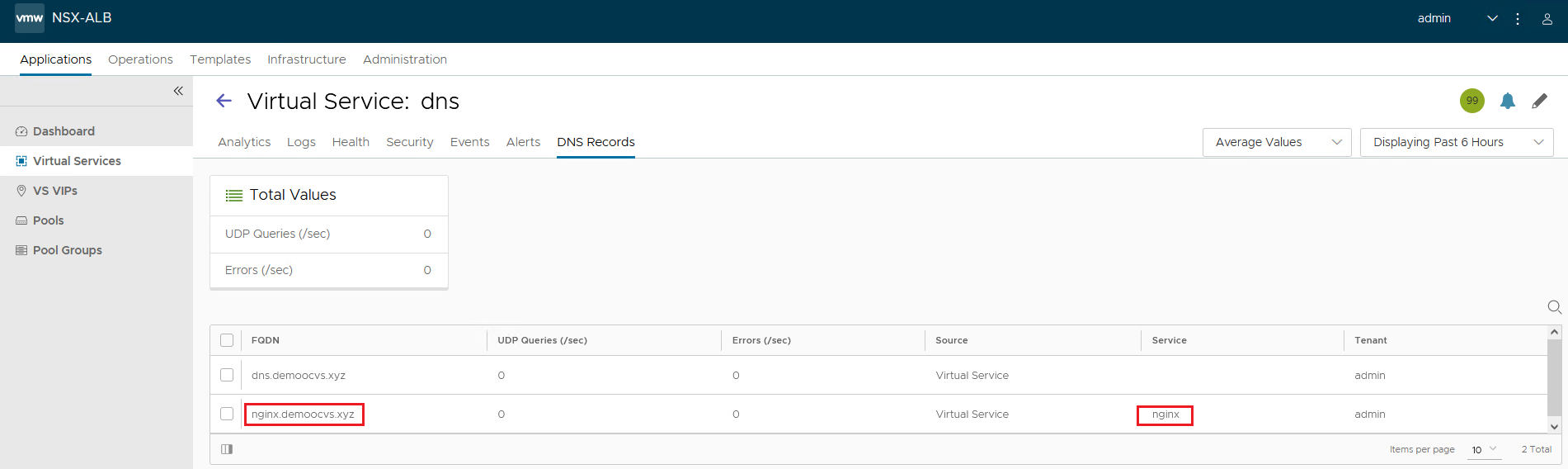
After creating HTTP virtual service, the web servers should be accessible over virtual service IP address. Within a couple of minutes the DNS entry for the HTTP virtual service should automatically get created. To verify the DNS entry for the HTTP virtual service, follow these steps:
Navigate to Application, DNS Virtual Service and click DNS Records. We should see the DNS entries mapped against their respective virtual services.
Task 4: Set up DNS forwarder to access HTTP Virtual Service via Domain Name
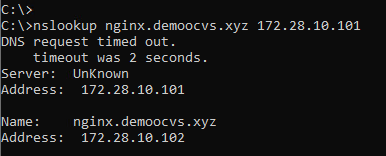
The virtual service is in green or available state and it is accessible over IP address. It is currently not accessible via domain name as we need to point the corporate DNS server to 172.24.10.101 (DNS virtual service IP) for domain demoocvs.xyz.
If we manually try to resolve the URL to point to the DNS virtual service IP, it should work as the DNS virtual service holds the DNS records.
-
Set up DNS forwarding from the Oracle Cloud VMware Solution VCN
To establish connectivity from Oracle Cloud VMware Solution NSX-T overlay segment to OCI VCN subnet, see Connecting an SDDC to Other Resources in the VCN.
-
Log in to the OCI tenancy, navigate to Networking, Virtual Cloud Networks, click the appropriate VCN and then DNS resolver.
-
Click Endpoints, Create Endpoints and enter the following information.
- Name: Enter name as
forwarder. - Endpoints: select endpoint as
Forwarding. - Select the Oracle Cloud VMware Solution provisioning subnet.
- Name: Enter name as
-
Click Rules and Manage rules.
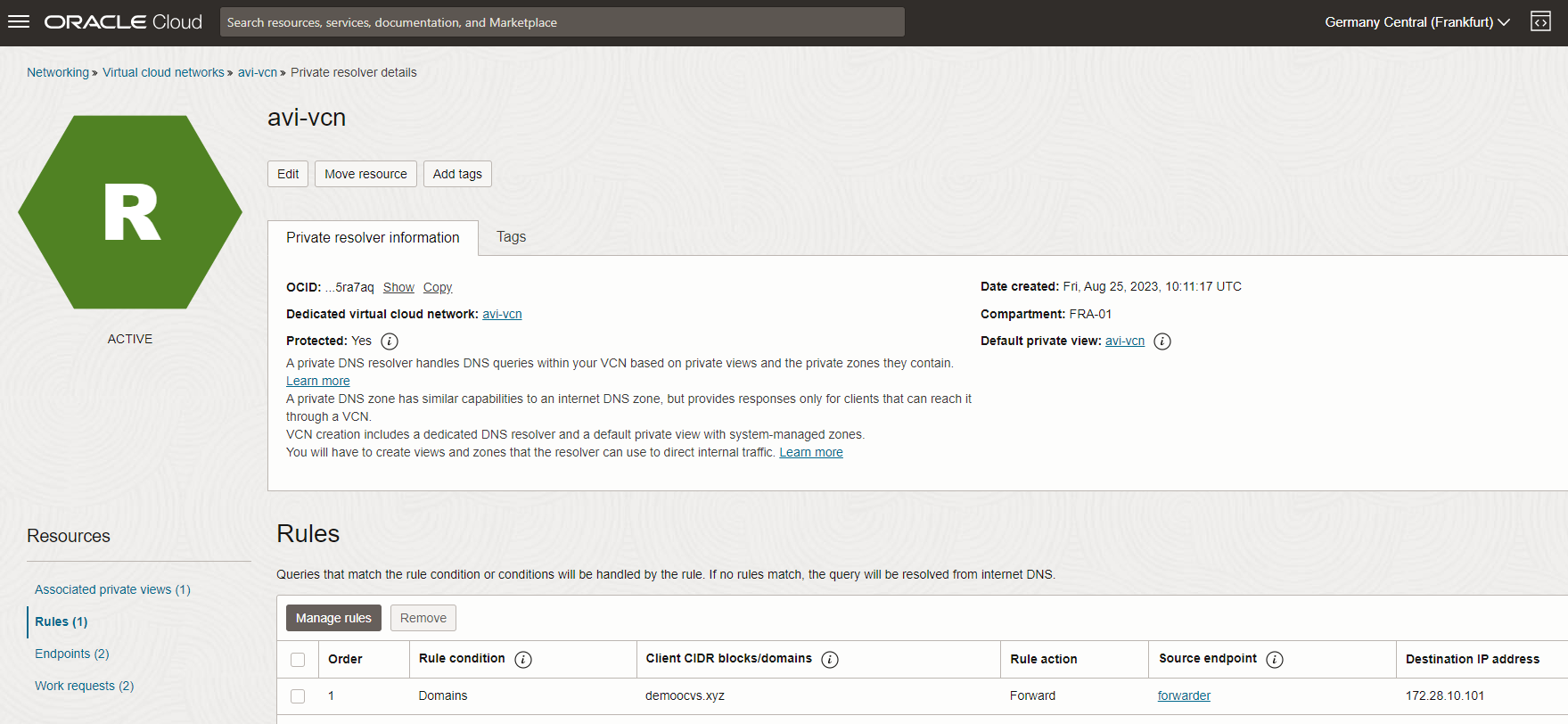
This will enable communication from OCI instances to NSX ALB virtual service hosted domain.
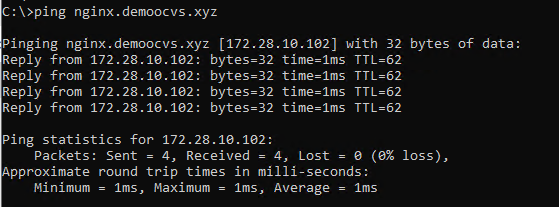
-
-
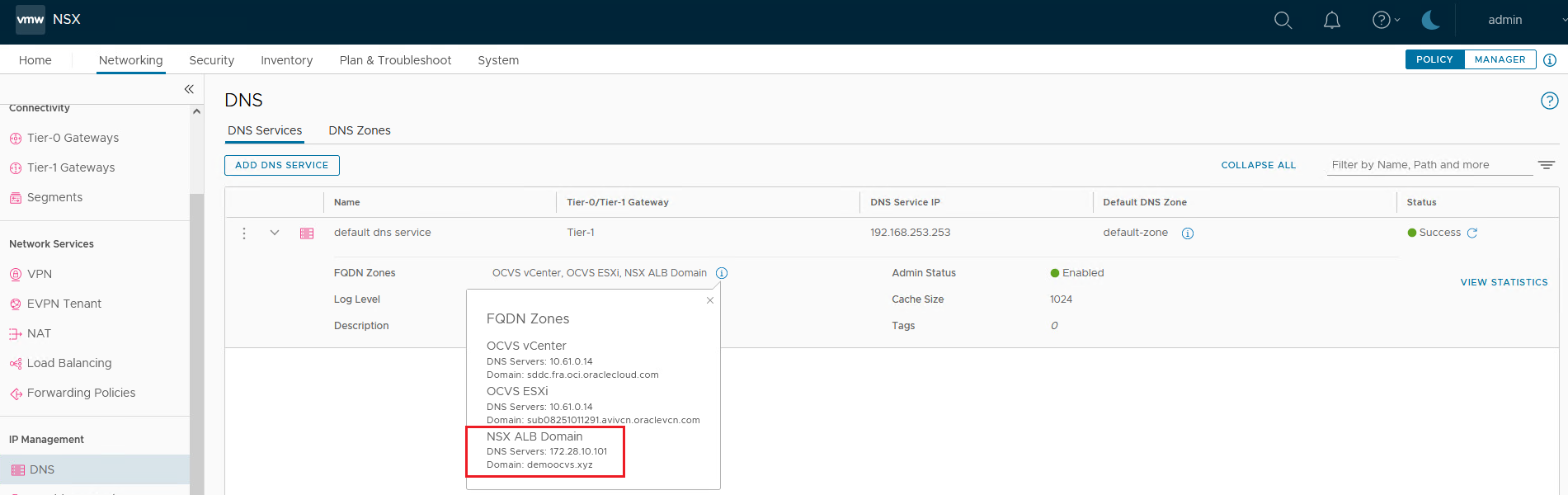
Set up Name Resolution from VM’s residing on the Oracle Cloud VMware Solution NSX-T Overlay Segment
To set up DNS service IP on NSX-T and create a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) DNS Zone to create a forwarder, see Enable DNS resolution for public URLs from Oracle Cloud VMware Solution NSX-T Overlay Segment.
This will set up the connectivity via domain name.
-
Set up Name Resolution from On-premises Data Center
To establish connectivity from on-premises network to the NSX-T overlay segment using Oracle Cloud VMware Solution wizard, see Connecting an SDDC to an On-premises Network.
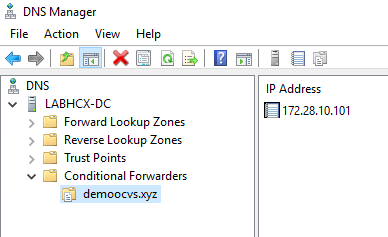
Enable Conditional Forwarders on the on-premises DNS server. This should enable access to the Avi domain from on-premises network.
Next Steps
To configure HTTP virtual service on the NSX ALB on Oracle Cloud VMware Solution for internet based access, see Tutorial 5: Configure HTTP Virtual service on the NSX Advanced Load Balancer (Avi)on Oracle Cloud VMware Solution for Internet-based access.
Acknowledgments
- Author - Vaibhav Tiwari (Cloud VMware Solutions Specialist)
More Learning Resources
Explore other labs on docs.oracle.com/learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. Additionally, visit education.oracle.com/learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.
For product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.
Configure HTTP Virtual Service on NSX Advanced Load Balancer in Oracle Cloud VMware Solution SDDC for Internal Users
F93337-01
February 2024
Copyright © 2024, Oracle and/or its affiliates.