2 Overview of the WLDF Architecture
Note:
Concepts are presented in this section in a way to help you understand how WLDF works. Some of this differs from the way WLDF is surfaced in its configuration and run-time APIs and in the WebLogic Server Console. If you want to start configuring and using WLDF right away, you can safely skip this discussion and start with Using the Built-in Diagnostic System Modules.
The following topics summarize WLDF and its architectural components:
- Overview of the WebLogic Diagnostics Framework
The WLDF components interact with each other to process data at the server level. - Data Creation, Collection, and Instrumentation
Diagnostic data is collected from a number of logically classified sources. - Archive
The Archive component of WLDF captures the state of the system and archives it for future access in diagnosing critical faults in the system. It creates a historical archive using several persistent components. - Policies and Actions
The Policies and Actions component of WLDF is used to create automated monitors that observe specific diagnostic states and send notifications based on configured rules. - Data Accessor
The Data Accessor component of WLDF provides access to all the data collected by WLDF, including log, event, and metric data. It interacts with the Archive component to get historical data including logged event data and persisted metrics. - Monitoring Dashboard and Request Performance Pages
The WebLogic Server Administration Console displays the Monitoring Dashboard and Diagnostics Request Performance pages. The diagnostics data collected is visually represented in these pages. The Monitoring Dashboard displays the current and historical operating state of WebLogic Server and hosted applications. The Diagnostics Request Performance page shows real-time and historical views of method performance information. - Diagnostic Image Capture
The Diagnostic Image Capture component captures the key server state as a diagnostic image. The diagnostic image is a diagnostic snapshot of the server state used in diagnosing problems. - How It All Fits Together
The components of the WLDF work together to collect data and diagnose faults in running server. - WLDF Support for Multitenancy
Oracle WebLogic Server supports multitenancy, which provides a sharable infrastructure for use by multiple organizations. These organizations are a conceptual grouping of your own choosing, which you can think of as tenants. Tenants have access to domain partitions, which provide an isolated slice of the domain’s configuration and runtime infrastructure.
Overview of the WebLogic Diagnostics Framework
-
Data creators (data publishers and data providers that are distributed across WLDF components)
-
Data collectors (the Logger and the Harvester components)
-
Archive component
-
Accessor component
-
Instrumentation component
-
Policies and Actions component
-
Image Capture component
-
Monitoring Dashboard
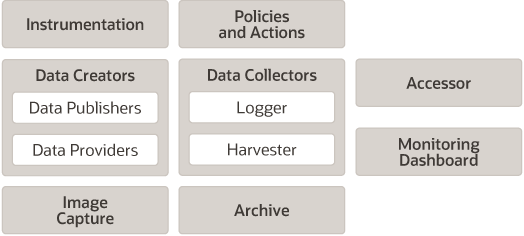
Data creators generate diagnostic data that is consumed by the Logger and the Harvester. Those components coordinate with the Archive to persist the data, and they coordinate with the Policies and Actions subsystem to provide automated monitoring. The Accessor interacts with the Logger and the Harvester to expose current diagnostic data and with the Archive to present historical data. The Image Capture facility provides the means for capturing a diagnostic snapshot of a key server state. The Major WLDF components are shown in Figure 2-1.
All of the framework components operate at the server level and are only aware of server scope. All the components exist entirely within the server process and participate in the standard server lifecycle. All artifacts of the framework are configured and stored on a per server basis.
Parent topic: Overview of the WLDF Architecture
Data Creation, Collection, and Instrumentation
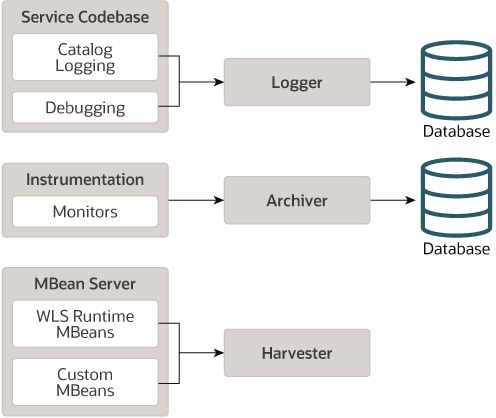
Data providers and data publishers are distributed across components, and the generated data can be collected by the Logger or the Harvester, as shown in Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-2 Relationship of Data Creation Components to Data Collection Components
Description of "Figure 2-2 Relationship of Data Creation Components to Data Collection Components"
Figure 2-2 shows that invocations of the server logging infrastructure serve as inline data publishers, and that the generated data is collected as events. (The logging infrastructure can be invoked through the catalog infrastructure, the debugging model, or directly through the Logger.)
The Instrumentation component creates monitors and inserts them at well-defined points in the flow of execution. These monitors publish data directly to the Archive.
Components registered with the MBean Server may also make themselves known as data providers by registering with the Harvester. Collected data is then exposed to both the Policies and Actions system for automated monitoring and to the Archive for persistence.
Parent topic: Overview of the WLDF Architecture
Archive
The Archive component of WLDF captures the state of the system and archives it for future access in diagnosing critical faults in the system. It creates a historical archive using several persistent components.
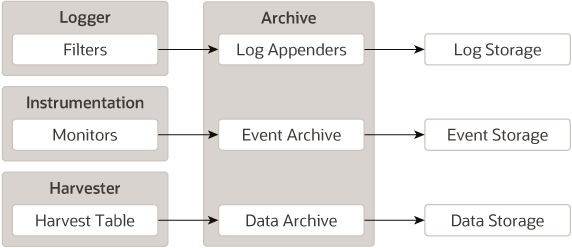
The past state is often critical in diagnosing faults in a system. This requires that the state be captured and archived for future access, creating a historical archive. In WLDF, the Archive meets this need with several persistence components. Both events and harvested metrics can be persisted and made available for historical review.
Traditional logging information, which is human readable and intended for inclusion in the server log, is persisted through the standard logging appenders. New event data that is intended for system consumption is persisted into an event store using an event archiver. Metric data is persisted into a data store using a data archiver. The relationship of the Archive to the Logger and the Harvester is shown in Figure 2-3.
The Archive provides access interfaces so that the Accessor may expose any of the persisted historical data.
Figure 2-3 Relationship of the Archive to the Logger and the Harvester
Description of "Figure 2-3 Relationship of the Archive to the Logger and the Harvester"
Parent topic: Overview of the WLDF Architecture
Policies and Actions
The Policies and Actions component of WLDF is used to create automated monitors that observe specific diagnostic states and send notifications based on configured rules.
A policy can monitor log data, event data from the Instrumentation component, or metric data from a data provider that is harvested by the Harvester. The Policy Manager is capable of managing policies that are composed of a number of policy expressions. These relationships are shown in Figure 2-4.
Figure 2-4 Relationship of the Logger and the Harvester to the Policies and Actions System
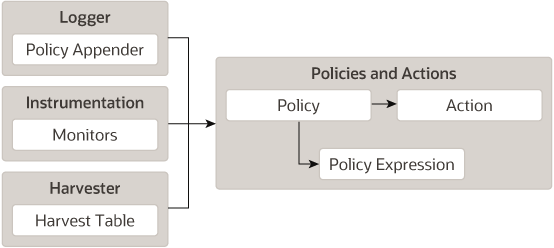
Description of "Figure 2-4 Relationship of the Logger and the Harvester to the Policies and Actions System"
One or more actions can be configured for use by a policy. By default, every policy logs an event in the server log. SMTP, SNMP, JMX, elastic, REST, script, log, and JMS actions are also supported.
Parent topic: Overview of the WLDF Architecture
Data Accessor
The Data Accessor component of WLDF provides access to all the data collected by WLDF, including log, event, and metric data. It interacts with the Archive component to get historical data including logged event data and persisted metrics.
When accessing data in a running server, a JMX-based access service is used. The Accessor provides for data lookup by type, by component, and by attribute. It permits time-based filtering and, in the case of events, filtering by severity, source and content.
Tools may need to access data that was persisted by a currently inactive server. In this case, an offline Accessor is also provided. You can use it to export archived data to an XML file for later access. To use the Accessor in this way, you must use the WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) and must have physical access to the machine.
The relationship of the Accessor to the Harvester and the Archive is shown in Figure 2-5.
Figure 2-5 Relationship of the Online and Offline Accessors to the Archive
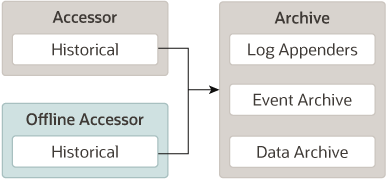
Description of "Figure 2-5 Relationship of the Online and Offline Accessors to the Archive"
Parent topic: Overview of the WLDF Architecture
Monitoring Dashboard and Request Performance Pages
The WebLogic Server Administration Console displays the Monitoring Dashboard and Diagnostics Request Performance pages. The diagnostics data collected is visually represented in these pages. The Monitoring Dashboard displays the current and historical operating state of WebLogic Server and hosted applications. The Diagnostics Request Performance page shows real-time and historical views of method performance information.
The following sections provide more information about the web pages that visually display the diagnostic data:
Parent topic: Overview of the WLDF Architecture
Monitoring Dashboard
The Monitoring Dashboard displays the current and historical operating state of WebLogic Server and hosted applications by providing visualizations of metric runtime MBean attributes, which surface some of the more critical runtime performance metrics and the change in those metrics over time. Historical operating state is represented by collected metrics that have been persisted into the Archive. To view collected metrics from the Archive, you must configure the Harvester to capture the data you want to monitor.
The Monitoring Dashboard displays metric information in a series of views. A view is a collection of one or more charts that display metrics. The Monitoring Dashboard includes a predefined set of built-in views of available runtime metrics for all running WebLogic Server instances in the domain. Built-in views surface some of the more critical runtime WebLogic Server performance metrics and serve as examples of the Monitoring Dashboard's graphic capabilities.
Custom views are available only to the user who creates them. Custom views are automatically persisted and can be accessed again when you restart the Monitoring Dashboard sessions. See Using the Monitoring Dashboard.
Parent topic: Monitoring Dashboard and Request Performance Pages
Diagnostics Request Performance Page
The Diagnostics Request Performance page of the WebLogic Server Administration Console shows real-time and historical views of method performance information that is captured using the Instrumentation component. To view request performance information, you must first configure the Instrumentation component to make that data available. See Creating Request Performance Data.
Parent topic: Monitoring Dashboard and Request Performance Pages
Diagnostic Image Capture
The Diagnostic Image Capture component captures the key server state as a diagnostic image. The diagnostic image is a diagnostic snapshot of the server state used in diagnosing problems.
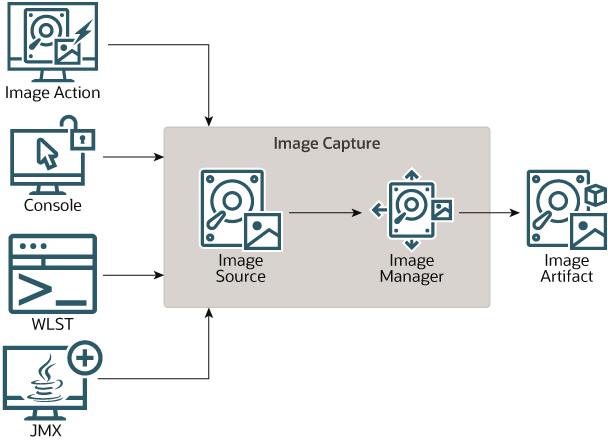
Diagnostic Image Capture support gathers the most common sources of the key server state used in diagnosing problems. It packages that state into a single artifact which can be made available to support technicians, as shown in Figure 2-6. The diagnostic image is in essence a diagnostic snapshot or dump from the server, analogous to a UNIX core dump.
If WebLogic Server is configured with Oracle HotSpot, and Java Flight Recorder is enabled, the diagnostic image capture includes all available Java Flight Recorder data from all producers. Furthermore, if WLDF is configured to generate WebLogic Server diagnostic information captured by Java Flight Recorder, the JFR file includes that information as well. The JFR file can be extracted from the diagnostic image capture and viewed in Java Mission Control. See Using WLDF with Java Flight Recorder.
Image Capture support includes:
-
On-demand capture, which is the creation of a diagnostic image capture by means of an operation or command issued from the WebLogic Server Administration Console, WLST script, or JMX application.
-
Image action, which is automatically creating a diagnostic image capture in response to the triggering of an associated Harvester policy, Log policy, or Instrumentation policy expression. For example, a Harvester policy that monitors runtime MBean attributes in a running server can execute an image action if the metrics harvested from specific runtime MBean instances indicate a performance issue. Data in the diagnostic image capture can be analyzed to determine the likely causes of the issue.
For more information about diagnostic image capture, see:
Parent topic: Overview of the WLDF Architecture
How It All Fits Together
The components of the WLDF work together to collect data and diagnose faults in running server.
Figure 2-7 shows how all the parts of WLDF fit together.
Figure 2-7 Overall View of the WebLogic Diagnostics Framework
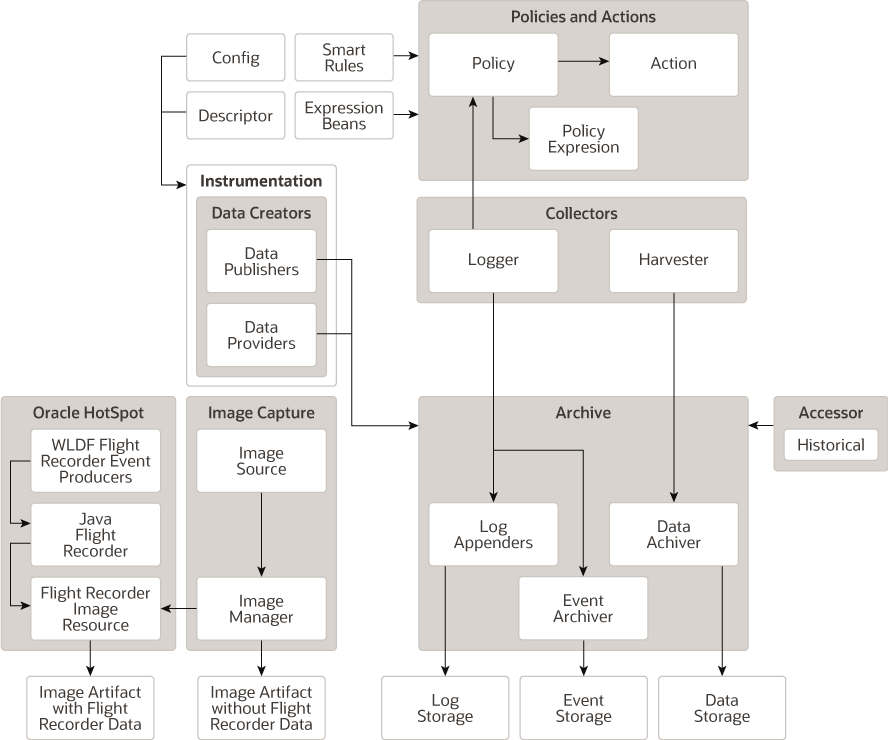
Description of "Figure 2-7 Overall View of the WebLogic Diagnostics Framework"
Parent topic: Overview of the WLDF Architecture
WLDF Support for Multitenancy
Oracle WebLogic Server supports multitenancy, which provides a sharable infrastructure for use by multiple organizations. These organizations are a conceptual grouping of your own choosing, which you can think of as tenants. Tenants have access to domain partitions, which provide an isolated slice of the domain’s configuration and runtime infrastructure.
Note:
WebLogic Server Multitenant domain partitions, resource groups, resource group templates, virtual targets, and Resource Consumption Management (RCM) are deprecated in WebLogic Server 12.2.1.4.0 and will be removed in the next release.
WebLogic Server MT support includes several diagnostic and monitoring capabilities for monitoring and debugging applications and resources deployed in domain partitions, including the following:
-
WebLogic Server MT allows configuration of levels for
java.util.loggingloggers that are used by applications deployed to a partition. In a MT environment, partition users can configure logger levels within the scope of the partition without affecting other partitions. -
Partition scoped log events to Server log and from partition deployed resources like JMS, SAF, and servlet resources, are made available to partition administrators from the WLDF Data Accessor.
-
A partition user can set debug flags on WebLogic Server components so that debug messages can be broadcast on behalf of work performed for that partition, without affecting other partitions.
-
The Harvester, and Policies and Actions components, can be defined within a resource group or resource group template deployed to a partition.
-
Applications deployed within a partition may be instrumented using WLDF instrumentation.
-
Image capture can be initiated either manually by a partition scope user, or by a policy configured in a partition scope diagnostic system module. Only the content specific to the partition is included in the generated diagnostic image.
-
WebLogic Server supports the ability to monitor RCM metrics within a partition scope.
-
WLDF provides integration with the Java Flight Recorder which enables WebLogic Server events to be included in the JFR flight recording. The JFR flight recording, which includes events from the JVM and from any other event producer, such as WebLogic Server and Oracle Dynamic Monitoring System (DMS), can include
partition-idandpartition-nameattributes to distinguish data among partitions.Note:
The data from JFR is not visible or accessible to the MT Administrator.
See Monitoring and Debugging Partitions in Using WebLogic Server Multitenant.
Parent topic: Overview of the WLDF Architecture