3 Configuring the Database User Management Connector for Oracle Database
While creating an application, you must configure connection-related parameters that the connector uses to connect Oracle Identity Governance with your target system and perform connector operations. In addition, you can view and edit attribute mappings between the process form fields in Oracle Identity Governance and target system columns, predefined correlation rules, situations and responses, and reconciliation jobs.
3.1 Basic Configuration Parameters for Oracle Database
These are the connection-related parameters that Oracle Identity Governance requires to connect to Oracle Database. These parameters are common for both target applications and authoritative applications.
Table 3-1 Parameters in the Basic Configuration Section for Oracle Database
| Parameter | Mandatory? | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Connection URL |
Yes |
Enter the database connection string using the Default value: |
|
User |
Yes |
Enter the user name of the target system account to be used for connector operations. Sample value: Note: If you are configuring the connector for Oracle Database Vault, then enter the user name of the account you created in Creating the Administrator Account on Oracle Database Vault. |
|
Password |
Yes |
Enter the password for the user name of the target system account to be used for connector operations. Note: If you are configuring the connector for Oracle Database Vault, then enter the password of the account you created in Creating the Administrator Account on Oracle Database Vault. |
|
Database Type |
Yes |
This parameter identifies the database type (such as Oracle or MySQL) and is used for loading respective scripts. |
|
Connector Server Name |
No |
If you created an IT resource of the type “Connector Server”, then enter its name. |
|
Database Drivers |
No |
Name of the JDBC driver class. Default value: |
|
Connection Properties |
No |
Enter the connection properties for the target system database. |
3.2 Advanced Settings Parameters for Oracle Database
These are the configuration-related entries that the connector uses during reconciliation and provisioning operations.
Note:
Unless specified, the parameters in the table are applicable to both target and authoritative applications.Table 3-2 Advanced Setting Parameters for Oracle Database
| Parameter | Mandatory? | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Connector Name |
Yes |
This parameter holds the name of the connector class. Default value: |
|
Connector Package Name |
Yes |
This parameter holds the name of the connector bundle package. Default value: |
|
Connector Package Version |
Yes |
This parameter hods the version of the connector bundle class. Default value: 1.0.1116 |
|
disableValuesSet |
No |
Enter the possible values for the disabled status of a user. Default value: |
|
Reserve Keywords |
No |
Enter the list of words that are reserved and are not allowed to be used in the names of the connector artifacts Default value: Note: This parameter is available only when you are creating a target application. |
|
Unsupported Character Set |
No |
Enter the characters that are not allowed to be used in the names of the connector artifacts Default value: "&","--","~","`","\"" Note: This parameter is available only when you are creating a target application. |
|
Pool Max Idle |
No |
Maximum number of idle objects in a pool. Sample value: |
|
Pool Max Size |
No |
Maximum number of connections that the pool can create. Sample value: |
|
Pool Max Wait |
No |
Maximum time, in milliseconds, the pool must wait for a free object to make itself available to be consumed for an operation. Sample value: |
|
Pool Min Evict Idle Time |
No |
Minimum time, in milliseconds, the connector must wait before evicting an idle object. Sample value: |
|
Pool Min Idle |
No |
Minimum number of idle objects in a pool. Sample value: |
3.3 Attribute Mappings for Oracle Database
The attribute mappings on the Schema page vary depending on whether you are creating a target application or an authoritative application.
3.3.1 Attribute Mappings for an Oracle Database Target Application
The Schema page for a target application displays the default schema (provided by the connector) that maps Oracle Identity Governance attributes to target system columns. The connector uses these mappings during reconciliation and provisioning operations.
Oracle Database User Account Attributes
Table 3-3 lists the user-specific attribute mappings between the process form fields in Oracle Identity Governance and Oracle Database columns. The table also lists whether a specific attribute is used during provisioning or reconciliation and whether it is a matching key field for fetching records during reconciliation.
If required, you can edit the default attribute mappings by adding new attributes or deleting existing attributes as described in Creating a Target Application of Oracle Fusion Middleware Performing Self Service Tasks with Oracle Identity Governance.
Table 3-3 Default Attribute Mappings for Oracle DB User Account
| Display Name | Target Attribute | Data Type | Mandatory Provisioning Property? | Provision Field? | Recon Field? | Key Field? | Case Insensitive? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Username |
__NAME__ |
String |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Authentication Type |
authType |
String |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Not applicable |
|
Global DN |
externalName |
String |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Not applicable |
|
Default Tablespace |
tablespace |
String |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Not applicable |
|
Default Tablespace Quota |
defaultQuota |
String |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Not applicable |
|
Temporary Tablespace |
tempTableSpace |
String |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Not applicable |
|
Profile Name |
profile |
String |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Not applicable |
|
Return Id |
__UID__ |
String |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Account Status |
status |
String |
No |
No |
Yes |
No |
Not applicable |
|
Status |
__ENABLE__ |
String |
No |
No |
Yes |
No |
Not applicable |
|
Password |
__PASSWORD__ |
String |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
Not applicable |
Figure 3-1 shows the default User account attribute mappings.
Figure 3-1 Default Attribute Mappings for Oracle Database User Account
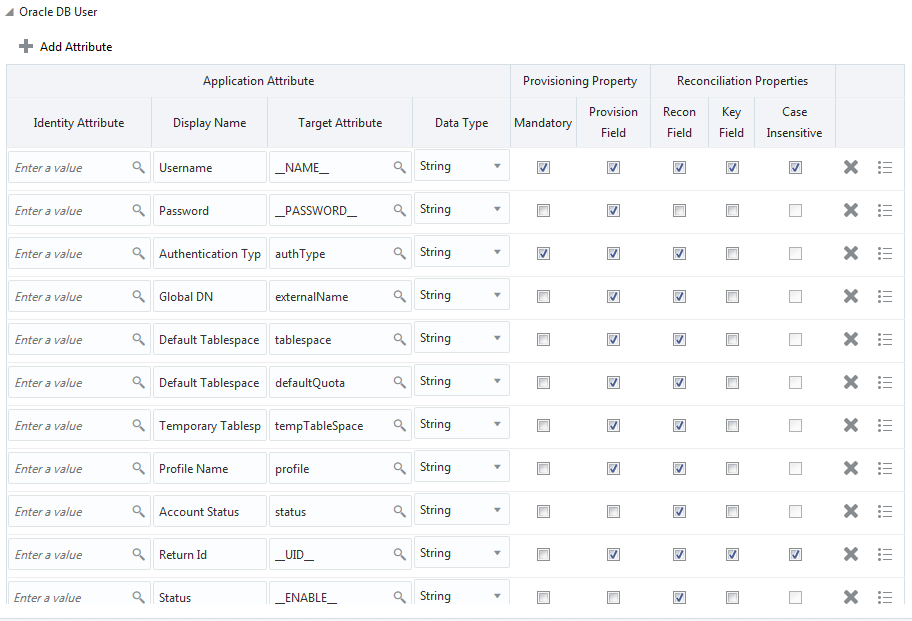
Description of "Figure 3-1 Default Attribute Mappings for Oracle Database User Account"
Role List Entitlement Attributes
Table 3-4 lists the roles-specific attribute mappings between the process form fields in Oracle Identity Governance and Oracle Database columns. The table lists whether a given attribute is mandatory during provisioning. It also lists whether a given attribute is used during reconciliation and whether it is a matching key field for fetching records during reconciliation.
If required, you can edit the default attribute mappings by adding new attributes or deleting existing attributes as described in Creating a Target Application of Oracle Fusion Middleware Performing Self Service Tasks with Oracle Identity Governance.
Table 3-4 Default Attribute Mappings for Oracle Database Role List Entitlement
| Display Name | Target Attribute | Data Type | Mandatory Provisioning Property? | Recon Field? | Key Field? | Case Insensitive? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Role |
roles~DBRole~__NAME__ |
String |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Role Admin Option |
roles~DBRole~adminOption |
String |
No |
Yes |
No |
Not applicable |
Figure 3-2 shows the default Role List entitlement mapping.
Figure 3-2 Default Attribute Mappings for Oracle Database Role List Entitlement
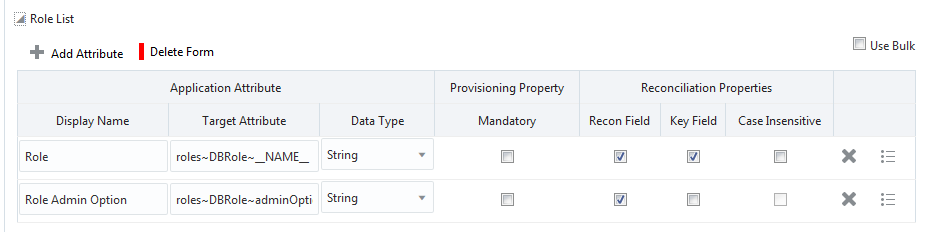
Description of "Figure 3-2 Default Attribute Mappings for Oracle Database Role List Entitlement"
Privilege List Entitlement Attributes
Table 3-5 lists the roles-specific attribute mappings between the process form fields in Oracle Identity Governance and Oracle Database columns. The table lists whether a given attribute is mandatory during provisioning. It also lists whether a given attribute is used during reconciliation and whether it is a matching key field for fetching records during reconciliation.
If required, you can edit the default attribute mappings by adding new attributes or deleting existing attributes as described in Creating a Target Application of Oracle Fusion Middleware Performing Self Service Tasks with Oracle Identity Governance.
Table 3-5 Default Attribute Mappings for Oracle Database Privilege List Entitlement
| Display Name | Target Attribute | Data Type | Mandatory Provisioning Property? | Recon Field? | Key Field? | Case Insensitive? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Privilege |
privileges~DBPrivilege~__NAME__ |
String |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Privilege Admin Option |
privileges~DBPrivilege~adminOption |
String |
No |
Yes |
No |
Not applicable |
Figure 3-2 shows the default Privilege List entitlement mapping.
Figure 3-3 Default Attribute Mappings for Oracle Database Privilege List Entitlement
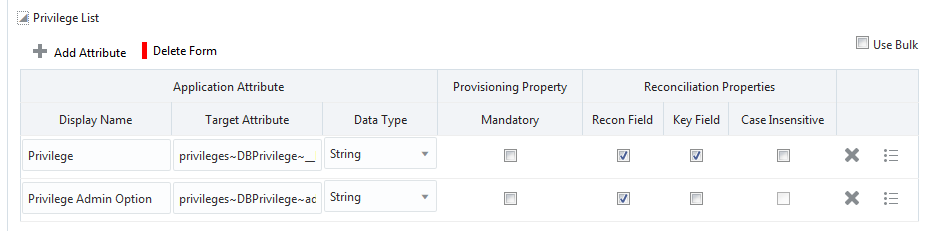
Description of "Figure 3-3 Default Attribute Mappings for Oracle Database Privilege List Entitlement"
3.3.2 Attribute Mappings for an Oracle Database Authoritative Application
The Schema page for an authoritative application displays the default schema (provided by the connector) that maps Oracle Identity Governance attributes to target system columns. The connector uses these mappings during reconciliation operations.
Table 3-6 lists the user-specific attribute mappings between the reconciliation fields in Oracle Identity Governance and Oracle Database columns. The table also lists the data type for a given attribute and specified whether it is a mandatory attribute for reconciliation.
If required, you can edit these attributes mappings by adding new attributes or deleting existing attributes on the Schema page as described in Creating an Authoritative Application in Oracle Fusion Middleware Performing Self Service Tasks with Oracle Identity Governance.
You may use the default schema that has been set for you or update and change it before continuing to the next step.
The Organization Name, Xellerate Type, and Role identity attributes are mandatory fields on the OIG User form. They cannot be left blank during reconciliation. The target attribute mappings for these identity attributes are empty by default because there are no corresponding columns in the target system. Therefore, the connector provides default values (as listed in the “Default Value for Identity Display Name” column of Table 3-6) that it can use during reconciliation. For example, the default target attribute value for the Organization Name attribute is Xellerate Users. This implies that the connector reconciles all target system user accounts into the Xellerate Users organization in Oracle Identity Governance. Similarly, the default attribute value for Xellerate Type attribute is End-User, which implies that all reconciled user records are marked as end users.
Table 3-6 Oracle DB User Account Schema Attributes
| Identity Display Name | Target Attribute | Data Type | Mandatory Reconciliation Property? | Recon Field? | Default Value for Identity Display Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Organization Name |
NA |
String |
No |
Yes |
Xellerate Users |
|
User Login |
__UID__ |
String |
No |
Yes |
NA |
|
Last Name |
__UID__ |
String |
No |
Yes |
NA |
|
Xellerate Type |
NA |
String |
No |
Yes |
End-User |
|
Status |
__ENABLE__ |
String |
No |
Yes |
NA |
|
Role |
NA |
String |
No |
Yes |
Full-Time |
Figure 3-4 shows the default User account attribute mappings.
Figure 3-4 Default Attribute Mappings for an Oracle Database User Account in an Authoritative Application
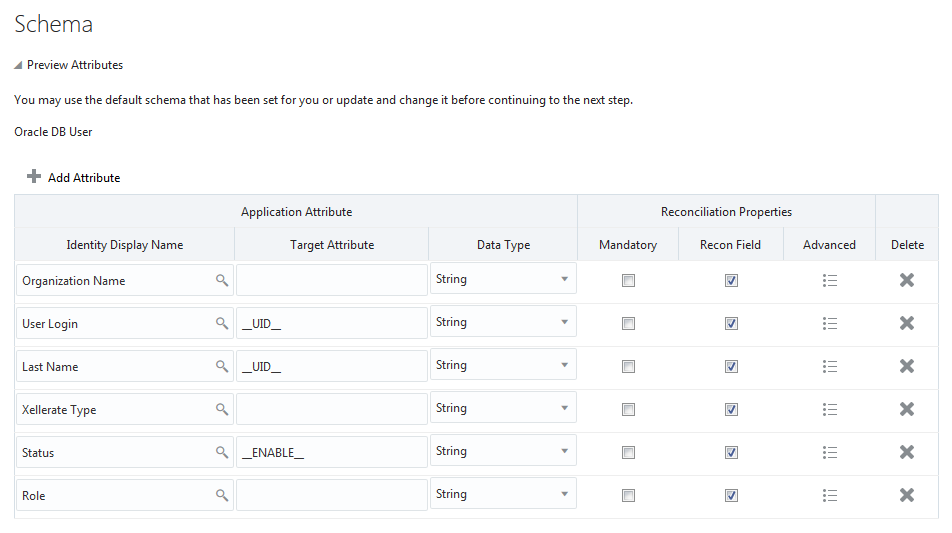
Description of "Figure 3-4 Default Attribute Mappings for an Oracle Database User Account in an Authoritative Application"
3.4 Correlation Rules for Oracle Database
Learn about the predefined rules, responses and situations for Target and Authoritative applications. The connector use these rules and responses for performing reconciliation.
3.4.1 Correlation Rules for an Oracle Database Target Application
When you create a Target application, the connector uses correlation rules to determine the identity to which Oracle Identity Governance must assign a resource.
Predefined Identity Correlation Rules
By default, the Database User Management connector provides a simple correlation rule when you create a Target application. The connector uses this correlation rule to compare the entries in Oracle Identity Governance repository and the target system repository, determine the difference between the two repositories, and apply the latest changes to Oracle Identity Governance.
Table 3-7 lists the default simple correlation rule for Oracle Database. If required, you can edit the default correlation rule or add new rules. You can create complex correlation rules also. For more information about adding or editing simple or complex correlation rules, see Creating a Target Application in Oracle Fusion Middleware Performing Self Service Tasks with Oracle Identity Governance.
Table 3-7 Predefined Identity Correlation Rule for an Oracle Database Target Application
| Target Attribute | Element Operator | Identity Attribute | Case Sensitive? |
|---|---|---|---|
|
__NAME__ |
Equals |
User Login |
No |
-
__NAME__ is a single-valued attribute on the target system that identifies the user account.
-
User Login is the field on the OIM User form.
Figure 3-5 shows the simple correlation rule for Oracle Database.
Figure 3-5 Simple Correlation Rule for an Oracle Database Target Application
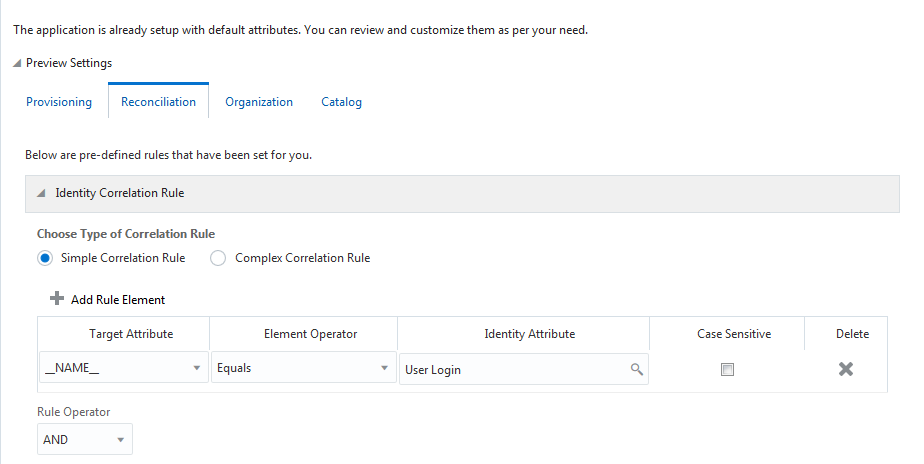
Description of "Figure 3-5 Simple Correlation Rule for an Oracle Database Target Application"
Predefined Situations and Responses
The Database User Management connector provides a default set of situations and responses when you create a Target application. These situations and responses specify the action that Oracle Identity Governance must take based on the result of a reconciliation event.
Table 3-8 lists the default situations and responses for Oracle Database. If required, you can edit these default situations and responses or add new ones. For more information about adding or editing situations and responses, see Creating a Target Application in Oracle Fusion Middleware Performing Self Service Tasks with Oracle Identity Governance
Table 3-8 Predefined Situations and Responses for an Oracle Database Target Application
| Situation | Response |
|---|---|
|
No Matches Found |
Assign to Administrator With Least Load |
|
One Entity Match Found |
Establish Link |
|
One Process Match Found |
Establish Link |
Figure 3-6 shows the situations and responses for Oracle Database that the connector provides by default.
Figure 3-6 Predefined Situations and Responses for an Oracle Database Target Application
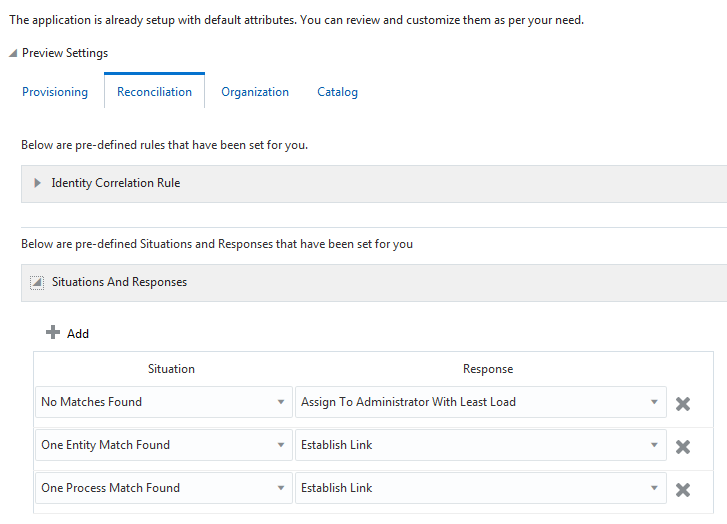
Description of "Figure 3-6 Predefined Situations and Responses for an Oracle Database Target Application"
3.4.2 Correlation Rules for an Oracle Database Authoritative Application
When you create an Authoritative application, the connector uses correlation rules to determine the identity that must be reconciled into Oracle Identity Governance.
Predefined Identity Correlation Rules
By default, the Database User Management connector provides a simple correlation rule when you create an Authoritative application. The connector uses this correlation rule to compare the entries in Oracle Identity Governance repository and the target system repository, determine the difference between the two repositories, and apply the latest changes to Oracle Identity Governance.
Table 3-9 lists the default simple correlation rule for an Oracle Database authoritative application. If required, you can edit the default correlation rule or add new rules. You can create complex correlation rules also. For more information about adding or editing simple or complex correlation rules, see Creating a Target Application in Oracle Fusion Middleware Performing Self Service Tasks with Oracle Identity Governance.
Table 3-9 Predefined Identity Correlation Rule for an Oracle Database Authoritative Application
| Target Attribute | Element Operator | Identity Attribute | Case Sensitive? |
|---|---|---|---|
|
__UID__ |
Equals |
User Login |
No |
-
__UID__ is an attribute on the target system that uniquely identifies the user account.
-
User Login is the field on the OIM User form.
Figure 3-7 shows the simple correlation rule for an Oracle Database Authoritative application.
Figure 3-7 Simple Correlation Rule for an Oracle Database Authoritative Application
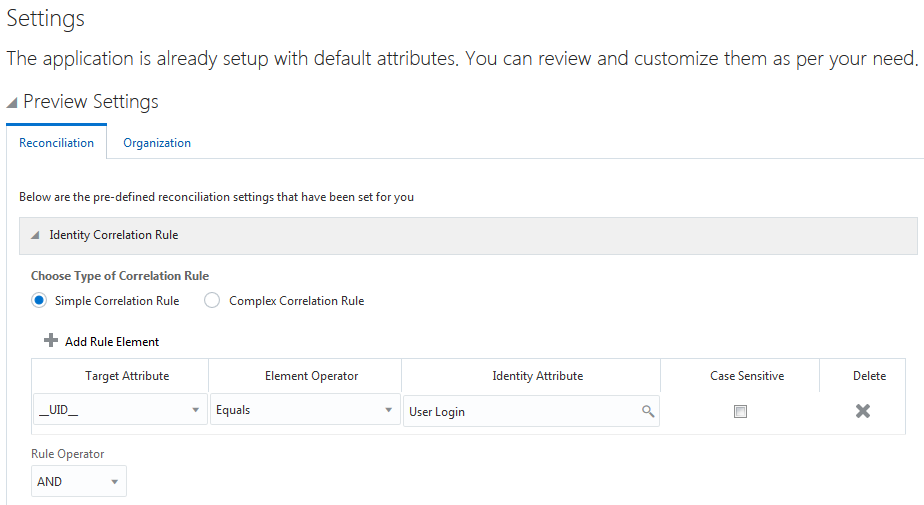
Description of "Figure 3-7 Simple Correlation Rule for an Oracle Database Authoritative Application"
Predefined Situations and Responses
The Database User Management connector provides a default set of situations and responses when you create an Authoritative application. These situations and responses specify the action that Oracle Identity Governance must take based on the result of a reconciliation event.
Table 3-10 lists the default situations and responses for Oracle Database. If required, you can edit these default situations and responses or add new ones. For more information about adding or editing situations and responses, see Creating a Target Application in Oracle Fusion Middleware Performing Self Service Tasks with Oracle Identity Governance
Table 3-10 Predefined Situations and Responses for an Oracle Database Authoritative Application
| Situation | Response |
|---|---|
|
No Matches Found |
Create User |
|
One Entity Match Found |
Establish Link |
Figure 3-8 shows the situations and responses for an Oracle Database Authoritative application that the connector provides by default.
Figure 3-8 Predefined Situations and Responses for an Oracle Database Authoritative Application
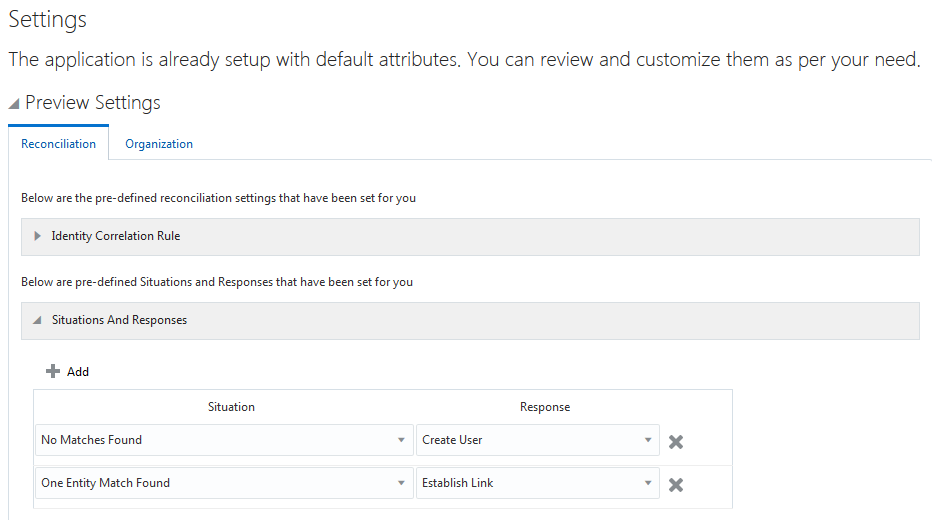
Description of "Figure 3-8 Predefined Situations and Responses for an Oracle Database Authoritative Application"
3.5 Reconciliation Jobs for Oracle Database
These are the reconciliation jobs that are automatically created in Oracle Identity Governance after you create the application for your target system.
You can either use these predefined jobs or edit them to meet your requirements. Alternatively, you can create custom reconciliation jobs. For information about editing these predefined jobs or creating new ones, see Updating Reconciliation Jobs in Oracle Fusion Middleware Performing Self Service Tasks with Oracle Identity Governance.
User Reconciliation Jobs
-
DBUM Oracle User Target Reconciliation: Use this reconciliation job to reconcile user data from a Target application.
-
DBUM Oracle User Trusted Reconciliation: Use this reconciliation job to reconcile user data from an Authoritative application.
The parameters for both these jobs are the same.
Table 3-11 Parameters of the User Reconciliation Jobs for Oracle Database
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Application Name |
Name of the application you created for your target system. This value is the same as the value that you provided for the Application Name field while creating your target application. Do not modify this value. |
|
Batch Size |
Enter the number of records that must be included in each batch fetched from the target system during reconciliation. |
|
Filter |
Enter the expression for filtering records that the scheduled job must reconcile. Sample value: For information about the filters expressions that you can create and use, see ICF Filter Syntax in Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Governance. |
|
Incremental Recon Attribute |
Name of the target system column that holds holds the timestamp at which the user record was modified. Default value: |
|
Object Type |
Type of object you want to reconcile. Default value: |
|
Latest Token |
The parameter holds the value of the target system column that is specified as the value of the Incremental Recon Attribute parameter. The Latest Token parameter is used for internal purposes. By default, this value is empty. Note: Do not enter a value for this attribute. The reconciliation engine automatically enters a value in this attribute. |
|
Scheduled Task Name |
Name of the scheduled job. Note: For the scheduled job included with this connector, you must not change the value of this attribute. However, if you create a new job or create a copy of the job, then enter the unique name for that scheduled job as the value of this attribute. |
Delete User Reconciliation Jobs
-
DBUM Oracle Delete User Target Reconciliation: Use this reconciliation job to reconcile data about deleted user accounts from a Target application.
-
DBUM Oracle Delete User Trusted Reconciliation: Use this reconciliation job to reconcile data about deleted user accounts from an Authoritative application.
The parameters for both these jobs are the same.
Table 3-12 Parameters of the Delete User Reconciliation Jobs for Oracle Database
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Application Name |
Name of the application you created for your target system. This value is the same as the value that you provided for the Application Name field while creating your target application. Do not modify this value. |
|
Object Type |
Type of object you want to reconcile. Default value: |
Reconciliation Jobs for Entitlements
The following jobs are available for reconciling entitlements:
-
DBUM Oracle Privileges Lookup Reconciliation
-
DBUM Oracle Profile Lookup Reconciliation
-
DBUM Oracle Roles Lookup Reconciliation
-
DBUM Oracle Tablespaces Lookup Reconciliation
-
DBUM Oracle Temporary Tablespaces Lookup Reconciliation
These reconciliation jobs are available only for a Target application. The parameters for all the reconciliation jobs are the same.
Table 3-13 Parameters of the Reconciliation Jobs for Entitlements
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Application Name |
Name of the application you created for your target system. This value is the same as the value that you provided for the Application Name field while creating your target application. Do not modify this value. |
|
Lookup Name |
This parameter holds the name of the lookup definition that maps each lookup definition with the data source from which values must be fetched. Depending on the reconciliation job you are using, the default values are as follows:
|
|
Object Type |
Enter the type of object whose values must be synchronized. Depending on the scheduled job you are using, the default values are as follows:
Note: Do not change the value of this attribute. |
|
Code Key Attribute |
Enter the name of the connector or target system attribute that is used to populate the Code Key column of the lookup definition (specified as the value of the Lookup Name attribute). Default value: Note: Do not change the value of this attribute. |
|
Decode Attribute |
Enter the name of the connector or target system attribute that is used to populate the Decode column of the lookup definition (specified as the value of the Lookup Name attribute). Default value: |