5 Performing the Postconfiguration Tasks
These are the tasks that you can perform after creating an application in Oracle Identity Governance.
5.1 Configuring Oracle Identity Governance
During application creation, if you did not choose to create a default form, then you must create a UI form for the application that you created by using the connector.
Note:
Perform the procedures described in this section only if you did not choose to create the default form during creating the application.The following topics describe the procedures to configure Oracle Identity Governance:
5.1.1 Creating and Activating a Sandbox
You must create and activate a sandbox to begin using the customization and form management features. You can then publish the sandbox to make the customizations available to other users.
See Creating a Sandbox and Activating a Sandbox in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Governance.
5.1.2 Creating a New UI Form
You can use Form Designer in Oracle Identity System Administration to create and manage application instance forms.
See Creating Forms By Using the Form Designer in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Governance.
While creating the UI form, ensure that you select the resource object corresponding to the newly created application that you want to associate the form with. In addition, select the Generate Entitlement Forms check box.
5.1.3 Publishing a Sandbox
Before publishing a sandbox, perform this procedure as a best practice to validate all sandbox changes made till this stage as it is difficult to revert the changes after a sandbox is published.
-
In Identity System Administration, deactivate the sandbox.
-
Log out of Identity System Administration.
-
Log in to Identity Self Service using the xelsysadm user credentials and then activate the sandbox that you deactivated in Step 1.
-
In the Catalog, ensure that the application instance form for your resource appears with correct fields.
-
Publish the sandbox. See Publishing a Sandbox in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Governance.
5.1.4 Updating an Existing Application Instance with a New Form
For any changes that you do in the schema of your application in Identity Self Service, you must create a new UI form and update the changes in an application instance.
To update an existing application instance with a new form:
-
Create and activate a sandbox.
-
Create a new UI form for the resource.
-
Open the existing application instance.
-
In the Form field, select the new UI form that you created.
-
Save the application instance.
-
Publish the sandbox.
See Also:
-
Creating a Sandbox and Activating a Sandbox in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Governance
-
Creating Forms By Using the Form Designer in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Governance
-
Publishing a Sandbox in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Governance
5.2 Harvesting Entitlements and Sync Catalog
You can populate Entitlement schema from child process form table, and harvest roles, application instances, and entitlements into catalog. You can also load catalog metadata.
To harvest entitlements and sync catalog:
-
Depending on the target system that you are using, run the scheduled jobs for lookup field synchronization as follows:
For Oracle Database: Run the reconciliation jobs for entitlements listed in Reconciliation Jobs for Oracle Database.
For MySQL: Run the reconciliation jobs for entitlements listed in Reconciliation Jobs for MySQL.
-
Run the Entitlement List scheduled job to populate Entitlement Assignment schema from child process form table.
-
Run the Catalog Synchronization Job scheduled job.
See Also:
Predefined Scheduled Tasks in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Governance for a description of the Entitlement List and Catalog Synchronization Job scheduled jobs5.3 Managing Logging for Oracle Identity Governance
Oracle Identity Governance uses the Oracle Diagnostic Logging (ODL) logging service for recording all types of events pertaining to the connector.
The following topics provide detailed information about logging:
5.3.1 Understanding Log Levels
When you enable logging, Oracle Identity Governance automatically stores in a log file information about events that occur during the course of provisioning and reconciliation operations.
ODL is the principle logging service used by Oracle Identity Governance and is based on java.util.logger. To specify the type of event for which you want logging to take place, you can set the log level to one of the following:
-
SEVERE.intValue()+100
This level enables logging of information about fatal errors.
-
SEVERE
This level enables logging of information about errors that might allow Oracle Identity Governance to continue running.
-
WARNING
This level enables logging of information about potentially harmful situations.
-
INFO
This level enables logging of messages that highlight the progress of the application.
-
CONFIG
This level enables logging of information about fine-grained events that are useful for debugging.
-
FINE, FINER, FINEST
These levels enable logging of information about fine-grained events, where FINEST logs information about all events.
These message types are mapped to ODL message type and level combinations as shown in Table 5-2.
Table 5-1 Log Levels and ODL Message Type:Level Combinations
| Java Level | ODL Message Type:Level |
|---|---|
|
SEVERE.intValue()+100 |
INCIDENT_ERROR:1 |
|
SEVERE |
ERROR:1 |
|
WARNING |
WARNING:1 |
|
INFO |
NOTIFICATION:1 |
|
CONFIG |
NOTIFICATION:16 |
|
FINE |
TRACE:1 |
|
FINER |
TRACE:16 |
Table 5-2 Log Levels and ODL Message Type:Level Combinations
| Java Level | ODL Message Type:Level |
|---|---|
|
SEVERE.intValue()+100 |
INCIDENT_ERROR:1 |
|
SEVERE |
ERROR:1 |
|
WARNING |
WARNING:1 |
|
INFO |
NOTIFICATION:1 |
|
CONFIG |
NOTIFICATION:16 |
|
FINE |
TRACE:1 |
|
FINER |
TRACE:16 |
|
FINEST |
TRACE:32 |
The configuration file for OJDL is logging.xml, which is located at the following path:
DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/servers/OIM_SERVER/logging.xml
Here, DOMAIN_HOME and OIM_SERVER are the domain name and server name specified during the installation of Oracle Identity Governance.
5.3.2 Enabling Logging
You can enable logging in Oracle WebLogic Server by updating the logging.xml file.
To enable logging:
-
Edit the logging.xml file as follows:
-
Add the following blocks in the file:
<log_handler name='db-um-handler' level='[LOG_LEVEL]' class='oracle.core.ojdl.logging.ODLHandlerFactory'> <property name='logreader:' value='off'/> <property name='path' value='[FILE_NAME]'/> <property name='format' value='ODL-Text'/> <property name='useThreadName' value='true'/> <property name='locale' value='en'/> <property name='maxFileSize' value='5242880'/> <property name='maxLogSize' value='52428800'/> <property name='encoding' value='UTF-8'/> </log_handler>
<logger name="ORG.IDENTITYCONNECTORS.DBUM" level="[LOG_LEVEL]" useParentHandlers="false"> <handler name="db-um-handler"/> <handler name="console-handler"/> </logger> -
Replace all occurrences of
[LOG_LEVEL]with the ODL message type and level combination that you require. Table 5-2 lists the supported message type and level combinations.Similarly, replace
[FILE_NAME]with the full path and name of the log file in which you want log messages to be recorded.The following blocks show sample values for
[LOG_LEVEL]and[FILE_NAME]:<log_handler name='db-um-handler' level='NOTIFICATION:1' class='oracle.core.ojdl.logging.ODLHandlerFactory'> <property name='logreader:' value='off'/> <property name='path' value='F:\MyMachine\middleware\user_projects\domains\base_domain1\servers\oim_server1\logs\oim_server1-diagnostic-1.log'/> <property name='format' value='ODL-Text'/> <property name='useThreadName' value='true'/> <property name='locale' value='en'/> <property name='maxFileSize' value='5242880'/> <property name='maxLogSize' value='52428800'/> <property name='encoding' value='UTF-8'/> </log_handler> <logger name="oracle.iam.connectors.icfcommon" level="NOTIFICATION:1" useParentHandlers="false"> <handler name="db-um-handler"/> </logger> <logger name="ORG.IDENTITYCONNECTORS.DBUM" level="NOTIFICATION:1" useParentHandlers="false"> <handler name="db-um-handler"/> </logger>
With these sample values, when you use Oracle Identity Governance, all messages generated for this connector that are of a log level equal to or higher than the
NOTIFICATION:1level are recorded in the specified file. -
-
Save and close the file.
-
Restart the application server.
5.4 Configuring the IT Resource for the Connector Server
If you have used the Connector Server, you must configure values for the parameters of the Connector Server IT resource.
Note:
This procedure is optional and is required only when the Connector Server is being used.
To configure or modify the IT resource for the Connector Server:
-
Log in to Oracle Identity System Administration.
-
Create and activate a sandbox.
-
In the left pane, under Configuration, click IT Resource.
-
In the IT Resource Name field on the Manage IT Resource page, enter
DBUM Connector Serverand then click Search. Figure 5-1 shows the Manage IT Resource page.Figure 5-1 Manage IT Resource Page for Connector Server IT Resource
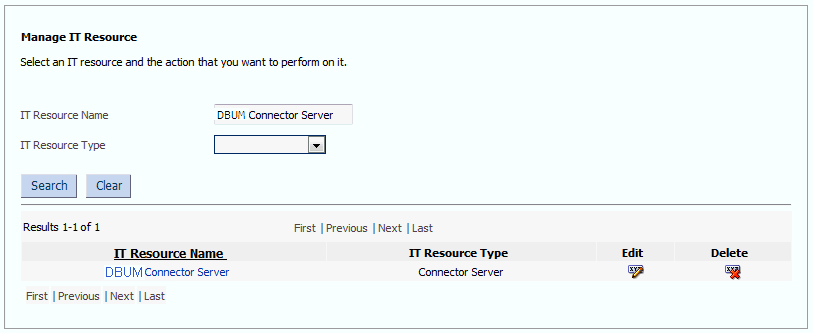
Description of "Figure 5-1 Manage IT Resource Page for Connector Server IT Resource" -
Click the edit icon corresponding to the Connector Server IT resource.
-
From the list at the top of the page, select Details and Parameters.
-
Specify values for the parameters of the Connector Server IT resource. Figure 5-2 shows the Edit IT Resource Details and Parameters page.
Figure 5-2 Edit IT Resource Details and Parameters Page for the Connector Server IT Resource
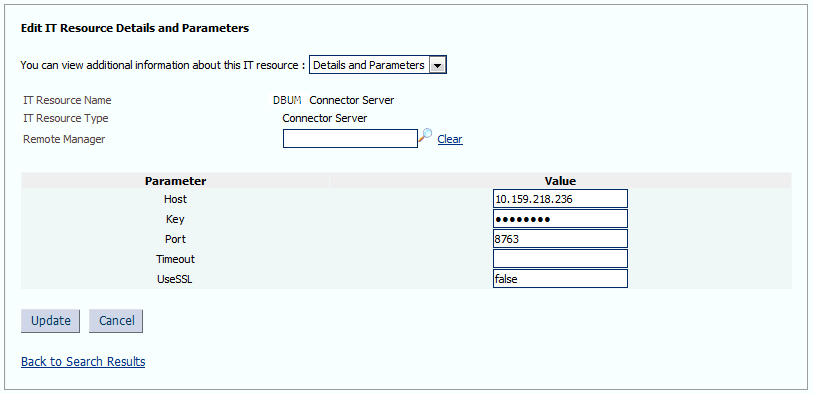
Description of "Figure 5-2 Edit IT Resource Details and Parameters Page for the Connector Server IT Resource"Table 5-3 provides information about the parameters of the IT resource.
Table 5-3 Parameters of the IT Resource for the Database User Management Connector Server
Parameter Description Host
Enter the host name or IP address of the computer hosting the Connector Server.
Sample value:
HostNameKey
Enter the key for the Connector Server.
Port
Enter the number of the port at which the Connector Server is listening.
Default value:
8763Timeout
Enter an integer value which specifies the number of milliseconds after which the connection between the Connector Server and Oracle Identity Governance times out.
If the value is zero or if no value is specified, the timeout is unlimited.
Sample value:
0(recommended value)UseSSL
Enter
trueto specify that you will configure SSL between Oracle Identity Governance and the Connector Server. Otherwise, enterfalse.Default value:
falseSee Also: Configuring Secure Communication Between the Target System and Oracle Identity Governance for information about enabling SSL.
-
To save the values, click Update.
5.5 Creating the Administrator Account on Oracle Database Vault
You must create an administrator account on Oracle Database Vault. This account is used by the connector for performing reconciliation and provisioning operations on Oracle Database Vault realms.
Note:
Perform the procedure described in this section only if you have Oracle Database Vault installed and you want to configure the connector for provisioning and reconciling authorization to Oracle Database Vault realms.
To create the administrator account on Oracle Database Vault:
5.6 Localizing Field Labels in UI Forms for Database User Management Connector
You can localize UI form field labels by using the resource bundle corresponding to the language you want to use. The resource bundles are available in the connector installation media.
Note:
Perform the procedure described in this section only if you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x or later and you want to localize UI form field labels.
To localize field label that you add to in UI forms:
-
Log in to Oracle Enterprise Manager.
-
In the left pane, expand Application Deployments and then select oracle.iam.console.identity.sysadmin.ear.
-
In the right pane, from the Application Deployment list, select MDS Configuration.
-
On the MDS Configuration page, click Export and save the archive to the local computer.
-
Extract the contents of the archive, and open the following file in a text editor:
SAVED_LOCATION\xliffBundles\oracle\iam\ui\runtime\BizEditorBundle.xlf
-
Edit the BizEditorBundle.xlf file in the following manner:
-
Search for the following text:
<file source-language="en" original="/xliffBundles/oracle/iam/ui/runtime/BizEditorBundle.xlf" datatype="x-oracle-adf">
-
Replace with the following text:
<file source-language="en" target-language="LANG_CODE" original="/xliffBundles/oracle/iam/ui/runtime/BizEditorBundle.xlf" datatype="x-oracle-adf">In this text, replace LANG_CODE with the code of the language that you want to localize the form field labels. The following is a sample value for localizing the form field labels in Japanese:
<file source-language="en" target-language="ja" original="/xliffBundles/oracle/iam/ui/runtime/BizEditorBundle.xlf" datatype="x-oracle-adf">
-
Search for the application instance code. This procedure shows a sample edit for Oracle Database application instance. The original code is:
<trans-unit id="${adfBundle['oracle.adf.businesseditor.model.util.BaseRuntimeResourceBundle']['persdef.sessiondef.oracle.iam.ui.runtime.form.model.user.entity.userEO.UD_DB_ORA_U_USERNAME__c_description']}"> <source>Username</source> </target> </trans-unit> <trans-unit id="sessiondef.oracle.iam.ui.runtime.form.model.OracleDBForm.entity.OracleDBForm.UD_DB_ORA_U_USERNAME__c_LABEL"> <source>Username</source> </target> </trans-unit> -
Open the resource file from the connector package, for example DB-UM_ja.properties, and get the value of the attribute from the file, for example, global.udf.UD_DB_ORA_U_USERNAME=\u30E6\u30FC\u30B6\u30FC\u540D.
-
Replace the original code shown in Step 6.b with the following:
<trans-unit id="${adfBundle['oracle.adf.businesseditor.model.util.BaseRuntimeResourceBundle']['persdef.sessiondef.oracle.iam.ui.runtime.form.model.user.entity.userEO.UD_DB_ORA_U_USERNAME__c_description']}"> <source>Username</source> <target>\u30E6\u30FC\u30B6\u30FC\u540D</target> </trans-unit> <trans-unit id="sessiondef.oracle.iam.ui.runtime.form.model.OracleDBForm.entity.OracleDBForm.UD_DB_ORA_U_USERNAME__c_LABEL"> <source>Username</source> <target>\u30E6\u30FC\u30B6\u30FC\u540D</target> </trans-unit> -
Repeat Steps 6.a through 6.d for all attributes of the process form.
-
Save the file as BizEditorBundle_LANG_CODE.xlf. In this file name, replace LANG_CODE with the code of the language to which you are localizing.
Sample file name: BizEditorBundle_ja.xlf.
-
-
Repackage the ZIP file and import it into MDS.
See Also:
Deploying and Undeploying Customizations in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Governance for more information about exporting and importing metadata files
-
Log out of and log in to Oracle Identity Governance.
5.7 Configuring Secure Communication Between the Target System and Oracle Identity Governance
You must configure SSL to secure the communication between your target system and Oracle Identity Governance.
5.7.1 Configuring Secure Communication Between Oracle Database and Oracle Identity Governance
It is recommended that you perform the procedure described in this section to configure secure communication between Oracle Database and Oracle Identity Governance.
To secure communication between Oracle Database and Oracle Identity Governance, you can perform either one or both of the following procedures:
5.7.1.1 Configuring Data Encryption and Integrity in Oracle Database
You can protect data against active attacks and ensure data privacy by configuring native Oracle Net Services data encryption and integrity for Oracle Advanced Security.
To configure data encryption and integrity, see Data Encryption in Oracle Database Advanced Security Administrator's Guide.
5.7.2 Configuring Secure Communication Between MySQL and Oracle Identity Governance
It is recommended that you perform the procedure described in this section to configure secure communication between your target system and Oracle Identity Governance.
To secure communication between MySQL and Oracle Identity Governance: