Note:
- This tutorial requires access to Oracle Cloud. To sign up for a free account, see Get started with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tier.
- It uses example values for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure credentials, tenancy, and compartments. When completing your lab, substitute these values with ones specific to your cloud environment.
Deploy Omnissa Horizon 8 on Oracle Cloud VMware Solution
Introduction
This tutorial provides a step-by-step guide to install and configure Omnissa Horizon 8 on an Oracle Cloud VMware Solution software-defined data center (SDDC). It is designed to help Oracle teams, partners, and customers perform a successful proof-of-concept (POC) deployment.
The focus of this tutorial is to configure the necessary components in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) to support a Omnissa Horizon deployment. While the Omnissa Horizon installation and configuration steps remain consistent with traditional on-premises environments, deploying in OCI introduces specific infrastructure requirements. These include:
- Create and configure virtual local area networks (VLANs).
- Provision Load Balancer as a Service (LBaaS).
- Deploy Database as a Service (DBaaS), if required,
- Deploy the Oracle Cloud VMware Solution SDDC cluster.
- Set up route rules and security lists.
These cloud-specific tasks form the foundation of the deployment and are the primary focus of this tutorial. Once these are complete, the standard Omnissa Horizon deployment process follows as it would in a vSphere 8.x environment.
Overview of Oracle Cloud VMware Solution for Omnissa Horizon
Oracle Cloud VMware Solution is a customer-managed platform that allows you to deploy and manage VMware vSphere clusters on OCI using bare metal compute instances and Layer 2 (L2) virtual networking.
Before deploying Omnissa Horizon, you must first provision an Oracle Cloud VMware Solution cluster with a minimum of three nodes to support a vSAN configuration. This tutorial outlines all the required prerequisites and OCI-specific tasks necessary for a successful deployment.
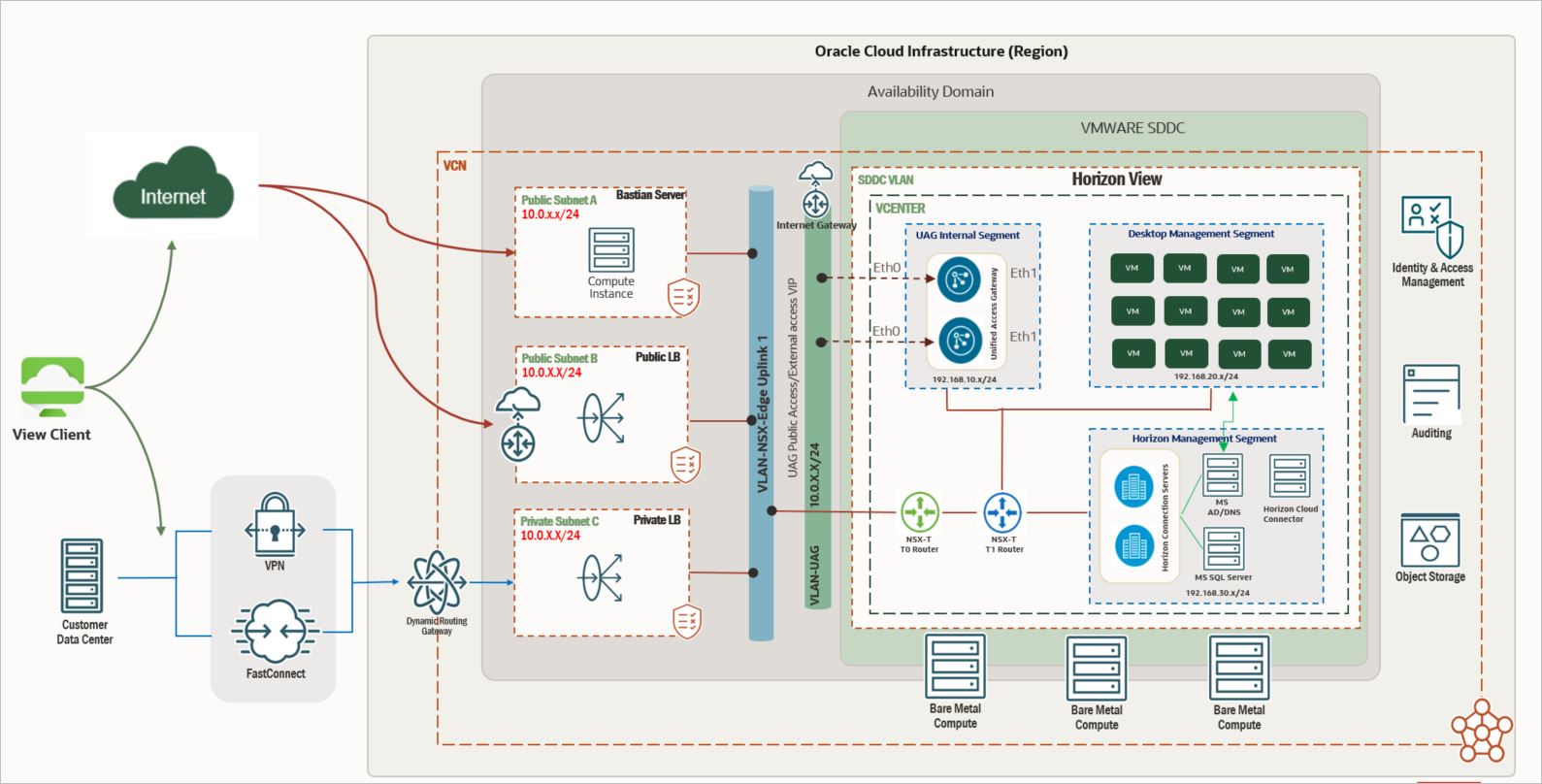
For the purposes of this tutorial, the following high-level reference architecture is used:
The architecture supports two primary deployment models:
-
Deployment Model 1: Internal Access Only
If the environment will be accessed only from within an internal network, you may skip the following steps
- Add a new VLAN for Unified Access Gateway (UAG) appliances.
- Deploy and configure UAG.
- Configure a public OCI Load Balancer.
-
Deployment Model 2: Public Access
If external (public) access to the environment is required, for example, users connecting from the internet then all sections of this tutorial must be completed, including UAG deployment and public OCI Load Balancer configuration.
Objectives
- Install and configure Omnissa Horizon 8 on Oracle Cloud VMware Solution.
Prerequisites
-
Ensure that you have the appropriate Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (OCI IAM) permissions to deploy Oracle Cloud VMware Solution resources within your designated OCI compartment.
-
Access to an Oracle Cloud VMware Solution console.
-
Your tenancy has been reviewed for relevant quotas, limits, and usage, particularly for ESXi hosts and SDDC resources. To verify your account is eligible for deploying Oracle Cloud VMware Solution SDDCs before proceeding, see OCI Service Limits, Quotas, and Usage.
-
You have allocated enough resources to deploy a minimum three-node cluster to support vSAN-based storage.
Task 1: Deploy and Access the Oracle Cloud VMware Solution SDDC Cluster
To deploy and configure a three-node Oracle Cloud VMware Solution cluster, ensure that your OCI tenancy has sufficient credits and quotas available.
-
Log in to the OCI Console.
-
Select the appropriate Region where you want to deploy the SDDC.
Note:
- See Deploy the SDDC to the Cloud and Create and Configure an Oracle Cloud VMware Solution for a full walkthrough.
- Make sure to consistently select the same region during all deployment and access steps.
-
After deployment completes, navigate to the same region and compartment used during setup.
-
Navigate to Hybrid, VMware Solution and click Software Defined Data Center.
-
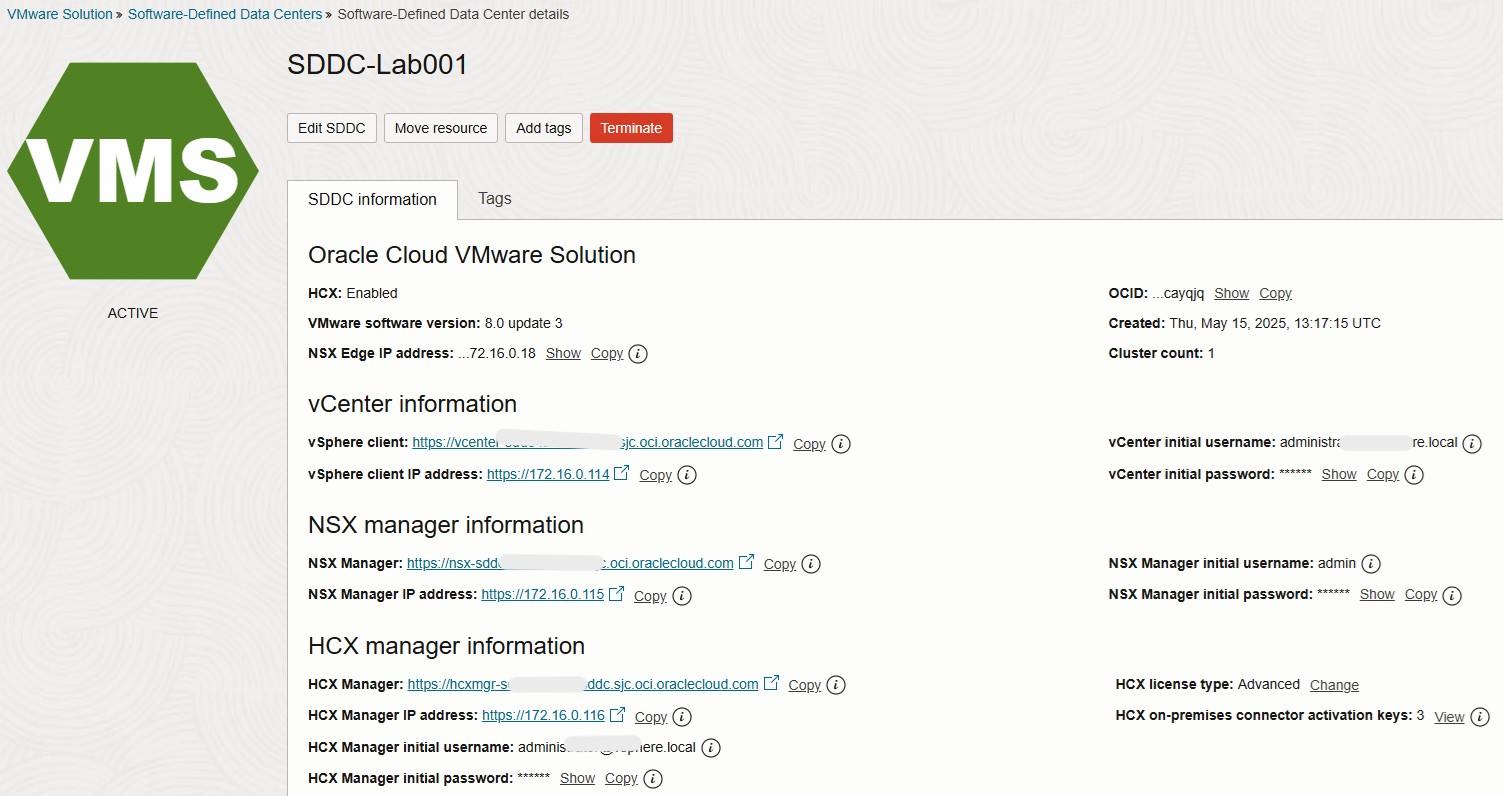
Locate and click your deployed SDDC (with Active status). For this tutorial, the SDDC is named
SDDC.Important:
- Note the IP addresses for vCenter and NSX Manager, along with the vCenter credentials.
- If access to vCenter is required from outside the private network, configure an OCI Bastion host. For more information about deploying and securing an OCI Bastion host, see OCI Bastion.
Task 2: Set up Omnissa Horizon on Oracle Cloud VMware Solution
This task outlines the prerequisites for deploying Omnissa Horizon 8.x in your Oracle Cloud VMware Solution environment.
Before beginning the installation, ensure the necessary infrastructure and network configurations are in place, including:
- DNS resolution for internal and external components.
- Proper time synchronization (NTP).
- Active Directory services.
- Functional vCenter and NSX Manager access.
- Properly configured firewall and security list rules.
For more information about network communication and port requirements for Horizon components, see Omnissa Horizon Ports and Network Connectivity Requirements.
Prerequisites:
-
Event Database Platform (select from supported Omnissa Horizon databases): This tutorial will be validated using Microsoft SQL Server but you may select any supported platform:
- Microsoft SQL Server.
- Oracle Database.
- PostgreSQL Database.
-
NSX Overlay Segments for Workloads in SDDC:
- Horizon Management Segment: Hosts Horizon management components are:
- Connection servers.
- Microsoft Active Directory Domain Controller (for local authentication and DNS).
- Microsoft SQL Server.
- Desktop Management Segment: Hosts all Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) desktops.
-
UAG Internal Segment: Hosts the second interface of UAG appliances.
Note: UAG appliances are deployed with two interfaces, one from a VLAN for external access, and one from the NSX-T overlay network for internal communication and performance scaling.
- Horizon Management Segment: Hosts Horizon management components are:
-
Active Directory Domain Controller:
- Setup details for Active Directory are not covered in this tutorial.
- Install and configure a Microsoft Certificate Authority (CA) role to handle connection server certificate renewal. CA setup details are outside the scope of this tutorial.
-
VLAN for UAG Appliances: A dedicated VLAN is required for hosting UAG appliances to enable external public access.
-
VDI-Ready Windows 10 Template for Desktop Pools (Optional):
- Optimize desktop images to avoid performance issues (for example, clean Metro Apps, run Sysprep).
- Configure guest customization to auto-join desktops to the domain post-provisioning.
- Use VMware OS Optimization Tool for guest OS tuning.
-
OCI Networking:
- VCN public subnet for the public OCI Load Balancer hosting UAG appliances.
- VCN private subnet for the private OCI Load Balancer hosting connection servers.
- VCN public subnet for the OCI Bastion host (public access point to OCI environment).
- VCN private subnet for Oracle Database (optional, if Oracle Database is used for the event database).
- Internet gateway to allow public access to UAG appliances.
-
OCI Load Balancer:
- Public OCI Flexible Network Load Balancer (LBaaS) for UAG appliances.
- Private OCI Flexible Network Load Balancer (LBaaS) for connection servers.
-
Bastion Host Requirements: Use a
VM.Standard.X.Xshape for the bastion host.
Version Details:
| Component Name | Validated Against |
|---|---|
| Omnissa Horizon | 8.1.0 build - 17351278 |
| Unified Access Gateway | V20.12 (Non-FIPS) |
| VMware vSphere | 8.x |
| VMware NSX-T | 4.x |
| Database | Microsoft SQL Server 2019 |
| Windows VDI Template | Windows 10 |
| Bastion Host | Windows Server 2016 Standard |
Task 2.1: Prepare NSX for Horizon
The steps in this task are applicable to NSX-T 4.x.
-
Access the Horizon SDDC (as listed earlier in this tutorial) to obtain the log in information for NSX-T and vCenter.
- Go to the OCI Console, select Hybrid and click VMware Solution – Software-Defined-Data Centers (SDDC).
- Select the SDDC and view the SDDC Information section for the vCenter and NSX Manager login credentials.
- Note the IP addresses and credentials for vCenter and NSX Manager. Use these credentials to log in through a web browser that has access to the SDDC.
-
Log in to the NSX-T Manager dashboard.
-
Navigate to Networking, Segments and click ADD SEGMENT.
-
Create three segments; one for Horizon management, one for hosting desktops, and one for UAG appliance internal traffic.
- Ensure these segments are connected to the Tier-1 gateway.
- Assign non-overlapping
RFC1918subnets to avoid conflicts and ensure VM connectivity.
Note:
- Fields marked with
*are required. - Select the overlay as the transport zone and ensure the segment status shows Success.
- If the segment creation fails, verify overlay connectivity and transport zone configurations based on your NSX-T environment.
Task 2.2: Create a Network Segment in NSX-T 4.x
-
Click ADD SEGMENT and enter the segment information as shown in the following image.

-
Click Set DHCP Config and define the DHCP settings as shown in the following image.

-
Repeat step 1 and 2 for all three segments:
- Horizon Management.
- UAG Internal.
- Desktop Management.
Note: For Deployment Model 1 (internal-only access), skip creating the UAG Internal segment.
-
Verify all segments are created with Success status and Admin State is Up.

Note:
- These segments should now be available for use.
- Corresponding networks should appear in the SDDC vCenter.
-
Navigate to the NSX-T Manager dashboard, select Networking Services and click NAT to add necessary NAT rules.
-
Create Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) and NO_SNAT rules for the new segments to enable communication between VCN CIDR blocks and provide internet access to overlay segments.
Task 2.3: Add SNAT and NO_SNAT rules in NSX-T 4.x
-
Log in to the NSX Manager, navigate to Networking, select NAT under Network Services and click the T0 logical router.
-
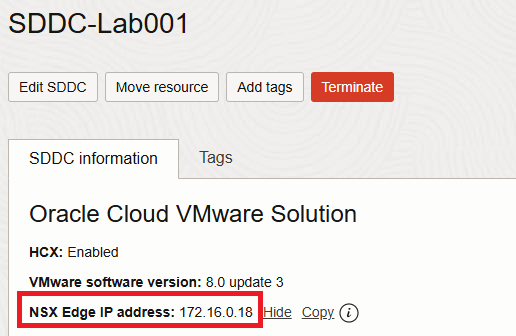
Select T0 as the logical router and click ADD to add the rule. Make sure to select the appropriate priority. The translated IP from the following image is an IP address of NSX Edge Uplink 1 VIP. To find the IP address, log in to OCI Console and navigate to the SDDC console summary page.
Note: It is advisable to add one time entry for the entire
/16subnet to avoid a single entry for all the individual segments. However, it is not mandatory and based on the design you can always add required Network Address Translation (NAT) and SNAT rules. The example in the following image shows the entry for the entire/16subnet, which covers all three overlay segments.
-
Add the NO_SNAT rule now. On the same screen, click ADD. The following image shows the sample rule.
Note: The source IP is an overlay segment CIDR and the destination IP is OCI VCN CIDR. In this example,
10.50.0.0/16is a VCN CIDR. Make sure to select the appropriate priority for proper execution.
You have to repeat the SNAT and NO_SNAT rules for all three overlay segments if /16 is not your desired design approach.
Task 2.4: Add a New VLAN for UAG Appliances (vSphere 8.x)
First, we will create a network security group and route table for the new UAG VLAN.
Note: The steps in this task are applicable to vSphere 8.x environments.
-
Go to the OCI Console, navigate to Networking, Virtual Cloud Networks, Network Security Groups and click Create Network Security Group.
Ensure you are in the correct compartment and region where the VCN for the SDDC is deployed.
-
Enter a Name for the network security group and click Next. Add security rules as shown in the following information.

-
Navigate to Networking, Virtual Cloud Networks, Internet Gateways, click Create Internet Gateway and follow the wizard to create an internet gateway.
-
Create a route table for the new UAG VLAN.
Navigate to Networking, Virtual Cloud Networks, Route Tables and click Create Route Table.
-
Under Route Rules, click Add Route Rules and enter the following information to configure.
- Target Type: Select Internet Gateway.
- Destination CIDR Block: Enter
0.0.0.0/0.

-
Update the route table created in step 4 to add a route to the overlay segments destination.
- Target Type: Private IP to NSX Edge VIP.
- Use the NSX Edge IP address (for example,
10.50.0.131) as the target IP.

-
To create the VLAN for UAG, navigate to Networking, Virtual Cloud Networks, select your SDDC VCN and click VLAN. Ensure you are in the correct region and compartment.
-
Click Create VLAN.
-
Specify the CIDR block within the VCN range and select the Availability Domain where the SDDC is deployed.

-
Select the network security group created in step 2 and the route table created in step 4.
Now, add this newly created VLAN to all ESXi hosts that are part of the SDDC cluster.
Task 2.5: Attach the VLAN to the SDDC Cluster in vSphere 8.x
-
Go to the OCI Console, navigate to Compute Instances and select ESXi Node.
Repeat this step for all ESXi bare metal nodes in the Oracle Cloud VMware Solution cluster.
-
In the Compute section, click one ESXi host (for example,
Eval-1).
-
Under Resources, select Attached VNICs and click Create VNIC. You need to create two vNICs per ESXi Node.

-
Create two VNICs.
- Enter a Name in the VNIC information page.
- Under Network, select Advanced Setup: VLAN and click the
VLAN-SDDC-UAGcreated in Task 2.4 for the UAG. - Select the physical network adapter card (NIC 0 for the first, NIC 1 for the second).
Review the NIC 0 example:

Review the NIC 1 example:

Summary of VNIC attachments:

-
-
Repeat step 1 for all other bare metal ESXi nodes (for example,
Eval-2andEval-3). -
Collect the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tag information.
- Go to the OCI Console, navigate to Networking and click Virtual Cloud Networks (VCN).
- Highlight the newly created VLAN and note the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tag (for example, VLAN tag
1052). Your VLAN ID will be shown here.
-
Log in to the vSphere 8.x SDDC environment through vCenter using
administrator@vsphere.local.-
Create a new distributed port group in vCenter referencing the VLAN details.
-
Navigate to Networking, DSwitch, Distributed Port Group and click New Distributed Port Group.
-
In the Name and Location section, enter a Name for the distributed port group.

-
In the Configure Settings section, enter the following information.
- Port Binding: Select Static binding.
- Number of ports: Enter 64.
- Add the VLAN ID you collected from OCI (for example,
1052).

-
Edit the newly created distributed port group and update the Teaming and Failover policy. Change Load Balancing Policy to Route based on physical NIC load.

-
Task 3: Deploy and Configure Horizon Components
This task provides high-level guidance on deploying and configuring key Horizon components such as Connection Servers, Unified Access Gateways (UAGs), and Desktops.
Since many configuration details depend on your specific environment and preferences, we highly recommend consulting VMware’s official best practices for Horizon deployments. The Omnissa Horizon View Best Practices knowledge base article is an excellent resource for comprehensive guidance.
Prerequisites:
Before proceeding with Horizon component deployment, ensure the following prerequisites are in place.
-
Active Directory Domain Controller: A functioning Active Directory (AD) domain controller with DNS services configured and a Certificate Authority (CA) server available for certificate issuance.
-
Microsoft SQL Server: Microsoft SQL Server installed with an event database created for Horizon’s event logging and monitoring.
Note: This tutorial does not cover Microsoft SQL Server installation or database creation steps.
Task 3.1: Deploy and Configure Connection Servers
-
Create two Windows server VMs in the SDDC for connection servers.
-
Join these two connection server VMs to the Windows Active Directory domain controller and create the necessary domain name system (DNS) records in the internal DNS server created as a prerequisite.
-
In the first connection server, click Next and select Horizon Standard Server.


-
Select Oracle Cloud as the deployment location and finish the installation of the first connection server.

-
In the second connection server, select the deployment type as Horizon Replica Server and point to the primary connection server from step 4. Follow the installation wizard and complete the installation of the second connection server.

-
Deploy the open virtual appliance (OVA) for Horizon Cloud Connector required for licensing. For more information, see Connect Horizon Cloud Service with an Existing Horizon Pod to Use Horizon Subscription Licenses or Cloud-Hosted Services or Both.
-
After successfully deploying both connection servers, launch the administration page by navigating to
https://your-primary-connection-server-IP/admin.-
Enter your Horizon serial number as required.
-
Under Servers, click vCenter Servers, Add and enter the vCenter information.

-
Leave the default Storage page and finish the wizard.
-
Under Servers, click Connection Servers and verify that both primary and replica connection servers are listed. Select the primary connection server and click Edit.
-
In the Edit Connection Server Settings page, enter the following information.
- Deselect Enable Host Redirection.
- Deselect PCoIP Secure Gateway.
- Select Do not use Blast Secure Gateway under Blast Secure Gateway.
Repeat these settings for the replica connection server as well.

-
Log in to the connection server, navigate to Event Configuration under Settings, and configure the event database to point to the Microsoft SQL Server database. Use
saas the username.
-
Note: Steps for configuring global settings, desktop pools, and farms are outside the scope of this tutorial as they vary based on requirements and follow standard VMware implementations.
Task 3.2: Deploy and Configure a UAG
We need to deploy two UAG appliances for high availability and scaling.
-
Run the Deploy OVF Template wizard and select the UAG Non-Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) UAG OVA bundle. Select the compute resources as desired.
-
In the Configuration page, select Two NIC and click Next.

-
In the Select networks page, select ManagementNetwork as the UAG distributed port group and select BackendNetwork as the UAG internal overlay segment created in an NSX environment. Leave the default for Internet and click Next.

-
Under Customize template, select Networking Properties, STATICV4 and configure the IPv4 address from the UAG VLAN network. Specify the unique identifier name for the Unified Gateway Appliance Name.
-
Under Password Options, set the root and admin password.
-
Under System Properties, enable SSH and finish the wizard.
-
Power on the UAG appliance. You should see two IP addresses, one from UAG VLAN and the other from the NSX overlay UAG internal segment.

-
Log in to the OCI Console, navigate to Networking, Virtual Cloud Networking, SDDC VCN, VLAN, select VLAN-SDDC-UAG VLAN and create external access to get the public IP addresses for your UAGs.
-
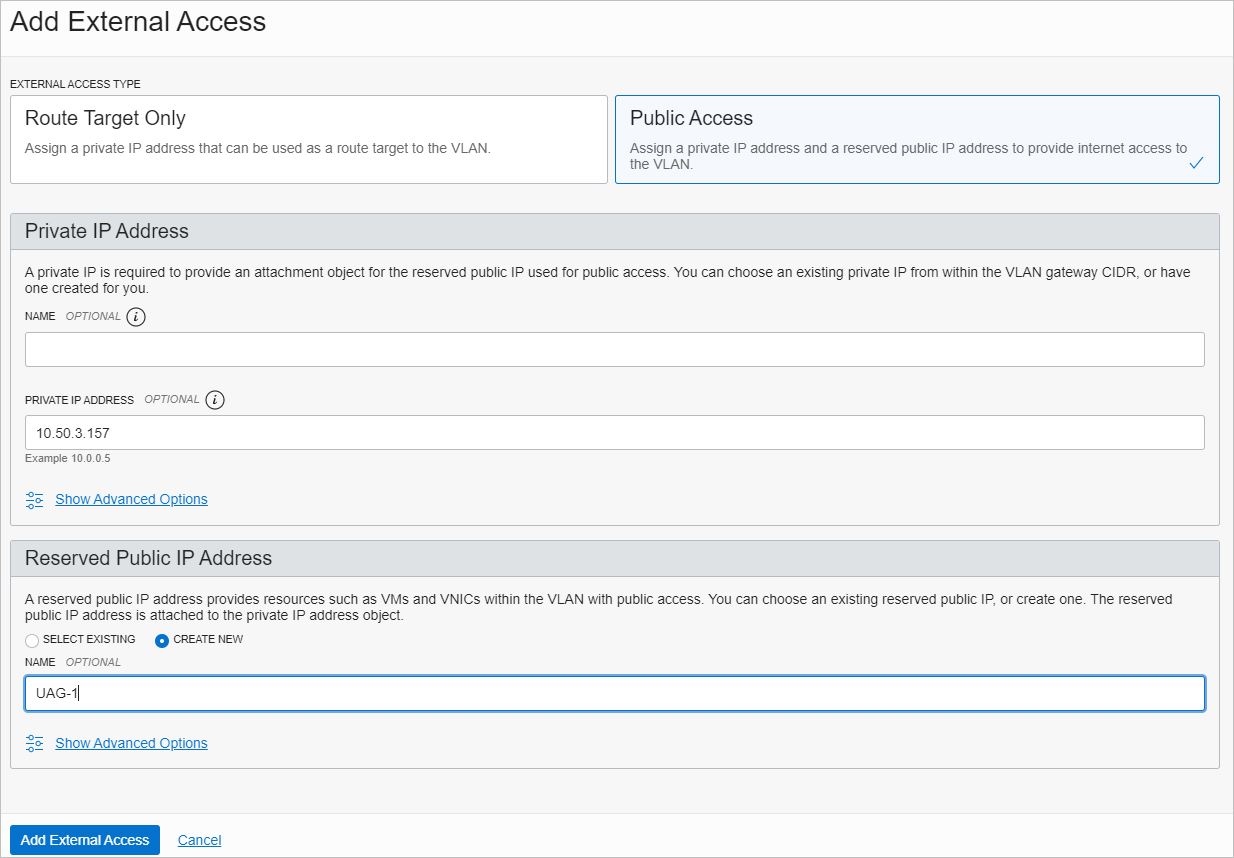
Click Add External Access and select Public Access as the External Access Type.
-
Enter the private IP address from the UAG VLAN of the first UAG appliance (for example,
10.50.3.157). -
In the Reserved Public IP Address section, select CREATE NEW, specify a unique name, and click Add External Access.
Note: You will see private to public IP address mapping for your UAG appliance after completing steps 8 to 10.
-
Repeat steps 1 to 11 for the second UAG appliance.
Note: At this stage, you have one public IP address for each UAG appliance.

-
Create a public DNS record using the public IP address received in step 8 for each UAG appliance. Next, create routes from the UAG appliance for communication to the load balancer segment and connection servers.
Note: Communication occurs between the bastion host and the NSX overlay segment for management purposes, which is required for UAG appliance management through the web Graphic User Interface (GUI).
-
Create an entry in the bastion host public subnet with the private IP as a target type to NSX Edge VIP IP address for destination
192.168.0.0/16(applicable if you want to access the UAG appliance web GUI from the bastion host). -
Log in to the UAG console from vSphere using the root user and add route entries.
-
Add these routes after the OCI Load Balancer is deployed and configured. These two IP addresses belong to the UAG load balancer health check instances.
The following image shows the route entry for the entire range for the explicit route from the overlay gateway.

The following image shows the overlay network to cover all segments part of this deployment.

The following image shows the summary of the routes from the UAG appliance.

Note:
eth0is from the VLAN backed network andeth1is from the Overlay segment. Refer to the yellow-marked route rules.- Before you proceed, make sure to complete the private OCI Load Balancer configuration for the connection server to obtain LBaaS virtual IP (VIP). Refer to the Deploy and Configure Private Load Balancer section in Task 4. Come back to this task after completing the OCI Load Balancer configuration.
-
Create a DNS record for the connection server load balancer VIP that you obtained.
-
Add entry in
/etc/resolv.confto point to the internal DNS server where all the DNS records are created. The UAG should communicate over the hostname of the connection server’s load balancer VIP. -
Configure UAG appliances by accessing the appliance web page using
https://<private-hostname-ip>:9443/admin. -
Log in with administration credentials and enable Edge Service Settings under General Settings.
-
Provide the connection server URL.
Note: This URL should be the internal DNS entry of the private OCI Load Balancer VIP, which load balances both standard and replica connection servers. For private OCI Load Balancer configuration, refer to the note on private LBaaS configuration after step 15.
-
Paste the connection server URL thumbprint and make sure to include both connection servers’ SHA1 thumbprints.
-
To get the thumbprint, access the connection server URL using
https://primary-connection-server/admin, click padlock, Certificate, Details, and then click Thumbprint. -
Repeat for the replication server.
-
Combine both thumbprints in one line.
sha1=6b 8f 21 f5 e3 7d ce 7f b0 8d 33 88 92 96 2b e9 86 3a 24 b3,sha1=6f 5d xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx b4 82 7e ae 11 b3 65 4f
-
-
Enable PC over IP (PCoIP) and enable Disable PCOIP Legacy Certificate.
-
In the PCoIP External URL field, enter the public IP address for the UAG appliance with port
4172. For example,150.100.222.23:4172. -
In the Horizon Settings page, select Enable Blast and enter the Blast External URL as the public DNS record associated with the UAG appliance with port
8443. For example,https://xyz.company.com:8443wherexyz.company.comis the public DNS host record for IP150.100.222.23.
-
Repeat steps 1 to 25 for the second UAG appliance.
-
You should see the status as green in the UAG appliance web GUI after successful configuration.

-
Log in to the connection servers web GUI and check if the UAGs are registered. Navigate to Settings, Servers and click Gateways.
Task 4: Select an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancer (LBaaS) Option For Horizon
To select the appropriate Horizon load balancing methodology, you must decide on the ingress and egress traffic patterns for the desktop userbase. The following are commonly used methods:
-
Method 1: Perform for internal-facing clients only (users connect to connection servers).
In this method, connections are generated only within the internal networks and clients may connect directly to the connection servers located on the SDDC network. In this case, the UAG/gateways may need to be bypassed so the clients can access the desktops.
- Perform only a private OCI Load Balancer configuration.
- Refer to the Deploy and Configure Private OCI Load Balancer section.
-
Method 2: Perform for internal and external user access.
In this method, both the public and private OCI Load Balancer are deployed.
- Refer to the Deploy and Configure a Public OCI Load Balancer section.
- Refer to the Deploy and Configure a Private OCI Load Balancer section.
Deploy and Configure a Private OCI Load Balancer
This section describes steps to configure OCI native LBaaS for connection servers. Refer to the following architecture for more details.

Note: The following table lists the backend, listener, and port and protocol configuration for the LBaaS.
| Backend Sets | Backends | Listener | Port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BS_443 (HTTPS) | Connection Server 1 & Connection Server 2 | Listener_443 | 443 | TCP |
| BS_4172 (PCOIP) | Connection Server 1 & Connection Server 2 | Listener_4172 | 4172 | TCP |
| BS_8443 (Blast) | Connection Server 1 & Connection Server 2 | Listener_8443 | 8443 | TCP |
-
Log in to the OCI Console and navigate to Networking and select Load Balancers. Change the Region and Compartment to your desired compartment and region.
-
Click Create Load Balancer and select Load Balancer for Type. Do not select Network Load Balancer.
-
Enter the Name of the load balancer and select Private for visibility type. In the bandwidth section, select Flexible Shapes and choose the required minimum and maximum bandwidth.
-
Select the VCN and private subnet created in the previous tasks to host the private LBaaS and click Next.
-
Select IP Hash as Load balancing policy.
Note: Do not add backends at this stage (we will do that later).
-
Select Health check policy protocol as TCP and change Port to
443. Leave the default settings for Intervals and Timeouts. Click Next to add a listener. -
Enter the Name of the listener and select TCP as your Listener traffic type. Specify
443as Port and leave the default settings.Note: If you are planning to use CA signed certificates, select HTTPS as the listener traffic type and upload the valid SSL certificates. For more information, see OCI LBaaS documentation.
-
Click Submit and wait for the load balancer status to turn green.
-
Add the backends and listeners according to the table shown earlier in this section.
-
Make a note of the LBaaS private IP and create an internal DNS record that will be referred to as Horizon connection server’s VIP URL.
-
Add the route rule for the private LBaaS subnet with the Target type as NSX overlay VIP. The following image shows the route table for private LBaas. The example shows
192.168.0.0/16is the NSX overlay subnet for management and10.50.0.131is the uplink interface for NSX Edge Uplink VLAN. This will cover all three overlay segments.
-
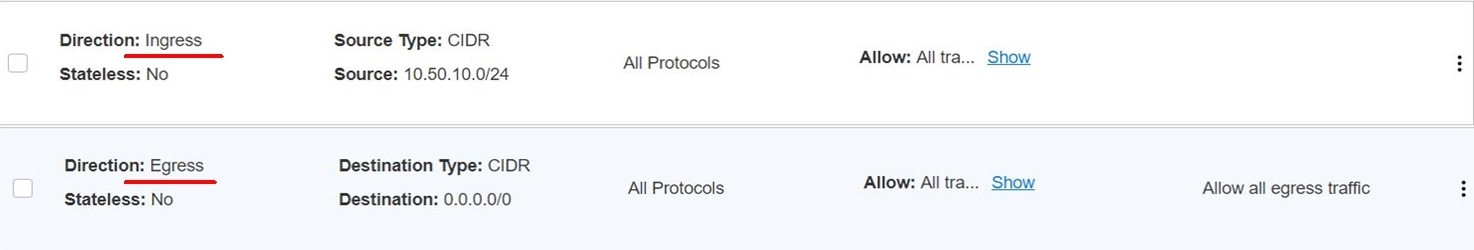
Update the private LBaaS subnet security rule to accept the communication from the NSX overlay segment. The following images shows the security list for the private OCI Load Balancer. The security rule accepts the communication from the NSX overlay subnet to LBaaS.
Ingress:

Egress:

-
Update the network security group for NSX-Edge-Uplink1 to accept the communication from the LBaaS private subnet. The following image shows the NSX-Edge-Uplink1 network security group where
10.50.10.0/24is the LBaaS private subnet CIDR.
-
Deploy and Configure a Public OCI Load Balancer
This section describes steps to configure OCI native LBaaS for UAG external access. Refer to the following architecture for more details.

Note: The following table lists the backend, listener, and port and protocol configuration for the LBaaS.
| Backend Sets | Backends | Listener | Protocol | Port |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BS_443 (HTTPS) | Unified Access Gateway 1 & Unified Access Gateway 2 | Listener_443 | TCP | 443 |
-
Log in to the OCI Console and navigate to Networking and select Load Balancers. Change the Region and Compartment to your desired compartment and region.
-
Click Create Load Balancer and select Load Balancer as Type. Do not select Network Load Balancer.
-
Enter the Name of the load balancer and select Public as Visibility type. Click Reserved IP Address and select Create new reserved IP address. Enter the name of the IP and select the compartment.
-
In the Bandwidth section, select Flexible Shapes and choose the required minimum and maximum bandwidth.
-
Select the VCN and public subnet created in the previous tasks to host the public LBaaS and click Next.
-
Select IP Hash as Load balancing policy.
Note: Do not add backends at this stage, we will do that later.
-
In the Specify Health Check Policy section, select TCP and change Port to
443. Leave the default settings for Intervals and Timeouts. Click Next to add a listener. -
Enter the Name of the listener and select TCP as your Listener traffic type. Specify port
443and leave default settings.Note: If you are planning to use CA signed certificates, select HTTPS as Listener traffic type and upload the valid SSL certificates. For more information, see OCI LBaaS documentation.
-
Click Submit and wait for the load balancer status to turn green.
-
Add the backends and listeners according to the table shown earlier in this section.
-
Make a note of the LBaaS public IP and create an external DNS record for public access to the VDI infrastructure.
-
Add the route table entry for the public OCI Load Balancer subnet.
The following image shows the route table entry for the public LBaaS subnet.

The following image shows the route table entry for
VLAN-SDDC-UAG. We covered this step while creating the UAG VLAN. If you followed the UAG VLAN creation steps, you should see a similar route entry in the route table for the UAG VLAN.
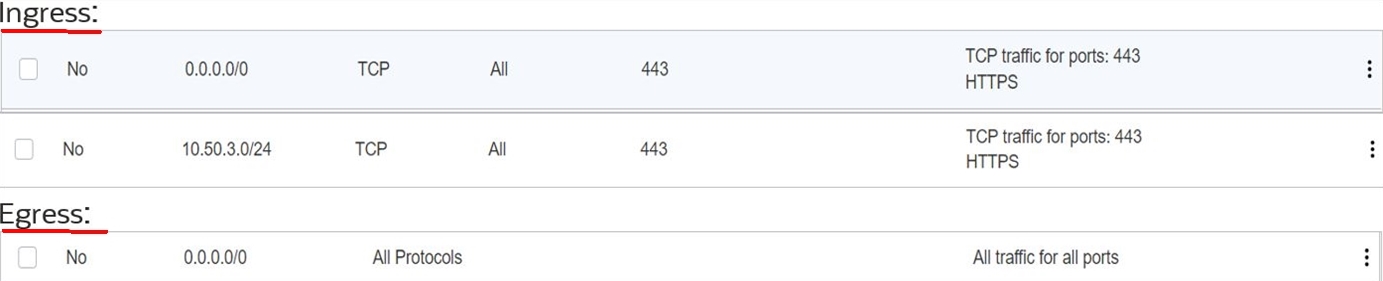
The following image shows the network communication security list and network security group rules for public LBaaS. In this example,
10.50.3.0/24is a VLAN subnet for Horizon UAG appliance.The following image shows the network security group for SDDC UAG VLAN. This step is already covered during the UAG VLAN creation process in the initial steps. If you followed the UAG VLAN creation steps, you should see a network security group similar to the following image.

After you finish the public and private OCI Load Balancer configuration, the Horizon setup can be tested using Horizon Client.
Related Links
Acknowledgments
-
Authors - Ryan Patel (Master Principal Cloud Architect), Devendra Gawale (Cloud Solution Architect)
-
Contributor - Adeel Amin (Cloud Solution Architect)
More Learning Resources
Explore other labs on docs.oracle.com/learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. Additionally, visit education.oracle.com/learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.
For product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.
Deploy Omnissa Horizon 8 on Oracle Cloud VMware Solution
G35584-01
Copyright ©2025, Oracle and/or its affiliates.