C Automating the Identity and Access Management Enterprise Deployment
A number of sample scripts have been developed which enable you to deploy Oracle Identity and Access Management on Kubernetes. These scripts are provided as samples for you to use to develop your own applications.
You must ensure that you are using the July 2022 or a later release of Identity and Access Management for this utility to work.
You can run the scripts from any host that has access to your Kubernetes cluster. If you want the scripts to automatically copy files to your Oracle HTTP Servers, you must have passwordless SSH set up from the deployment host to each of your web hosts.
If you are deploying Oracle Advanced Authentication, you must have passwordless SSH set up from the deployment host to one of your database nodes. In addition, for the duration of the deployment, your OAA database service must only be running on this database host.
This appendix includes the following topics:
- Obtaining the Scripts
The automation scripts are available for download from GitHub. - Scope of Scripts
Learn about the actions that the scripts perform as part of the deployment process. There are also tasks that the scripts do not perform. - Key Concepts of the Scripts
To make things simple and easy to manage, the scripts include these files: a response file with details of the environment and template files you can easily modify or add as required. - Directory Structure
After you deploy the scripts, they will have a directory structure. In addition, while the scripts are working, they create a working directory. - Getting Started
- Creating a Response File
A sample response and password file is created for you in theresponsefiledirectory. You can edit these files either directly or by running thestart_here.shshell script in the script's home directory. - Validating Your Environment
You can run theprereqchecks.shscript, which exists in the script's home directory, to check your environment. This script is based on the response file you created earlier. - Provisioning the Environment
There are a number of provisioning scripts located in the script directory. These scripts use a working directory defined in the response file for temporary files. - Log Files
The provisioning scripts create log files for each product inside the working directory in alogssub-directory. - Files You Need to Keep
After a provisioning run that creates a domain is complete, there are files that you need to keep safely. These files are used to start and stop the domain as well as contain instructions to start the domain. - Archiving Files After Installation/Configuration
As part of running the scripts, a number of working files are created in theWORKDIRdirectory prior to copying to the persistent volume in/u01/user_projects/workdir. - Oracle HTTP Server Configuration Files
Each provisioning script creates sample files for configuring your Oracle HTTP Server. These files are generated and stored in the working directory under theOHSsubdirectory. - Utilities
In thescriptsdirectory, there is a subdirectory calledutils. This directory contains sample utilities you may find useful. - Reference - Response File
The parameters in the response file are used to control the provisioning of the various products in the Kubernetes cluster. These parameters are divided into generic and product-specific parameters. - Components of the Deployment Scripts
For reference purposes, this section includes the name and function of all the objects that make up the deployment scripts.
Obtaining the Scripts
The automation scripts are available for download from GitHub.
git clone https://github.com/oracle/fmw-kubernetes.gitfmw-kubernetes/FMWKubernetesMAA/OracleEnterpriseDeploymentAutomation/OracleIdentityManagementcp -R kubernetes/FMWKubernetesMAA/OracleEnterpriseDeploymentAutomation/OracleIdentityManagement/* /workdir/scriptsIf you are provisioning Oracle Identity Governance, you must also download the Oracle
Connector Bundle for OUD and extract it to a location which is accessible by the
provisioning scripts. For example,
/workdir/connectors/OID-12.2.1.3.0. The connector directory
name must start with OID-12.2.1.
If you are provisioning Oracle HTTP Server, you must download the Oracle HTTP
installer and place it in the $SCRIPTDIR/templates/ohs/installer
location. The installer must be the ZIP file. For example,
fmw_12.2.1.4.0_ohs_linux64_Disk1_1of1.zip.
Scope of Scripts
Learn about the actions that the scripts perform as part of the deployment process. There are also tasks that the scripts do not perform.
What the Scripts Will do
The scripts will deploy Oracle Unified Directory (OUD), Oracle Access Manager (OAM), and Oracle Identity Governance (OIG). They will integrate each of the products. You can choose to integrate one or more products.
The scripts perform the following actions:
- Create an Ingress controller as described in Creating the Ingress Controller.
- Create an Elasticsearch deployment as described in Installing Elasticsearch (ELK) Stack and Kibana.
- Create a Prometheus and Grafana deployment as described in Installing the Monitoring Software.
- Install and configure the Oracle HTTP Server. See Installing and Configuring Oracle HTTP Server.
- Deploy and configure Oracle WebGate.
- Create any number of OUD instances as described in Configuring Oracle Unified Directory.
- Extend OUD with OAM object classes as described in Creating the Schema Extensions File.
- Seed the directory with users and groups required by Oracle Identity and Access Management as described in Creating the Seeding File.
- Create indexes and ACI’s in OUD as described in Creating OUD Containers.
- Set up replication agreements between different OUD instances.
- Create OUDSM.
- Setup Kubernetes Namespaces, Secrets, and Persistent Volumes.
- Create Kubernetes NodePort Services as required.
- Create the RCU schema objects for the product being installed.
- Deploy the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator as described in Installing the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator.
- Create an Oracle Access Manager Domain with user defined Managed Servers as described in Creating the Access Domain.
- Perform an initial configuration of the OAM domain as described in Updating the Domain.
- Perform post configuration tasks as described in Performing the Post-Configuration Tasks for Oracle Access Management Domain.
- Removing the OAM server from the default Coherence cluster.
- Tune the
oamDSdata source as described in unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-E8DE356A-2075-4DE7-AB23-B77BE76DBD1D. - Configure the WebLogic Proxy Plug-in as described in unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-248D5494-A25B-483F-92A7-E40E44E93BF9.
- Configure and Integrate OAM with LDAP as described in Configuring and Integrating with LDAP.
- Add OAM Host Identifiers as described in Updating Host Identifiers.
- Add OAM policies as described in Adding the Missing Policies to OAM.
- Configure ADF and OPSS as described in Configuring Oracle ADF and OPSS Security with Oracle Access Manager.
- Set the initial server count as described in Setting the Initial Server Count.
- Create an Oracle Identity Governance Domain.
- Integrate OIG and SOA as described in Integrating Oracle Identity Governance with Oracle SOA Suite.
- Integrate OIG with LDAP as described in Integrating Oracle Identity Governance with LDAP.
- Add missing object classes as described in Adding Missing Object Classes.
- Integrate OIG and OAM as described in Integrating Oracle Identity Governance and Oracle Access Manager.
- Configure SSO integration in the Governance domain Configuring SSO Integration in the Governance Domain.
- Enable OAM Notifications as described in Enabling OAM Notifications.
- Update the Match Attribute as described in Updating the Value of MatchLDAPAttribute in oam-config.xml.
- Update the TAP Endpoint as described in Updating the TapEndpoint URL.
- Run Reconciliation Jobs as described in Running the Reconciliation Jobs.
- Configure Oracle Unified Messaging with Email/SMS server details as described in Managing the Notification Service.
- Enable Design Console access as described in Enabling Design Console Access.
- Add load balancer certificates to Oracle Key Store Service as described in Adding the Oracle Access Manager Load Balancer Certificate to the Oracle Keystore Service and Adding the Business Intelligence Load Balancer Certificate to Oracle Keystore Trust Service.
- Update the OIG initial server count as described in Setting the Initial Server Count.
- Set up the Business Intelligence Reporting links.
- Configure OIM to use BIP as described in Configuring Oracle Identity Manager to Use BI Publisher.
- Store the BI credentials in OIG as described in Storing the BI Credentials in Oracle Identity Governance.
- Deploy Oracle Identity Role Intelligence as described in Deploying OIRI Using Helm.
- Create OIRI users in Oracle Identity Governance as described in Creating User Names and Groups in Oracle Identity Governance.
- Perform an initial OIG data load into OIRI as described in Performing an Initial Data Load Using the Data Ingester.
- Create OIRI Kubernetes services either NodePort or Ingress as described in Creating the Kubernetes NodePort Services.
- Deploy Oracle Advanced Authentication and Risk Management as described in Deploying Oracle Advanced Authentication.
- Create OAA users as described in unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-278C0CB3-9CC1-400C-B06B-B5DF8603B2EC.
- Create OAA test user as described in Creating a Test User.
- Integrate OAA with Unified Messaging Service as described in Configuring Email/SMS Servers and Automatic User Creation.
- Integrate OAA with OAM as described in unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-D4FE27D2-6441-4C27-B720-79396A898C8F.
- Copy the WebGate artifacts to Oracle HTTP Server as described in Copying WebGates Artifacts to Web Tier.
- Optionally send OUD, OUDSM, OAM, and OIG log files to Elasticsearch.
Parent topic: Scope of Scripts
What the Scripts Will Not Do
While the scripts perform the majority of the deployment, they do not perform the following tasks:
- Deploy the Container Runtime Environment, Kubernetes, or Helm.
- Configure the load balancer.
- Download the container images for these products.
- Tune the WebLogic Server.
- Configure the One Time Pin (OTP) forgotten password functionality for OAM.
- Configure the OIM workflow notifications to be sent by email.
- Set up the OIM challenge questions.
- Provision Business Intelligence Publisher (BIP).
- Set up the links to the Oracle BI Publisher environment. However, the scripts will deploy reports into the environment.
- Enable the BI certification reports in OIG as described in Enable Certification Reports.
- Configure Oracle HTTP Server to send log files and monitoring data to Elasticsearch and Prometheus.
- Configure Oracle Database Server to send log files and monitoring data to Elasticsearch and Prometheus.
Parent topic: Scope of Scripts
Key Concepts of the Scripts
To make things simple and easy to manage, the scripts include these files: a response file with details of the environment and template files you can easily modify or add as required.
Note:
Provisioning scripts are re-enterant. If something fails, you can restart the script from the point at which it failed.Directory Structure
After you deploy the scripts, they will have a directory structure. In addition, while the scripts are working, they create a working directory.
Figure C-1 Directory Structure of the Scripts
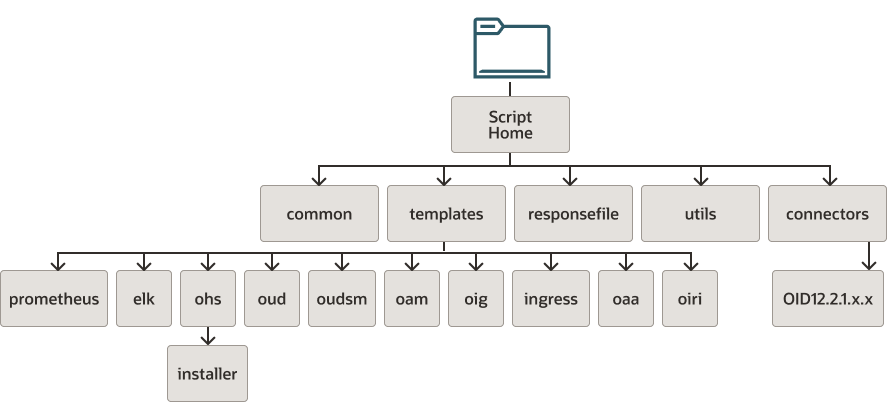
Figure C-2 Working Directory of the Scripts

Getting Started
If you are provisioning Oracle Identity Governance, you must also download the Oracle Connector Bundle for OUD and extract it to a location which is accessible by the provisioning scripts. For example, /workdir/connectors/OID-12.2.1.3.0. The connector directory name must start with OID-12.2.1.
If you are provisioning the Oracle HTTP Server, you must download the Oracle HTTP installer and place it in the location $SCRIPTDIR/templates/ohs/installer. The installer must be the ZIP file. For example: fmw_12.2.1.4.0_ohs_linux64_Disk1_1of1.zip.
If you want to install the Oracle HTTP Server or copy files to it, you must set up passwordless SSH from the deployment host, during provisioning.
Creating a Response File
responsefile directory. You can edit these files either directly or by running the start_here.sh shell script in the script's home directory.
./start_here.sh [ -r responsefile -p passwordfile ]You can run the above script as many times as you want on the same file. Pressing the Enter key on any response retains the existing value.
Values are stored in the idm.rsp and .idmpwds files
unless the command is started with the -r and -p
options, in which case the files updated will be that specified.
Note:
- The file consists of key/value pairs. There should be no spaces between the name
of the key and its value. For example:
Key=value - If you are using complex passwords, that is, passwords which contain characters such as !, *, and $, then you should separate these characters by a \. For example: hello!$ should be entered as hello\!\$. Complex passwords used for databases should be enclosed in quotes (""). For example: "hello!$"
Validating Your Environment
prereqchecks.sh script, which exists
in the script's home directory, to check your environment. This script is based on the
response file you created earlier. See Creating a Response File.
The script performs several checks such as (but not limited to) the following:
- Ensures that the container images are available on each node.
- Checks that the NFS file shares have been created.
- Ensures that the load balancers are reachable.
cd <SCRIPTDIR>
./prereqchecks.sh [-r responsefile -p passwordfile]Where, -r and -p are optional.
Provisioning the Environment
There are a number of provisioning scripts located in the script directory. These scripts use a working directory defined in the response file for temporary files.
Table C-1 Provisioning Scripts Located in the Script Directory
| File | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
|
Umbrella script that invokes each of the scripts (which can be invoked manually) mentioned in the following rows. |
|
|
Deploys an Ingress controller. |
|
|
Deploys Elasticsearch and Kibana. |
|
|
Deploys Prometheus and Grafana. |
|
|
Installs Oracle HTTP Server and deploys WebGate. |
|
|
Deploys Oracle Unified Directory. |
|
|
Deploys Oracle Unified Directory Services Manager. |
|
|
Deploys WebLogic Operator. |
|
|
Deploys Oracle Access Manager. |
|
|
Deploys Oracle Identity Governance. |
|
|
Deploys Oracle Identity Role Intelligence. |
|
|
Deploys Oracle Advanced Authentication. |
idm.rsp) and password file (default is .idmpwds),
by appending:-r responsefile -p passwordfileThese files must exist in the response file directory.
Log Files
logs sub-directory.
progressfile– This file contains the last successfully executed step. If you want to restart the process at a different step, update this file.timings.log– This file is used for informational purposes to show how much time was spent on each stage of the provisioning process.
Files You Need to Keep
TO_KEEP subdirectory.
You should also keep any override files that are generated.
Archiving Files After Installation/Configuration
WORKDIR directory prior to copying to the persistent volume in
/u01/user_projects/workdir.
The response file uses a hidden file in the
responsefile directory to store passwords.
Oracle HTTP Server Configuration Files
OHS subdirectory. If required, the scripts can also
copy these configuration files to Oracle HTTP server and restart it.
Utilities
In the scripts directory, there is a subdirectory called
utils. This directory contains sample utilities you may find
useful.
These utilities are used for:
- Loading container images to each of the Kubernetes nodes.
- Deleting deployments.
Reference - Response File
The parameters in the response file are used to control the provisioning of the various products in the Kubernetes cluster. These parameters are divided into generic and product-specific parameters.
- Products to Deploy
- Control Parameters
- Registry Parameters
- Image Parameters
- Generic Parameters
- Ingress Parameters
- Elasticsearch Parameters
- Prometheus Parameters
- OHS Parameters
- OUD Parameters
- OUDSM Parameters
- LDAP Parameters
- SSL Parameters
- WebLogic Operator for Kubernetes Parameters
- OAM Parameters
- OIG Parameters
- OIRI Parameters
- OAA Parameters
- Port Mappings
Products to Deploy
These parameters determine which products the deployment scripts attempt to deploy.
Table C-2 List of Products to Deploy
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
INSTALL_INGRESS |
|
Set the value to true to configure an Ingress controller. |
|
INSTALL_ELK |
|
Set the value to true to install and configure Elasticsearch and Kibana. |
|
INSTALL_PROM |
|
Set the value to |
|
INSTALL_OHS |
|
Set the value to |
|
INSTALL_OUD |
|
Set the value to true to configure OUD. |
|
INSTALL_OUDSM |
|
Set the value to true to configure OUDSM. |
|
INSTALL_WLSOPER |
|
Set the value to true to deploy Oracle WebLogic Operator. |
|
INSTALL_OAM |
|
Set the value to true to configure OAM. |
|
INSTALL_OIG |
|
Set the value to true to configure OIG. |
|
INSTALL_OIRI |
|
Set the value to true to configure OIRI. |
|
INSTALL_OAA |
|
Set the value to true to configure OAA. |
|
INSTALL_RISK |
|
Set the value to true to configure RISK. |
|
INSTALL_OUA |
|
Set the value to true to configure OUA. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
Control Parameters
These parameters are used to specify the type of Kubernetes deployment and the names of the temporary directories you want the deployment to use, during the provisioning process.
Table C-3 List of Control Parameters in the Response File
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
USE_REGISTRY |
|
Set to true to pull images from a container registry. |
|
IMAGE_TYPE |
|
Set to crio or docker depending on your container engine. |
|
IMAGE_DIR |
|
The location where you have downloaded the container
images. Used by the |
|
LOCAL_WORKDIR |
|
The location where you want to create the working directory. |
|
K8_WORKDIR |
|
The location inside the Kubernetes containers to which working files are copied. |
|
K8_WORKER_HOST1 |
|
The name of a Kubernetes worker node used in generating the OHS sample files. |
|
K8_WORKER_HOST2 |
|
The name of a Kubernetes worker node used in generating the OHS sample files. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
Registry Parameters
These parameters are used to determine whether or not you are using a container registry. If you are, then it allows you to store the login credentials to the repository so that you are able to store the credentials as registry secrets in the individual product namespaces.
If you are pulling images from GitHub or Docker hub, then you can also specify the login parameters here so that you can create the appropriate Kubernetes secrets.
Table C-4 List of Registry Parameters in the Response File
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
REGISTRY |
|
Set to the location of your container registry. |
|
REG_USER |
|
Set to your registry user name. |
|
REG_PWD |
<password> |
Set to your registry password. |
|
CREATE_REGSECRET |
|
Set to true to create a registry secret for automatically pulling images. |
|
CREATE_GITSECRET |
|
Specify whether to create a secret for GitHub. This parameter ensures that you do not see errors relating to GitHub not allowing anonymous downloads. |
|
GIT_USER |
|
The GitHub user's name. |
|
GIT_TOKEN |
|
The GitHub token. |
|
DH_USER |
username |
The Docker user name for
|
|
DH_PWD |
mypassword |
The Docker password for
|
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
Image Parameters
These parameters are used to specify the names and versions of the container images you want to use for the deployment. These images must be available either locally or in your container registry. The names and versions must be identical to the images in the registry or the images stored locally.
These can include registry prefixes if you use a registry. Use the
local/ prefix if you use the Oracle Cloud Native
Environment.
Table C-5 List of Image Parameters in the Response File
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OPER_IMAGE |
|
The WebLogic Operator image name. |
|
OUD_IMAGE |
|
The OUD image name. |
|
OUDSM_IMAGE |
|
The OUDSM image name. |
|
OAM_IMAGE |
|
The OAM image name. |
|
OIG_IMAGE |
|
The OIG image name. |
|
OIRI_CLI_IMAGE |
|
The OIRI CLI image name. |
|
OIRI_IMAGE |
|
The OIRI image name. |
|
OIRI_UI_IMAGE |
|
The OIRI UI image name. |
|
OIRI_DING_IMAGE |
|
The OIRI DING image name. |
|
OAA_MGT_IMAGE |
|
The OAA Management container image. |
|
KUBECTL_REPO |
|
The kubectl image used by OUD. |
|
BUSYBOX_REPO |
|
The busybox image used by OUD. |
|
PROM_REPO |
- |
If you are using your own container registry and have staged the Prometheus and Grafana images in this registry, then set this variable to the location of your registry. Leave it blank if you want to obtain the images from the public repositories. |
|
ELK_REPO |
- |
If you are using your own container registry and have staged the Elastic Search and Kibana images in this registry, then set this variable to the location of your registry. Leave it blank if you want to obtain the images from the public repositories. |
|
OPER_VER |
|
The version of the WebLogic Operator. |
|
OUD_VER |
|
The OUD version. |
|
OUDSM_VER |
|
The OUDSM version. |
|
OAM_VER |
|
The OAM version. |
|
OIG_VER |
|
The OIG version. |
|
OIRICLI_VER |
|
OIRI CLI version. |
|
OIRI_VER |
|
The OIRI version. |
|
OIRIUI_VER |
|
The OIRI UI version. |
|
OIRIDING_VER |
|
The OIRI DING version. |
|
OAAMGT_VER |
|
The OAA MGMT container version. |
|
OAA_VER |
|
The OAA version. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
Generic Parameters
These generic parameters apply to all deployments.
Table C-6 Parameters to Control the Deployment of all Products
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
PVSERVER |
|
The name or IP address of the NFS server used for persistent volumes. Note: If you use a name, then the name must be resolvable inside the Kubernetes cluster. If it is not resolvable, you can add it by updating CoreDNS. See Adding Individual Host Entries to CoreDNS. |
|
IAM_PVS |
|
The export path on the NFS server where persistent volumes are located. |
|
PV_MOUNT |
|
The path to mount the PV inside the Kubernetes container. Oracle recommends you to not change this value. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
Ingress Parameters
These parameters determine how the Ingress controller is deployed.
Table C-7 Ingress Parameters that Determine the Deployment of Ingress Controller
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
INGRESSNS |
|
The Kubernetes namespace used to hold the Ingress objects. |
|
INGRESS_TYPE |
|
The type of Ingress controller you wan to deploy. At
this time, The script supports only |
|
INGRESS_ENABLE_TCP |
|
Set to |
|
INGRESS_NAME |
|
The name of the Ingress controller used to create an Nginx Class. |
|
INGRESS_SSL |
|
Set to |
|
INGRESS_DOMAIN |
|
Used when creating self-signed certificates for the Ingress controller. |
|
INGRESS_REPLICAS |
|
The number of Ingress controller replicas to start with. This value should be a minimum of two for high availability. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
Elasticsearch Parameters
These parameters determine how to send log files to Elasticsearch.
Table C-8 Parameters to Send Log Files to Elasticsearch
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
USE_ELK |
|
Set to true if you want to send log files to Elasticsearch. |
|
ELKNS |
|
The Kubernetes namespace used to hold Elasticsearch objects. |
|
ELK_OPER_VER |
|
The version of the Elastic Search operator you want to use. |
|
ELK_VER |
|
The version of Elasticsearch/Logstash to use. |
|
ELK_HOST |
|
The address of the Elasticsearch server to which log files are to be sent. If you are using ELK inside a Kubernetes cluster, specify the address provided as the sample value. If you are using an Elasticsearch outside of the Kubernetes cluster, specify the external address. The host name you specify must be resolvable inside the Kubernetes cluster. |
|
ELK_SHARE |
|
The mount point on the NFS server where the ELK persistent volume is exported. |
|
ELK_STORAGE |
|
The storage class to use for the Elasticsearch stateful sets. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
Prometheus Parameters
These parameters determine how to send monitoring information to Prometheus.
Table C-9 Parameters for Sending Monitoring Information to Prometheus
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
USE_PROM |
|
Set to true if you want to send monitoring data to Prometheus. |
|
PROMNS |
|
The Kubernetes namespace used to hold the Prometheus deployment. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
OHS Parameters
OHS parameters are used to formulate how sample OHS configuration files are created. They also control whether you want the Oracle HTTP server files to be propagated to the Oracle HTTP server hosts automatically. If you choose automatic propagation, you should ensure that a passwordless SSL is possible from the deployment host to the Oracle HTTP servers.
Table C-10 Parameters Used by Oracle HTTP Server to Create Sample OHS Configuration Files
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
UPDATE_OHS |
|
Set this value to Note: This value is independent of whether you are installing the Oracle HTTP Server or not. |
|
OHS_HOST1 |
|
The fully qualified name of the host running the first Oracle HTTP Server. |
|
OHS_HOST2 |
|
The fully qualified name of the host running the second Oracle HTTP Server. Leave it blank if you do not have a second Oracle HTTP Server. |
|
OHS_LBR_NETWORK |
|
The Network subnets where the OHS health checks originate. Multiple entries must be enclosed in quotes and separated by space. |
|
DEPLOY_WG |
|
Deploys WebGate in |
|
COPY_WG_FILES |
|
Set this to Note: You should have first deployed the WebGate. |
|
OHS_INSTALLER |
fmw_12.2.1.4.0_ohs_linux64_Disk1_1of1.zip |
The name of the OHS installer ZIP file. |
|
OHS_BASE |
|
The location of the OHS base directory. The binaries and the configuration files are below this location. The Oracle inventory is also placed in this location when installing the Oracle HTTP Server. |
|
OHS_ORACLE_HOME |
|
The location of the OHS binaries. |
|
OHS_DOMAIN |
|
The location of the OHS domain on OHS_HOST1 and OHS_HOST2. |
|
OHS1_NAME |
|
The component name of the first OHS instance (on OHS_HOST1). |
|
OHS2_NAME |
|
The component name of the second OHS instance (on OHS_HOST2). |
|
NM_ADMIN_USER |
|
The name of the admin user you want to assign to Node Manager if you install the Oracle HTTP Server. |
|
OHS_PORT |
|
The port your Oracle HTTP Servers listen on. |
|
OHS_HTTPS_PORT |
|
The SSL port on which Oracle HTTP Servers listen. |
|
NM_PORT |
|
The port to use for Node Manager. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
OUD Parameters
These parameters are specific to OUD. When deploying OUD, you also require the generic LDAP parameters.
Table C-11 OUD Parameters that Determine the Deployment of Oracle Unified Directory
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OUDNS |
|
The Kubernetes namespace used to hold the OUD objects. |
|
OUD_SHARE |
|
The mount point on the NFS server where the OUD persistent volume is exported. |
|
OUD_CONFIG_SHARE |
|
The mount point on the NFS server where the OUD configuration persistent volume is exported. |
|
OUD_LOCAL_SHARE |
|
The local directory where OUD_CONFIG_SHARE is mounted. Used to hold seed files. |
|
OUD_LOCAL_PVSHARE |
|
The local directory where OUD_SHARE is mounted. Used for deletion. |
|
OUD_POD_PREFIX |
|
The prefix used for the OUD pods. |
|
OUD_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OUD replicas to create. If you require two OUD instances, set this to 1. This value is in addition to the primary instance. |
|
OUD_REGION |
|
The OUD region to use should be the first part of
the searchbase without the |
|
LDAP_USER_PWD |
|
The password to assign to all users being created in LDAP. Note: This value should have at least one capital letter, one number, and should be at least eight characters long. |
|
OUD_PWD_EXPIRY |
|
The date when the user passwords you are creating expires. |
|
OUD_CREATE_NODEPORT |
|
Set to True if you want to create NodePort Services for OUD. These services are used to interact with OUD from outside of the Kubernetes cluster. |
|
OUD_MAX_CPU |
|
Maximum CPU cores allocated to the OUD containers. |
|
OUD_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to the OUD Pods where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OUD_MAX_MEMORY |
|
Maximum amount of memory that an OUD container can consume. |
|
OUD_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to the OUD pods. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
OUDSM Parameters
These parameters are used to control the way OUDSM is deployed.
Table C-12 Parameters that Determine the Deployment of Oracle Directory Services Manager
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OUDSMNS |
|
The Kubernetes namespace used to hold the OUDSM objects. |
|
OUDSM_USER |
|
The name of the administration user you want to use for the WebLogic domain that is created when you install OUDSM. |
|
OUDSM_PWD |
|
The password you want to use for OUDSM_USER. |
|
OUDSM_SHARE |
|
The mount point on the NFS server where the OUDSM persistent volume is mounted. |
|
OUDSM_LOCAL_SHARE |
|
The local directory where OUDSM_SHARE is mounted. It is used by the deletion procedure. |
|
OUDSM_INGRESS_HOST |
|
Used when you are using an Ingress controller. This name must resolve in DNS and point to one of the Kubernetes worker nodes or to the network load balancer entry for the Kubernetes workers. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
LDAP Parameters
This table lists the parameters which are common to all LDAP type of deployments.
Table C-13 Parameters for All LDAP Deployments
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
LDAP_OAMADMIN_USER |
|
The name of the user you want to create for the OAM administration tasks. |
|
LDAP_ADMIN_USER |
|
The name of the OUD administrator user. |
|
LDAP_ADMIN_PWD |
|
The password you want to use for the OUD administrator user. |
|
LDAP_SEARCHBASE |
|
The OUD search base. |
|
LDAP_GROUP_SEARCHBASE |
|
The search base where names of groups are stored in the LDAP directory. |
|
LDAP_USER_SEARCHBASE |
|
The search base where names of users are stored in the LDAP directory. |
|
LDAP_RESERVE_SEARCHBASE |
|
The search base where reservations are stored in the LDAP directory. |
|
LDAP_SYSTEMIDS |
|
The special directory tree inside the OUD search base to store system user names, which will not be managed through OIG. |
|
LDAP_OIGADMIN_GRP |
|
The name of the group you want to use for the OIG administration tasks. |
|
LDAP_OAMADMIN_GRP |
|
The name of the group you want to use for the OAM administration tasks. |
|
LDAP_WLSADMIN_GRP |
|
The name of the group you want to use for the WebLogic administration tasks. |
|
LDAP_OAMLDAP_USER |
|
The name of the user you want to use to connect the OAM domain to LDAP for user validation. |
|
LDAP_OIGLDAP_USER |
|
The name of the user you want to use to connect the OIG domain to LDAP for integration. This user will have read/write access. |
|
LDAP_WLSADMIN_USER |
|
The name of a user you want to use for logging in to the WebLogic Administration Console and Fusion Middleware Control. |
|
LDAP_XELSYSADM_USER |
|
The name of the user to administer OIG. |
|
LDAP_USER_PWD |
|
The password to be assigned to all the LDAP user accounts. |
|
LDAP_EXTERNAL_HOST |
Specify only if the LDAP host does not reside inside the current Kubernetes cluster. In this case, enter the host name where LDAP is running. |
|
|
LDAP_EXTERNAL_PORT |
Specify only if the LDAP host does not reside inside the current Kubernetes cluster. In this case, enter the port on which LDAP is listening. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
SSL Parameters
The deployment scripts create self-signed certificates. The parameters are used to determine what values will be added to those certificates.
Table C-14 Parameters Used to Create Self-Signed Certificates
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
SSL_COUNTRY |
|
The abbreviation for the name of the country. |
|
SSL_ORG |
|
The name of the organization. |
|
SSL_CITY |
|
The name of the city. |
|
SSL_STATE |
|
The name of the state. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
WebLogic Operator for Kubernetes Parameters
These parameters determines how the Oracle WebLogic Operator is provisioned.
Table C-15 Parameter that Determines the Deployment of Oracle WebLogic Operator for Kubernetes
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OPERNS |
|
The Kubernetes namespace used to hold the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator. |
|
OPER_ACT |
|
The Kubernetes service account for use by the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator. |
|
OPER_ENABLE_SECRET |
|
Set to true while using your own Container Registry that requires authentication. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
OAM Parameters
These parameters determine how OAM is deployed and configured.
Table C-16 Parameters that Determine the Deployment of Oracle Access Manager
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OAMNS |
|
The Kubernetes namespace used to hold the OAM objects. |
|
OAM_SHARE |
|
The mount point on the NFS server where the OAM persistent volume is exported. |
|
OAM_LOCAL_SHARE |
|
The local directory where OAM_SHARE is mounted. It is used by the deletion procedure. |
|
OAM_SERVER_COUNT |
|
The number of OAM servers to configure. This value should be more than you expect to use. |
|
OAM_SERVER_INITIAL |
|
The number of OAM Managed Servers you want to start for normal running. You will need at least two servers for high availability. |
|
OAM_DB_SCAN |
|
The database scan address to be used by the grid infrastructure. |
|
OAM_DB_LISTENER |
|
The database listener port. |
|
OAM_DB_SERVICE |
|
The database service that connects to the database you want to use for storing the OAM schemas. |
|
OAM_DB_SYS_PWD |
|
The SYS password of the OAM database. |
|
OAM_RCU_PREFIX |
|
The RCU prefix to use for the OAM schemas. |
|
OAM_SCHEMA_PWD |
|
The password to use for the OAM schemas that get created. If you are using special characters, you may need to escape them with a '\'. For example: 'Password\#'. |
|
OAM_WEBLOGIC_USER |
|
The OAM WebLogic administration user name. |
|
OAM_WEBLOGIC_PWD |
|
The password to be used for OAM_WEBLOGIC_USER. |
|
OAM_DOMAIN_NAME |
|
The name of the OAM domain you want to create. |
|
OAM_LOGIN_LBR_HOST |
|
The load balancer name for logging in to OAM. |
|
OAM_LOGIN_LBR_PORT |
|
The load balancer port to use for logging in to OAM. |
|
OAM_LOGIN_LBR_PROTOCOL |
|
The protocol of the load balancer port to use for logging in to OAM. |
|
OAM_ADMIN_LBR_HOST |
|
The load balancer name to use for accessing OAM administrative functions. |
|
OAM_ADMIN_LBR_PORT |
|
The load balancer port to use for accessing OAM administrative functions. |
|
OAM_COOKIE_DOMAIN |
|
The OAM cookie domain is generally similar to the search base. Ensure that you have a '.' (dot) at the beginning. |
|
OAM_OIG_INTEG |
|
Set to true if OAM is integrated with OIG. |
|
OAM_OAP_HOST |
|
The name of one of the Kubernetes worker nodes used for OAP calls. |
|
OAM_OAP_PORT |
|
The internal Kubernetes port used for OAM requests. |
|
OAMSERVER_JAVA_PARAMS |
|
The Java memory parameters to use for OAM Managed Servers. |
|
OAM_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to OUD pods where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAM_MAX_CPU |
|
Maximum CPU cores allocated to the OAM pods. |
|
OAM_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to OAM pods. |
|
OAM_MAX_MEMORY |
|
Maximum amount of that an OAM pods can consume. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
OIG Parameters
These parameters determine how OIG is provisioned and configured.
Table C-17 Parameters that determine the Deployment of Oracle Identity Governance
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OIGNS |
|
The Kubernetes namespace used to hold the OIG objects. |
|
CONNECTOR_DIR |
|
The location on the file system where you have downloaded and extracted the OUD connector bundle. |
|
OIG_SHARE |
|
The mount point on the NFS server where the OIG persistent volume is exported. |
|
OIG_LOCAL_SHARE |
|
The local directory where OIG_SHARE is mounted. It is used by the deletion procedure. |
|
OIG_SERVER_COUNT |
|
The number of OIM/SOA servers to configure. This value should be more than you expect to use. |
|
OIG_SERVER_INITIAL |
|
The number of OIM/SOA Managed Servers you want to start for normal running. You will need at least two servers for high availability. |
|
OIG_DOMAIN_NAME |
|
The name of the OIG domain you want to create. |
|
OIG_DB_SCAN |
|
The database scan address used by the grid infrastructure. |
|
OIG_DB_LISTENER |
|
The database listener port. |
|
OIG_DB_SERVICE |
|
The database service which connects to the database you want to use for storing the OIG schemas. |
|
OIG_DB_SYS_PWD |
|
The SYS password of the OIG database. |
|
OIG_RCU_PREFIX |
|
The RCU prefix to use for OIG schemas. |
|
OIG_SCHEMA_PWD |
|
The password to use for the OIG schemas that get created. If you are using special characters, you may need to escape them with a '\'. For example: 'Password\#'. |
|
OIG_WEBLOGIC_USER |
|
The OIG WebLogic administration user. |
|
OIG_WEBLOGIC_PWD |
|
The password you want to use for OIG_WEBLOGIC_USER. |
|
OIG_ADMIN_LBR_HOST |
|
The load balancer name to use for accessing OIG administrative functions. |
|
OIG_ADMIN_LBR_PORT |
|
The load balancer port you use for accessing the OIG administrative functions. |
|
OIG_LBR_HOST |
|
The load balancer name to use for accessing the OIG Identity Console. |
|
OIG_LBR_PORT |
|
The load balancer port to use for accessing the OIG Identity Console. |
|
OIG_LBR_PROTOCOL |
|
The load balancer protocol to use for accessing the OIG Identity Console. |
|
OIG_LBR_INT_HOST |
|
The load balancer name you will use for accessing OIG internal callbacks. |
|
OIG_LBR_INT_PORT |
|
The load balancer port to use for accessing the OIG internal callbacks. |
|
OIG_LBR_INT_PROTOCOL |
|
The load balancer protocol to use for accessing OIG internal callbacks. |
|
OIG_ENABLE_T3 |
|
Set this value to true if you want to enable access to the Design Console. |
|
OIG_BI_INTEG |
|
Set to true to configure BIP integration. |
|
OIG_BI_HOST |
|
The load balancer name you will use for accessing BI Publisher. |
|
OIG_BI_PORT |
|
The load balancer port you will use for accessing BI Publisher. |
|
OIG_BI_PROTOCOL |
|
The load balancer protocol you will use for accessing BI Publisher. |
|
OIG_BI_USER |
|
The BI user name you want to use for running reports in the BI Publisher deployment. |
|
OIG_BI_USER_PWD |
|
The password of the OIG_BI_USER. |
|
OIMSERVER_JAVA_PARAMS |
|
The memory parameters to use for the
|
|
SOASERVER_JAVA_PARAMS |
"-Xms4096 -XMx8192m" |
The memory parameters to use for
|
|
OIG_EMAIL_CREATE |
|
If set to true, OIG will be configured for email notifications. |
|
OIG_EMAIL_SERVER |
|
The name of your SMTP email server. |
|
OIG_EMAIL_PORT |
|
The port of your SMTP server. The valid values are None or TLS. |
|
OIG_EMAIL_SECURITY |
|
The security mode of your SMTP server. |
|
OIG_EMAIL_ADDRESS |
|
The user name that is used to connect to the SMTP server, if one is required. |
|
OIG_EMAIL_PWD |
<password> |
The password of your SMTP server. |
|
OIG_EMAIL_FROM_ADDRESS |
|
The 'From' email address used when emails are sent. |
|
OIG_EMAIL_REPLY_ADDRESS |
|
The 'Reply' to email address of the emails that are sent. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
OIRI Parameters
These parameters determine how OIRI is provisioned and configured.
Table C-18 Parameters that Determine the Deployment of Oracle Identity Role Intelligence
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OIRINS |
|
The Kubernetes namespace used to hold the OIRI objects. |
|
DINGNS |
|
The Kubernetes namespace used to hold the OIRI DING objects. |
|
OIRI_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OIRI servers to start the deployment. |
|
OIRI_UI_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OIRI UI Servers to start the deployment. |
|
OIRI_SPARK_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OIRI UI servers to start the deployment. |
|
OIRI_SHARE |
|
The mount point on the NFS server where the OIRI persistent volume is exported. |
|
OIRI_LOCAL_SHARE |
|
The local directory where OIRI_SHARE is mounted. It is used by the deletion procedure. |
|
OIRI_SHARE_SIZE |
|
The size of the OIRI persistent volume. |
|
OIRI_DING_SHARE |
|
The mount point on the NFS server where the OIRI DING persistent volume is exported. |
|
OIRI_DING_LOCAL_SHARE |
|
The local directory where OIRI_DING_SHARE is mounted. It is used by the deletion procedure. |
|
OIRI_DING_SHARE_SIZE |
|
The size of the OIRI DING persistent volume. |
|
OIRI_WORK_SHARE |
|
The mount point on the NFS server where the OIRI work persistent volume is exported. |
|
OIRI_DB_SCAN |
|
The database SCAN address of the grid infrastructure. |
|
OIRI_DB_LISTENER |
|
The database listener port. |
|
OIRI_DB_SERVICE |
|
The database service which connects to the database you want to use for storing the OIRI schemas. |
|
OIRI_DB_SYS_PWD |
|
The SYS password of the OIRI database. |
|
OIRI_RCU_PREFIX |
|
The RCU prefix to use for the OIRI schemas. |
|
OIRI_SCHEMA_PWD |
|
The password to use for the OIRI schemas that get
created. If you are using special characters, you may need to
escape them with a '\'. For example:
' |
|
OIRI_OIG_DB_SCAN |
|
The database SCAN address of the grid infrastructure for OIG Database. |
|
OIRI_OIG_DB_LISTENER |
|
The OIG database listener port. |
|
OIRI_OIG_DB_SERVICE |
|
The database service which connects to the database you want to use for storing mining OIG schemas.| |
|
OIRI_CREATE_OHS |
|
This value instructs the scripts to generate OHS
entries for connecting to OIRI. You should set this to
|
|
OIRI_INGRESS_HOST |
|
If you are creating a fully integrated deployment and
want OIRI to be included in the OHS deployment, then this value
should be set to the OIG Administration host name. For example:
If you are deploying OIRI standalone using Ingress
to route requests, then set this value to the virtual hostname
you want to use. For example:
|
|
OIRI_KEYSTORE_PWD |
|
The password to use for the OIRI keystore. |
|
OIRI_ENG_GROUP |
|
The name of the OIG OIRI group - DO NOT CHANGE. |
|
OIRI_ENG_USER |
|
The user to be created in OIG for UI login. |
|
OIRI_ENG_PWD |
|
The password of the OIRI_ENG_USER. |
|
OIRI_SERVICE_USER |
|
The user name for the OIG OIRI service account. |
|
OIRI_SERVICE_PWD |
|
The password for OIRI_SERVICE_USER. |
|
OIRI_OIG_URL |
|
The URL to access OIG. If internal to the Kubernetes
cluster, use the Kubernetes service name as shown in the sample
value. If external, use the |
|
OIRI_OIG_SERVER |
|
The T3 URL to access the OIG oim server (used to create users in OIG) |
|
OIRI_LOAD_DATA |
|
Set to |
|
OIRI_OIG_XELSYSADM_USER |
|
Set to an OIM Administrator which is used to create users in OIG. |
|
OIRI_OIG_USER_PWD |
|
Password of the OIRI_OIG_XELSYSADM_USER. |
|
OIRI_OIG_XELL_FILE |
|
If your OIG is not inside Kubernetes, you need to manually aquire the OIG rest certificate. See Obtaining the OIG SSL Certificate. Set this parameter to the location of that file. Leave it blank if OIG is in Kubernetes. |
|
OIRI_CREATE_OIG_USER |
|
Set to true to allow the automation scripts to create the OIRI users in OIG. |
|
OIRI_SET_OIG_COMPLIANCE |
|
Set to true to allow the automation scripts place OIG in compliance mode. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
OAA Parameters
These parameters determine how OAA is provisioned and configured.
Table C-19 Parameters that Determine the Deployment of Oracle Advanced Authentication and Risk Management
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OAANS |
|
The Kubernetes namespace used to hold the OAA objects. |
|
OAACONS |
|
The Kubernetes namespace used to hold the Coherence objects. |
|
OAA_DEPLOYMENT |
|
A name for your OAA deployment. Do not use the name
|
|
OAA_DOMAIN |
|
The name of the OAM OAuth domain you want to create. |
|
OAA_VAULT_TYPE |
|
The type of vault to use: file system or OCI. |
|
OAA_CREATE_OHS |
|
Set to |
|
OAA_CONFIG_SHARE |
|
The mount point on the NFS server where the OAA configuration persistent volume is exported. |
|
OAA_CRED_SHARE |
|
The mount point on the NFS server where the OAA credentials persistent volume is exported. |
|
OAA_LOG_SHARE |
|
The mount point on the NFS server where the OAA log files persistent volume is exported. |
|
OAA_LOCAL_CONFIG_SHARE |
|
The local directory where OAA_CONFIG_SHARE is mounted. It is used by the deletion procedure. |
|
OAA_LOCAL_CRED_SHARE |
|
The local directory where OAA_CRED_SHARE is mounted. It is used by the deletion procedure. |
|
OAA_LOCAL_LOG_SHARE |
|
The local directory where OAA_LOG_SHARE is mounted. It is used by the deletion procedure. |
|
OAA_DB_SCAN |
|
The database SCAN address of the grid infrastructure. |
|
OAA_DB_LISTENER |
|
The database listener port. |
|
OAA_DB_SERVICE |
|
The database service which connects to the database you want to use for storing the OAA schemas. |
|
OAA_DB_SYS_PWD |
|
The SYS password of the OAA database. |
|
OAA_RCU_PREFIX |
|
The prefix to use for the OAA schemas. |
|
OAA_SCHEMA_PWD |
|
The password to use for the OAA schemas that are
created. If you are using special characters, you may need to
escape them with a ' |
|
OAA_DB_SID |
|
The SID of the database on the database server. |
- OAA Users/Groups/Passwords
- OAA File System Vault Parameters
- OAA OCI Vault Parameters
- Ingress Parameters
- Email Server Parameters
- Test User Parameters
- HA Parameters
- Resource Parameters
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
OAA Users/Groups/Passwords
Table C-20 User Names and Groups Used for OAA
| Users/Groups | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
OAA_ADMIN_GROUP |
|
The OIG role to create for OAA administration functions. This group is created in OIG. |
|
OAA_USER_GROUP |
|
The group which will be assigned to the OAA users. This group is created in OIG. |
|
OAA_ADMIN_USER |
|
The name of the user to use for OAA administration functions. This user name is created in OIG. |
|
OAA_ADMIN_PWD |
|
The password to be assigned to the OAA_ADMIN_USER. |
|
OAA_KEYSTORE_PWD |
|
The password to be used for OAA keystores. |
|
OAA_OAUTH_PWD |
|
The password to be used for OAA OAuth domain. |
|
OAA_API_PWD |
|
The password to be used for OAA API interactions. |
|
OAA_POLICY_PWD |
|
The password to be used for OAA policy interactions. |
|
OAA_FACT_PWD |
|
The password to be used for OAA keystores for factor interactions. |
|
OAA_ADD_USERS_LDAP |
|
Adds all existing LDAP users to the OAA_USER_GROUP LDAP group, allowing existing users to log in via OAA. |
|
OAA_ADD_USERS_OUA_OBJ |
|
Adds the OUA Object class to all existing users in LDAP thereby allowing all existing users to log in via Oracle Universal Authentication. |
Parent topic: OAA Parameters
OAA File System Vault Parameters
Table C-21 Parameters Used for File System Vault
| Users/Groups | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
OAA_VAULT_SHARE |
|
The mount point on the NFS server where the OAA file vault persistent volume is exported. |
|
OAA_LOCAL_VAULT_SHARE |
|
The local directory where OAA_VAULT_SHARE is mounted. It is used by the deletion procedure. |
|
OAA_VAULT_PWD |
|
The password to use for the file-based vault. |
Parent topic: OAA Parameters
OAA OCI Vault Parameters
Table C-22 Parameters Used for OAA OCI Vault
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OAA_OCI_OPER |
- |
To obtain this value, encode the value of the API key that you downloaded at the time of creating the vault. See Creating a Vault. |
|
OAA_OCI_TENANT |
- |
To obtain this value, log in to the OCI console, navigate to Profile and click Tenancy. Use the OCID value. |
|
OAA_OCI_USER |
- |
To obtain this value, log in to the OCI console, navigate to Profile and click Username. Use the OCID value. |
|
OAA_OCI_FP |
- |
To obtain this value, log in to the OCI console, navigate to Profiles, select User Settings, and then click API Keys. Use the value of the fingerprint for the API Key you created earlier. See Creating a Vault. |
|
OAA_OCI_COMPARTMENT |
- |
To obtain this value, log in to the OCI console, navigate to Identity and Security and click Compartments. Select the compartment in which you created the vault and use the OCID value. |
|
OAA_OCI_VAULT_ID |
- |
To obtain this value, log in to the OCI console, navigate to Identity and Security and select Vault. Click the vault you created earlier. See Creating a Vault. Use the OCID value. |
|
OAA_OCI_KEY |
- |
To obtain this value, log in to the OCI console, navigate to Identity and Security, select Vault, and then click the vault you created earlier. See Creating a Vault. Click the key you created earlier. For example, vaultkey. Use the OCID value. |
Parent topic: OAA Parameters
Ingress Parameters
Table C-23 Parameters Used for the Deployment of Ingress
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OAA_ADMIN_HOST |
|
The virtual host used for administration operations. Unless you are using OAA in the standalone mode, set this value to the OAM admin virtual host. |
|
OAA_RUNTIME_HOST |
|
The virtual host used for OAA runtime operations. Unless you are using OAA in the standalone mode, set this vale to the OAM virtual host. |
Parent topic: OAA Parameters
Email Server Parameters
Table C-24 Parameters Used for the Email Server
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OAA_EMAIL_SERVER |
|
The entry point of the Oracle Unified Messaging
server. If the OIG domain is internal to the Kubernetes cluster,
you can use the internal Kubernetes service name. For example:
If your UMS server is external to the Kubernetes
cluster, you can use the URL you configured to access it. For
example:
|
|
OAA_EMAIL_USER |
|
The user name you use to connect to the UMS server. |
|
OAA_EMAIL_PWD |
|
The password you use to connect to the UMS server. |
|
OAA_SMS_SERVER |
|
The entry point of the Oracle Unified Messaging server you use to send SMS messages. This is usually the same as OAA_EMAIL_SERVER. |
|
OAA_SMS_USER |
|
The user name you use to connect to the UMS server. |
|
OAA_SMS_PWD |
|
The password you use to connect to the UMS server. |
Parent topic: OAA Parameters
Test User Parameters
Table C-25 Parameters Used for Creating a Test User
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OAA_CREATE_TESTUSER |
|
Set this value to |
|
OAA_USER |
|
The name you want to assign to the test user. |
|
OAA_USER_PWD |
|
The password you want to assign to the test user. |
|
OAA_USER_EMAIL |
|
The email address of the test user you are creating. |
|
OAA_USER_POSTCODE |
- |
The post code/zip code of the test user you are creating. |
Parent topic: OAA Parameters
HA Parameters
Table C-26 Parameters Used for High Availability
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OAA_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OAA service pods to be created. For HA, the minimum number is two. |
|
OAA_ADMIN_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OAA administration pods to be created. For HA, the minimum number is two. |
|
OAA_POLICY_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OAA policy pods to be created. For HA, the minimum number is two. |
|
OAA_SPUI_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OAA SPUI service pods to be created. For HA, the minimum number is two. |
|
OAA_TOTP_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OAA TOTP service pods to be created. For HA, the minimum number is two. |
|
OAA_YOTP_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OAA YOTP service pods to be created. For HA, the minimum number is two. |
|
OAA_FIDO_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OAA FIDO service pods to be created. For HA, the minimum number is two. |
|
OAA_EMAIL_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OAA EMAIL service pods to be created. For HA, the minimum number is two. |
|
OAA_SMS_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OAA SMS service pods to be created. For HA, the minimum number is two. |
|
OAA_PUSH_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OAA PUSH service pods to be created. For HA, the minimum number is two. |
|
OAA_RISK_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OAA RISK service pods to be created. For HA, the minimum number is two. |
|
OAA_RISKCC_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OAA RISK CC service pods to be created. For HA, the minimum number is two. |
|
OAA_DRSS_REPLICAS |
|
The number of OUA service pods to be created. For HA, the minimum number is two. |
Parent topic: OAA Parameters
Resource Parameters
Table C-27 Resource Parameters
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
OAA_OAA_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to OAA pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAA_OAA_MEMORY |
|
Initial Memory allocated to OAA pod. |
|
OAA_ADMIN_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to ADMIN pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAA_ADMIN_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to ADMIN pod. |
|
OAA_POLICY_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to POLICY pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAA_POLICY_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to POLICY pod. |
|
OAA_SPUI_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to a SPUI pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAA_SPUI_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to SPUI pod. |
|
OAA_TOTP_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to TOTP pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core.| |
|
OAA_TOTP_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to TOTP pod. |
|
OAA_YOTP_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to YOTP pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAA_YOTP_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to YOTP pod. |
|
OAA_FIDO_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to FIDO pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAA_FIDO_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to FIDO pod. |
|
OAA_EMAIL_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to EMAIL pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAA_EMAIL_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to EMAIL pod. |
|
OAA_PUSH_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to PUSH pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAA_PUSH_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to PUSH pod. |
|
OAA_SMS_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to SMS pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAA_SMS_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to SMS pod. |
|
OAA_KBA_CPU |
|
Initial CPU Units allocated to KBA pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAA_KBA_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to KBA pod. |
|
OAA_RISK_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to RISK pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAA_RISK_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to RISK pod. |
|
OAA_RISKCC_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to RISKCC pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAA_RISKCC_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to RISKCC pod. |
|
OAA_DRSS_CPU |
|
Initial CPU units allocated to DRSS pod where 1000m is equal to 1 CPU core. |
|
OAA_DRSS_MEMORY |
|
Initial memory allocated to DRSS pod. |
Parent topic: OAA Parameters
Port Mappings
In some cases, you can specify your own ports. The scripts allow you to override the default values by setting these parameters.
Table C-28 Parameters that Determine the Ports Used in the Deployment
| Parameter | Sample Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
ELK_KIBANA_K8 |
|
The port to use for the Kibana requests. Note: This value must be within the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
ELK_K8 |
|
The port to use for the Elasticsearch requests. Note: This value must be within the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
PROM_GRAF_K8 |
|
The port to use for Grafana requests. Note: This value must be within the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
PROM_K8 |
|
The port to use for Prometheus requests. Note: This value must be within the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
PROM_ALERT_K8 |
|
The port to use for Alert Manager requests. Note: This value must be within the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
OUD_LDAP_K8 |
|
The port to use for OUD LDAP requests. Note: This value must be within the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
OUD_LDAPS_K8 |
|
The port to use for OUD LDAPS requests. Note: This value must be within the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
OUDSM_SERVICE_PORT |
|
The port to use for OUDSM requests. Note: This value must be within the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
OAM_ADMIN_PORT |
|
The internal WebLogic administration port to use for the OAM domain. This port is available only in the Kubernetes cluster. |
|
OAM_ADMIN_K8 |
|
The external port to use for the OAM Administration Server requests. Note: This value must be within the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
OAM_OAM_K8 |
|
The external port to use for the OAM Managed Server requests. Note: This value must be within the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
OAM_POLICY_K8 |
|
The external port to use for the OAM Policy server requests. Note: This value must be within the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
OAM_OAP_SERVICE_PORT |
|
The external port to use for the OAP server requests. This port is for legacy WebGates and is optional. Note: This value must be within the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
OIG_SOA_PORT_K8 |
|
The external port to use for the SOA Managed Server requests. Note: This value must be in the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
OAM_OAP_PORT |
|
The internal Kubernetes port used for OAM requests. |
|
OIG_ADMIN_PORT |
|
The internal port used for the OIG WebLogic Administration Server. |
|
OIG_ADMIN_K8 |
|
The external port to use for the OIG Administration Server requests. Note: This value must be in the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
OIG_OIM_PORT_K8 |
|
The external port to use for the OIM Managed Server requests. Note: this must be in the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
OIG_OIM_T3_PORT_K8 |
|
The external port to use for the OIM Managed Server T3 requests. Note: This value must be in the Kubernetes service port range. |
|
OHS_PORT |
|
The HTTP Server listen address. |
Parent topic: Reference - Response File
Components of the Deployment Scripts
For reference purposes, this section includes the name and function of all the objects that make up the deployment scripts.
Table C-29 Components of the Deployment Scripts
| Name | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The file that contains the details of the target environment. Must be updated for each deployment. |
|
|
The file that populates the response file. |
|
|
|
The file that checks the environment prior to provisioning. |
|
|
|
The file that provisions everything. |
|
|
|
The file that installs/configures the Ingress controller. |
|
|
|
The file that installs/configures Elastic Search and Kibana. |
|
|
|
The file that installs/configures Prometheus and Grafana. |
|
|
|
The file that installs/configures OUD. |
|
|
|
The file that installs/configures OUDSM. |
|
|
|
The file that installs/configures OAM. |
|
|
|
The file that installs/configures OIG. |
|
|
|
The file that installs/configures OIRI. |
|
|
|
The file that installs/configures OAA. |
|
|
|
|
The common functions/procedures used by the Ingress provisioning scripts. |
|
|
|
The common functions/procedures used by all the provisioning scripts. |
|
|
|
The common functions/procedures used by the Prometheus provisioning scripts. |
|
|
|
The common functions/procedures used by the OUD and OUDSM provisioning scripts. |
|
|
|
The common functions/procedures used by the OAM provisioning scripts. |
|
|
|
The common functions/procedures used by the OIG provisioning scripts. |
|
|
|
The common functions/procedures used by the OIRI provisioning scripts. |
|
|
|
The common functions/procedures used by the OAA provisioning scripts. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create an ELK cluster. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create a Kibana deployment. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create an ELK NodePort Service. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create a Kibana NodePort Service. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create a Prometheus deployment. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the Alert Manager NodePort Service. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the Grafana NodePort Service. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the Prometheus NodePort Service. |
|
|
|
The template file used to seed OUD with users and groups. |
|
|
|
The template file used to seed OUD schema changes. |
|
|
|
The template used to create the OUD NodePort Services for Kubernetes. |
|
|
|
The OUD Helm override template file. |
|
|
|
The template used to create the OUDSM NodePort Services for Kubernetes. |
|
|
|
The OUD Helm override template file. |
|
|
|
The template used to add LDAP groups to the WebLogic administration role. |
|
|
|
The template property file used to run
|
|
|
|
The template file used to run
|
|
|
|
The template file used to enable gridlink on data sources. |
|
|
|
The template file used to perform the initial OAM setup. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OAM Managed Server NodePort Service. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OAM OAP internal Managed Server NodePort Service. |
|
|
|
the template file used to create the OAM OAP external Managed Server NodePort Service. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the Policy Manager Managed Server NodePort Service. |
|
|
|
The list of resources to add to the |
|
|
|
The template file used to enable WebLogic plug-in in the domain. |
|
|
|
The template file used to manually create the WebGate agent. |
|
|
|
The template property file used to manually create the WebGate agent. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the SSO partner application. |
|
|
|
The template |
|
|
|
The |
|
|
|
The template file used to remove OAM from the default coherence cluster. |
|
|
|
The template file used to update the OAMDS data source. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the sample OHS Config. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the sample OHS Config. |
|
|
|
The template file used to assign LDAP groups to the WebLogic administration role. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OUD authenticator. |
|
|
|
The template file used to obtain the global passphrase from OAM. |
|
|
|
The template file used to obtain the OAM global passphrase. |
|
|
|
The template file used to run
|
|
|
|
The |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the SOA external Managed Server NodePort Service. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OIM external Managed Server NodePort Service. |
|
|
|
The template file used to run
|
|
|
|
The template file used to run
|
|
|
|
The template file used to run
|
|
|
|
The template file used to run
|
|
|
|
The template file used to run
|
|
|
|
The template shell script used to run the reconciliation jobs. |
|
|
|
The Java script used to run the reconciliation jobs. |
|
|
|
The OIM libraries required by
|
|
|
|
The template script used to update SOA URLs. |
|
|
|
The |
|
|
|
The supplementary |
|
|
|
The template script used to generate the
|
|
|
|
The template script used to enable gridlink on data sources. |
|
|
|
The template script used to update the Match attribute. |
|
|
|
The template script used to update the
|
|
|
|
The template file used to update the MDS data source. |
|
|
|
The template file used to set the WebLogic plug-in. |
|
|
|
The template file used to enable BI integration. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the sample OHS Config. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the sample OHS Config. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the sample OHS Config. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OIRI user names in OIG. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create, compile, and run
|
|
|
|
The template file used to place OIG into the Compliance Mode. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create, compile, and run
|
|
|
|
The template file used to start the OIRI CLI. |
|
|
|
The template file used to start the OIRI DING CLI. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OIRI NodePort Service. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OIRI UI NodePort Service. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the sample OHS Config. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the sample OHS Configuration. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OAM authentication module. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OAM authentication policy. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OAM authentication scheme. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create an Oracle HTTP server wallet. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OAA schemas. |
|
|
|
The template file used to delete OAA schemas. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OAM TAP partner. |
|
|
|
The template file used to enable OAM OAuth. |
|
|
|
The template file for |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OAA management pod when using the OCI vault. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OAA management pod when using the file system vault. |
|
|
|
The template file used for |
|
|
|
The template file used for OAA administration OHS entries. |
|
|
|
The template file used for OAA runtime OHS entries. |
|
|
|
The template file used for OAM OAuth header entries for OHS. |
|
|
|
The template file used to add existing user names to the OAA LDAP group. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create OAA users and groups. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OAA users and groups in LDAP. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OAA test user. |
|
|
|
The template file used to create the OAA test user in LDAP. |
|
|
|
The file used to delete all the deployments. |
|
|
|
The file used to delete the Elastic Search deployment. |
|
|
|
The file used to delete the Prometheus deployment. |
|
|
|
The file used to delete a container image from the Kubernetes worker hosts. |
|
|
|
The file used to delete the OAM deployment. |
|
|
|
The file used to delete the OIG deployment. |
|
|
|
The file used to delete the WLS Kubernetes Operator deployment. |
|
|
|
The file used to delete the OUD deployment. |
|
|
|
The file used to delete the OUDSM deployment. |
|
|
|
The file used to delete the OIRI deployment. |
|
|
|
The file used to delete the OAA deployment. |
|
|
|
The file used to delete the Ingress controller. |
|
|
|
The file used to load the container image onto each Kubernetes worker host. |