9 Configuring Storage Devices for Operating System Installation
This section provides instructions for preparing Oracle Server X9-2 or Oracle Server X9-2L storage devices for operating system (OS) installation. If applicable, prepare storage drives and configure RAID.
| Section | Description | Links |
|---|---|---|
|
Lists devices, including hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid state drives (SSDs) that are supported on Oracle Server X9-2 or Oracle Server X9-2L. Provides links to procedures for configuring RAID on HDD and SSD devices. |
Updated device support information is available in the Oracle Server X9-2 Product Notes and Oracle Server X9-2L Product Notes. To learn more about HDDs and SSDs, refer to Oracle Storage Drives Documentation Library (https://docs.oracle.com/cd/F24175_01/index.html). |
|
|
Overview of RAID levels, Hardware RAID and Software RAID differences, drive requirements, and operating systems. |
||
|
Configure RAID on Oracle Storage 12 Gb SAS PCIe RAID Host Bus Adapter, Internal 16 Port |
Information and procedures to configure RAID on Oracle Server X9-2L Host Bus Adapters (HBAs). Storage devices can connect to HBAs. You can use a BIOS utility to combine storage drives into RAID arrays. The Oracle Storage 12 Gb SAS PCIe RAID Host Bus Adapter, Internal 16 Port controls the HDDs and SSD drives, which are shipped with RAID 0 volumes. |
Oracle Storage 12 Gb SAS PCIe RAID HBA, Internal: 16 Port and 2 GB Memory Documentation |
|
3.84 TB U.2 NVMe SSDs 6.8 TB U.2 NVMe SSD |
You can install an operating system on an 3.84 and 6.8 TB U.2 NVMe SSDs without any additional configuration. Or, you can use the BIOS Setup Utility to configure these SSDs before installing an operating system. |
To learn more about 3.84 and 6.8 TB U.2 NVMe SSDs, refer to Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Card and NVMe SSD Documentation. |
|
Configure SATA RAID Using VROC 240 GB M.2 SATA SSD |
You can install an operating system on an M.2 SATA SSD without any additional configuration. Or, you can use the BIOS Setup Utility to configure these SSDs with Intel Virtual RAID On CPU (VROC) before installing an operating system. |
To learn more about 240 GB M.2 SATA SSDs, refer to 240 Gbyte, M.2 SATA, Solid State Drive Specification, 6 Gbps SATA-3 Interface Documentation . |
|
Identifying Installed Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Cards in BIOS Setup Utility |
Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Cards should be ready to install an OS without any additional configuration. You can use the BIOS Setup Utility to see a list of installed Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Cards. |
To learn more about Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Card v3, refer to Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Card and NVMe SSD Documentation |
|
After you have configured storage drives, you can install an operating system on them. |
Refer to operating system support information in Oracle Server X9-2 Product Notes and Oracle Server X9-2L Product Notes. |
Supported Storage Devices
Note:
Updated supported drive information is available in the server product notes.
Your server might be equipped with one of the following storage devices:
| Device | Description | Links |
|---|---|---|
|
Combination of U.2 small form factor (SFF) hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid state drives (SSDs) controlled by internal Host Bus Adapter (HBA) PCIe card. |
Oracle Storage 12 Gb SAS PCIe RAID Host Bus Adapter, Internal 16 Port manages the server's SSDs and HDDs. |
Instructions to configure RAID on the internal HBA: Configure RAID on Oracle Storage 12 Gb SAS PCIe RAID Host Bus Adapter, Internal 16 Port. |
|
6.8 TB U.2 NVMe SSDs 3.84 TB U.2 NVMe SSDs |
You can install an operating system on 6.8 TB and 3.84 TB NVMe SSDs without any additional configuration. 6.8 TB and 3.84 TB small form factor (SFF) NVMe solid state drive (SSD) boot devices do not support hardware RAID. |
U.2 NVMe SSD Documentation: Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Card and NVMe SSD Documentation. |
|
240 GB M.2 SATA SSDs |
The 240 GB M.2 SATA SSD supports software RAID. |
Instructions to configure RAID on M.2 SATA SSDs: Configure SATA RAID Using VROC. |
|
Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Cards |
You can install an operating system on Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Card v3: 6.4 TB, NVMe SSDs without any additional configuration. |
Instructions to identify Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Cards: Identifying Installed Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Cards in BIOS Setup Utility. |
RAID Overview
RAID (redundant array of independent disks) configures drives into logical units called "volumes." RAID configuration types are distinguished as numerical RAID levels (RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, and so forth). Each supported RAID level requires a specified number of storage devices to complete the array.
The following table lists drive quantity requirements for each supported RAID level.
| RAID Level | Number of Drives Required |
|---|---|
|
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
2 (SATA VROC) |
|
5 |
3 |
|
6 |
3 |
|
10 |
4 |
|
50 |
6 |
|
60 |
6 |
RAID types are Hardware RAID and Software RAID:
-
Hardware RAID - A Host Bus Adapter (HBA) manages the array and presents the volumes to the OS as simple disks. Hardware RAID unburdens the operating system, and is more robust than software RAID.
Oracle Storage 12 Gb SAS PCIe RAID Host Bus Adapter, Internal 16 Port HBA on your server supports hardware RAID. For instructions, see Configure RAID on Oracle Storage 12 Gb SAS PCIe RAID Host Bus Adapter, Internal 16 Port. To learn more about this HBA, refer to the Oracle Storage 12 Gb/s SAS PCIe RAID HBA, Internal Installation Guide.
Tip:
You can use Oracle Hardware Management Pack
raidconfigCLI commands to view and configure RAID storage (hardware RAID controllers only). Before usingraidconfigto create volumes (which will overwrite any existing data), use operating system tools to take an inventory of attached disks, their enumeration, and whether they contain data that you want to preserve. -
Software RAID - The operating system manages the array, which is created and configured using an OS or utility. In a typical use case, you boot an OS on one device to create a software RAID volume on a different device. For details, refer to the instructions in your operating system documentation. See Installing an Operating System.
Note the following conditions:
-
Your server might have other storage devices where you can install an operating system as well. These might or might not support or require RAID; however, if you do configure a RAID volume on these devices, you must do so before installing an OS. For instructions, refer to the documentation for the device, and Installing an Operating System.
-
The UEFI BIOS utility in your server does not display items in the boot list until after an operating system is installed on the storage device and then the server is booted. This is unlike older BIOS utilities that display devices where you can install an OS. To see devices where you can install an OS, you have to use an OS installation program.
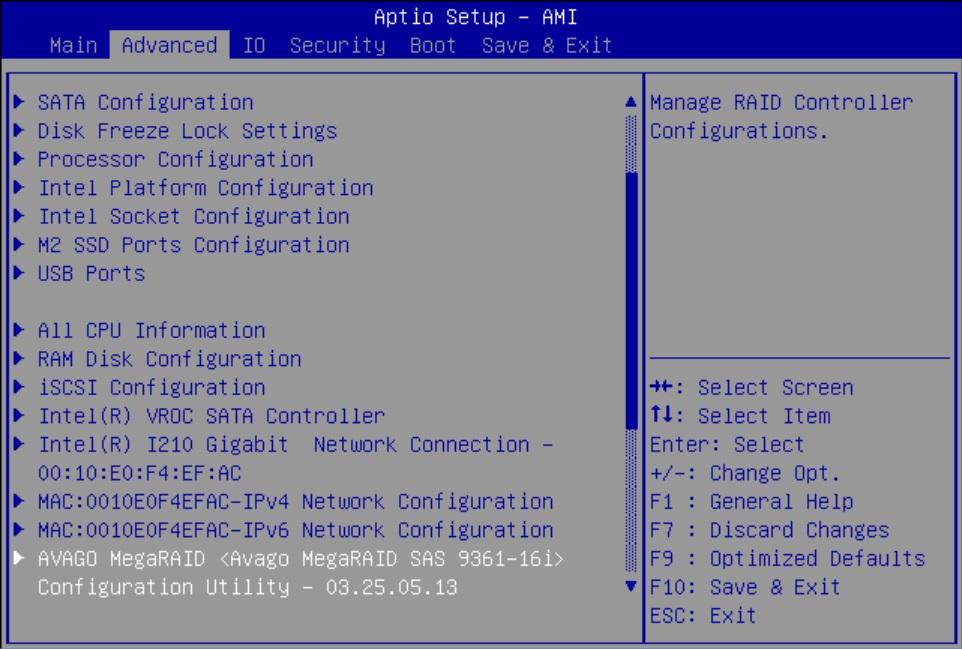
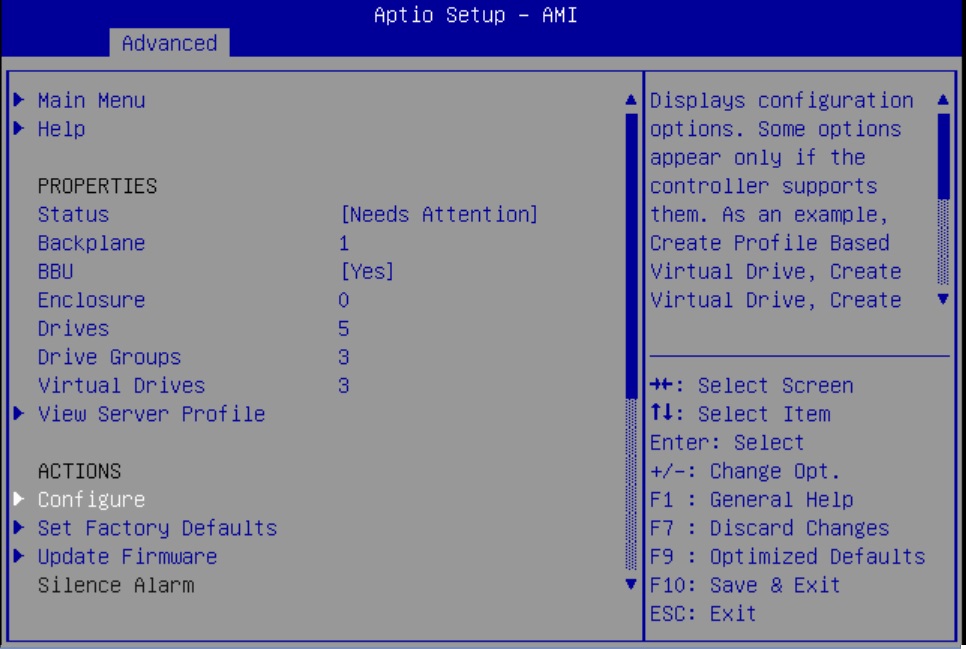
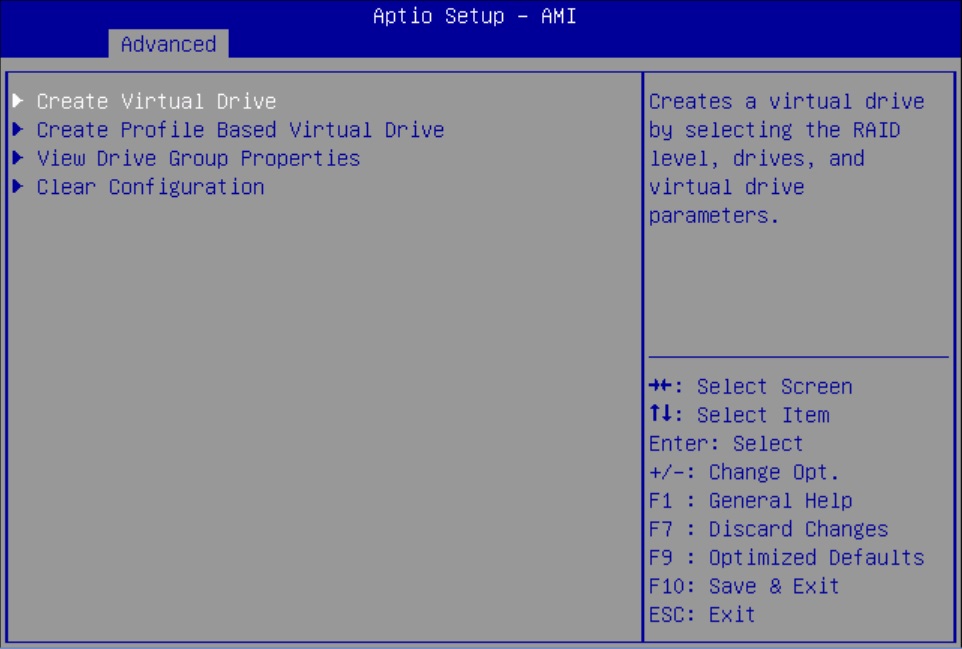
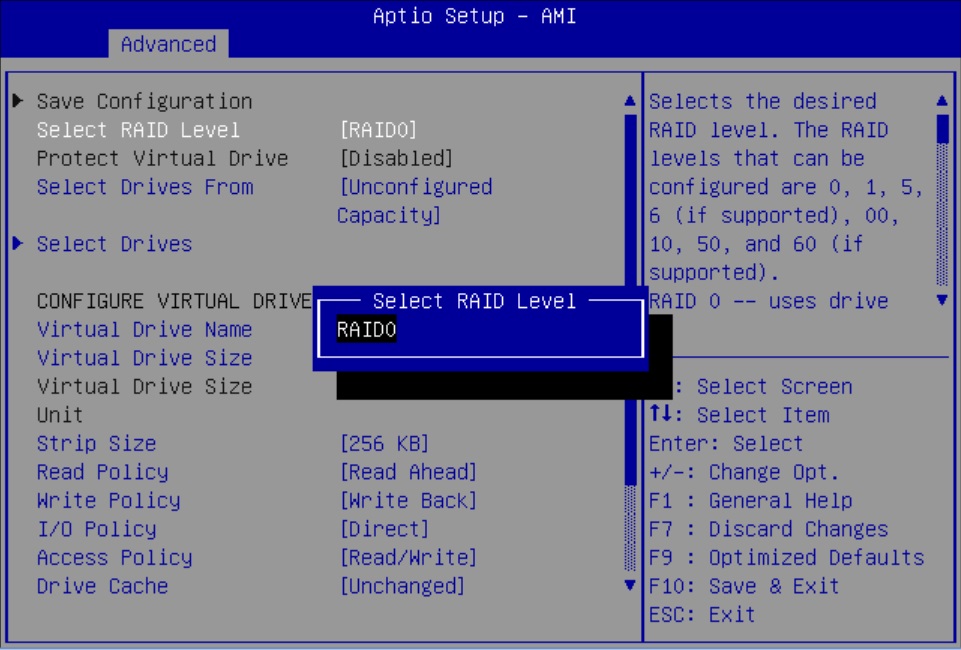
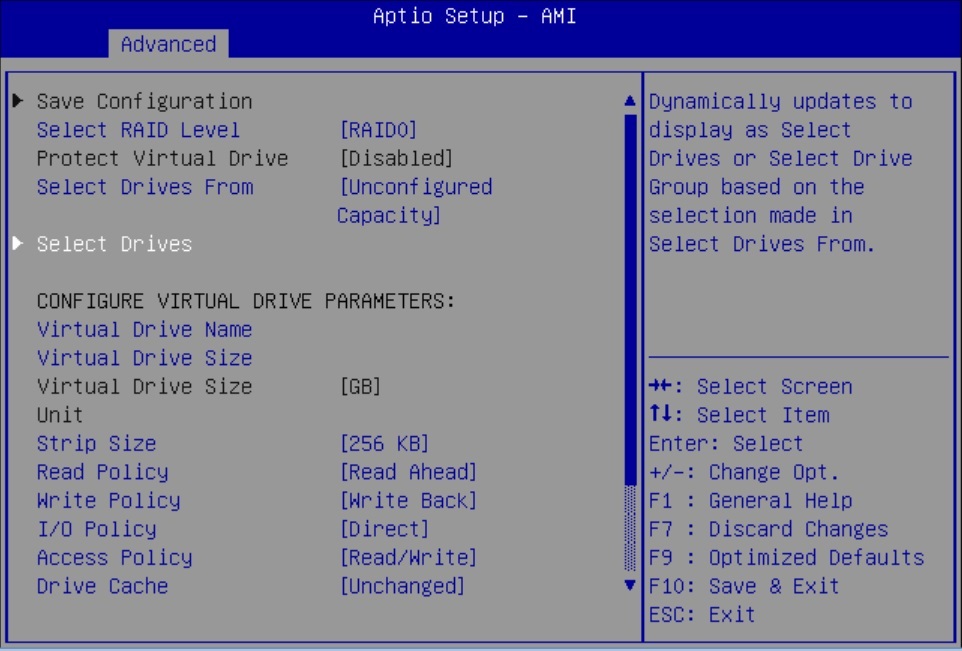
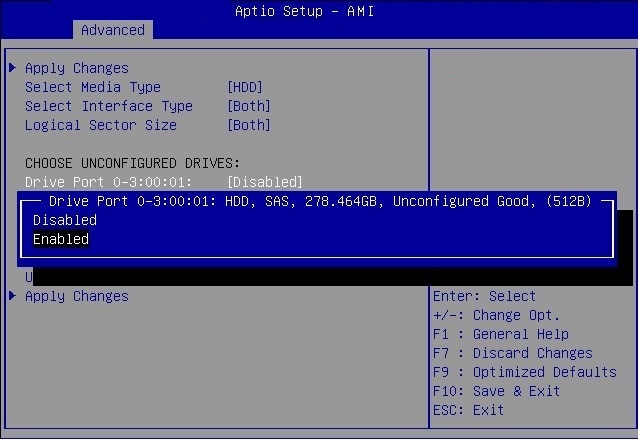
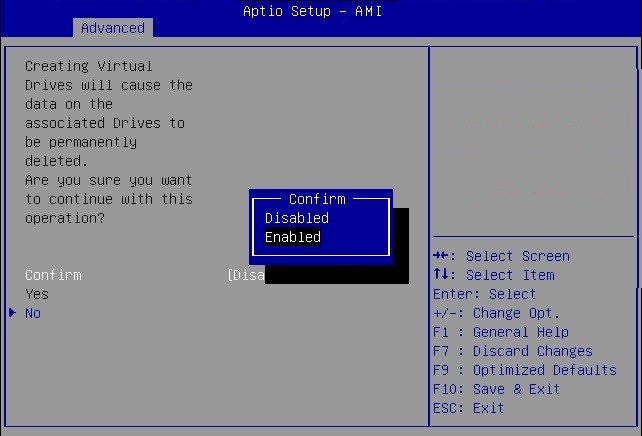
Configure RAID on Oracle Storage 12 Gb SAS PCIe RAID Host Bus Adapter, Internal 16 Port
Some devices, including Oracle Storage 12 Gb SAS PCIe RAID Host Bus Adapter, Internal 16 Port, must include a RAID volume before they can present a valid target for operating system installation programs.
The server is shipped with Oracle Storage 12 Gb SAS PCIe RAID Host Bus Adapter, Internal 16 Port configured as RAID 0 volumes, meaning that each volume includes a single disk drive. Other volumes combine multiple disks into arrays, which can increase performance and provide redundancy.
Oracle Storage 12 Gb SAS PCIe RAID Host Bus Adapter, Internal 16 Port manages the HDDs and SSDs in your system. When the system is shipped, the HDD and SSD drives are configured into RAID 0 volumes. Use this procedure to reconfigure these drives into RAID volumes according to your performance and redundancy needs.
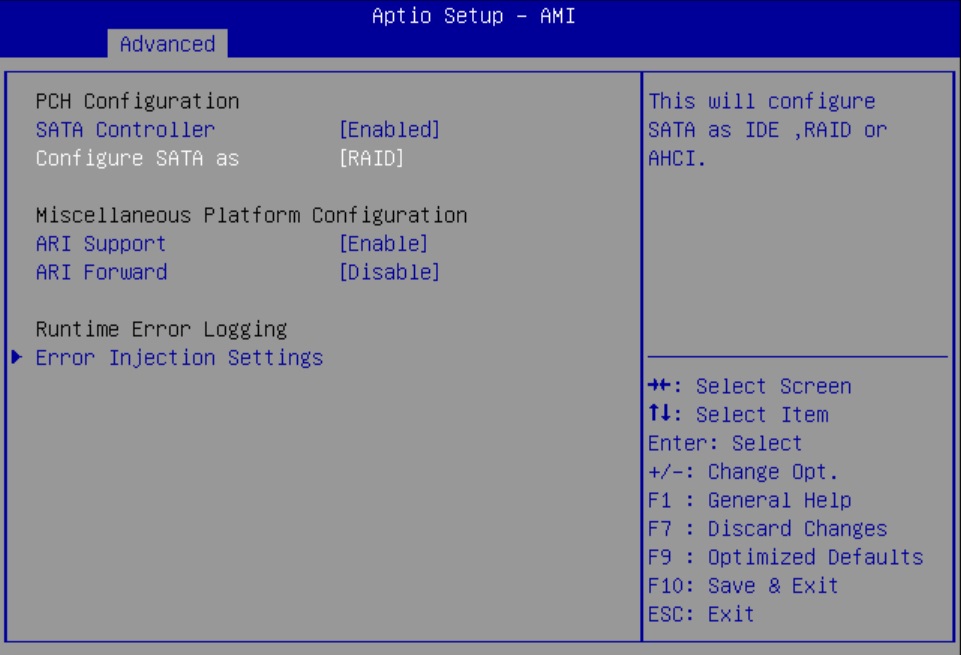
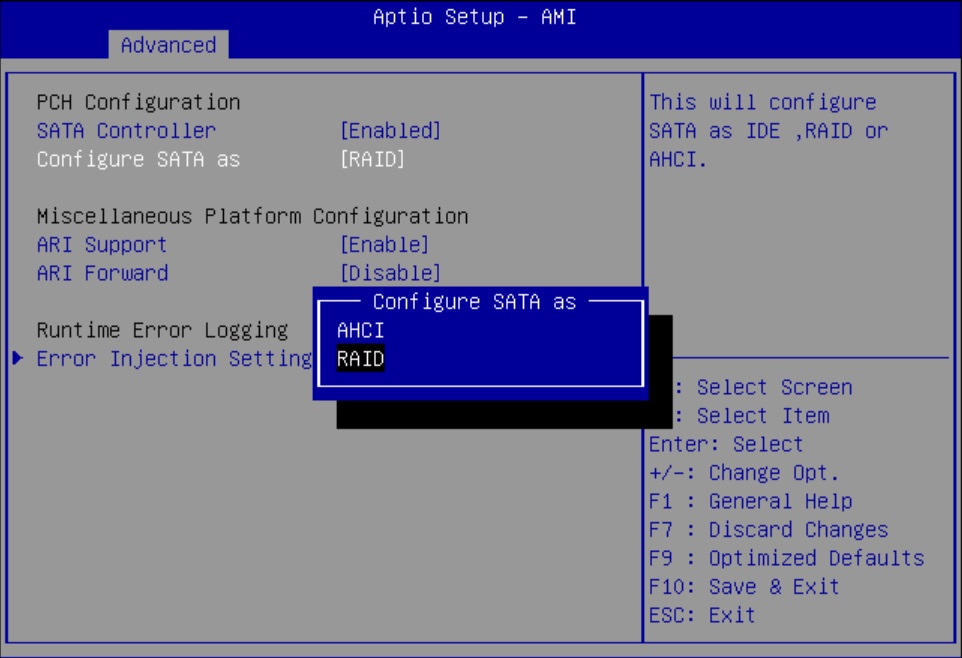
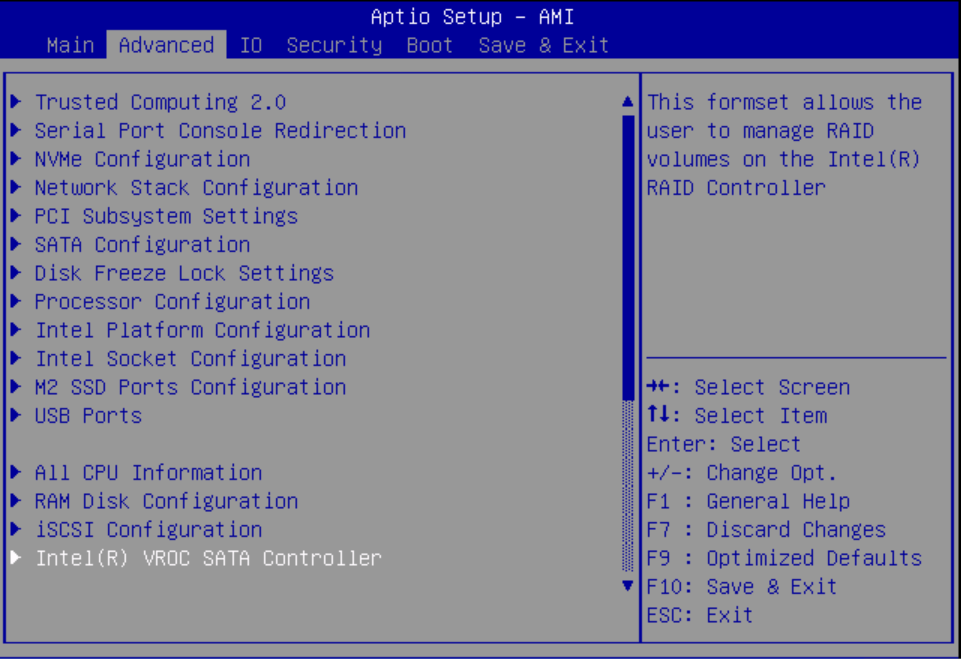
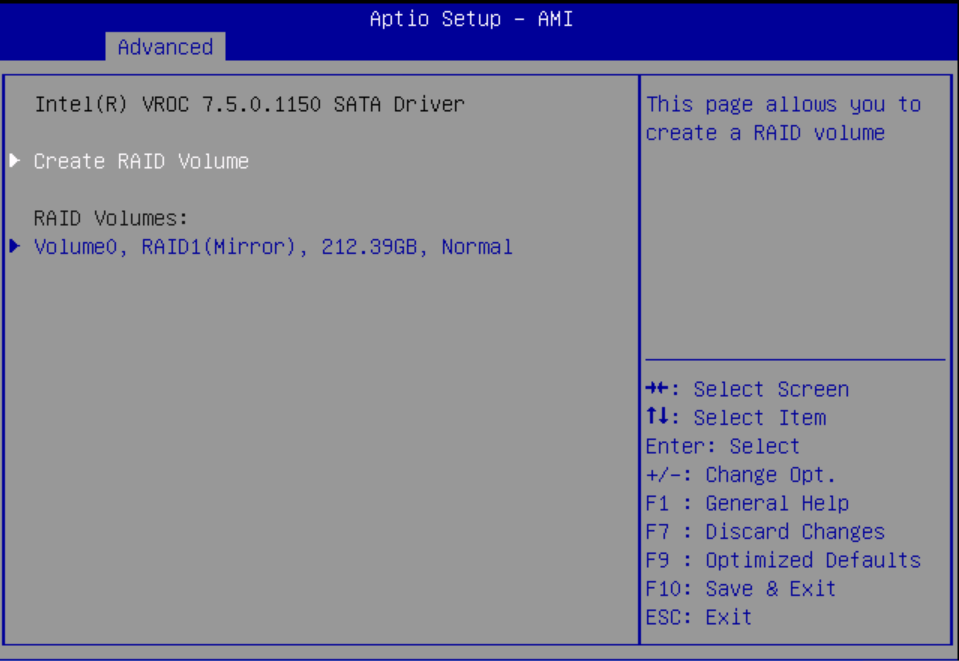
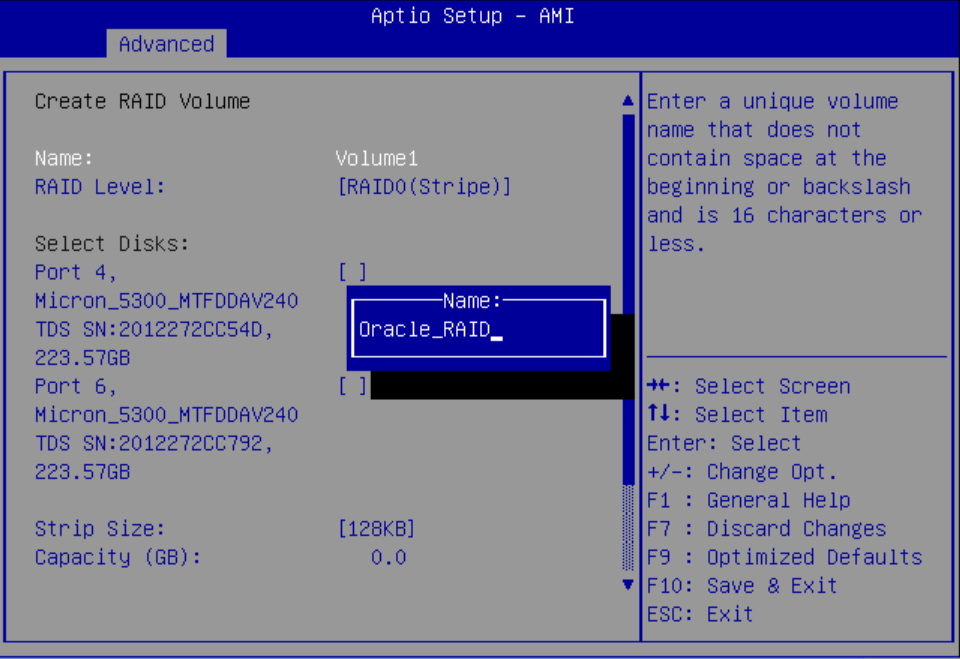
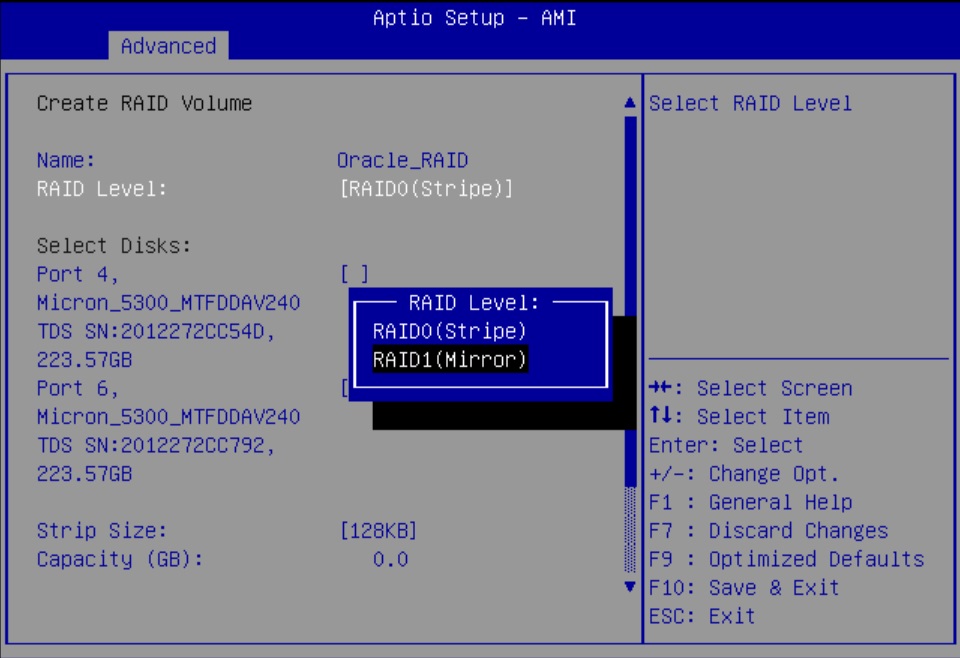
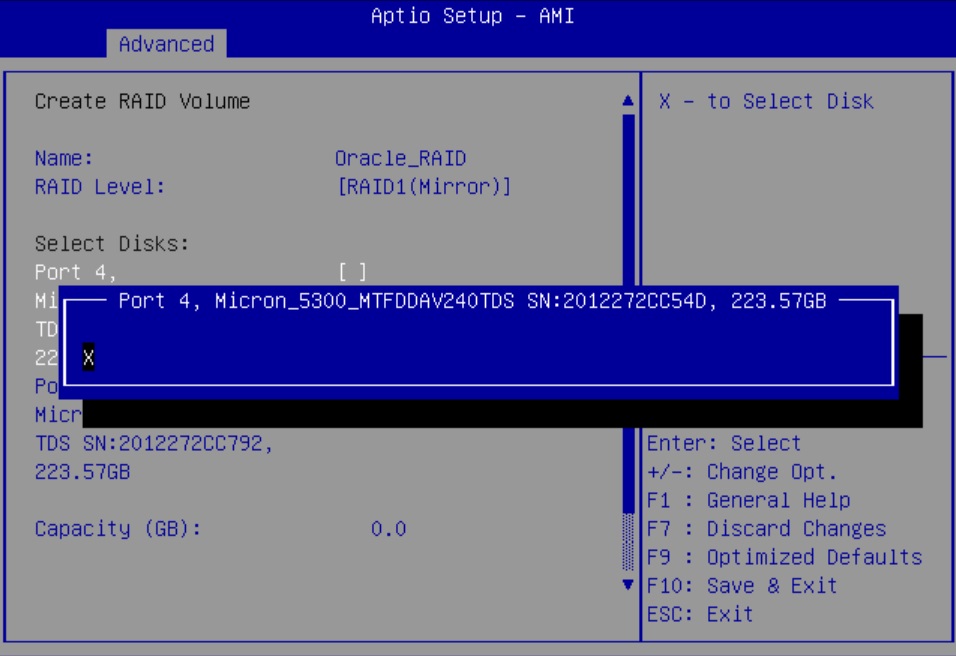
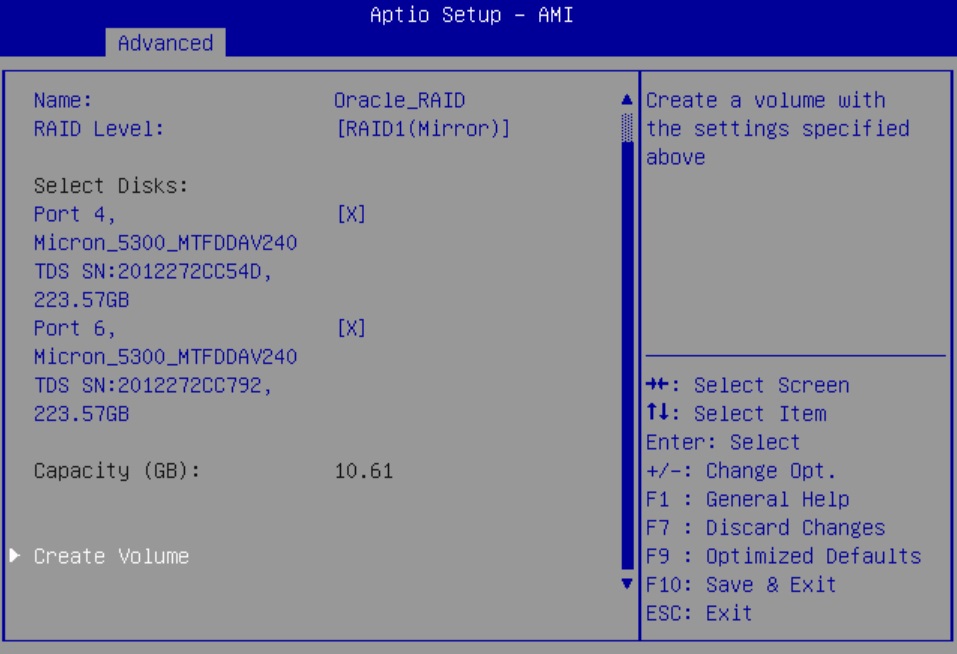
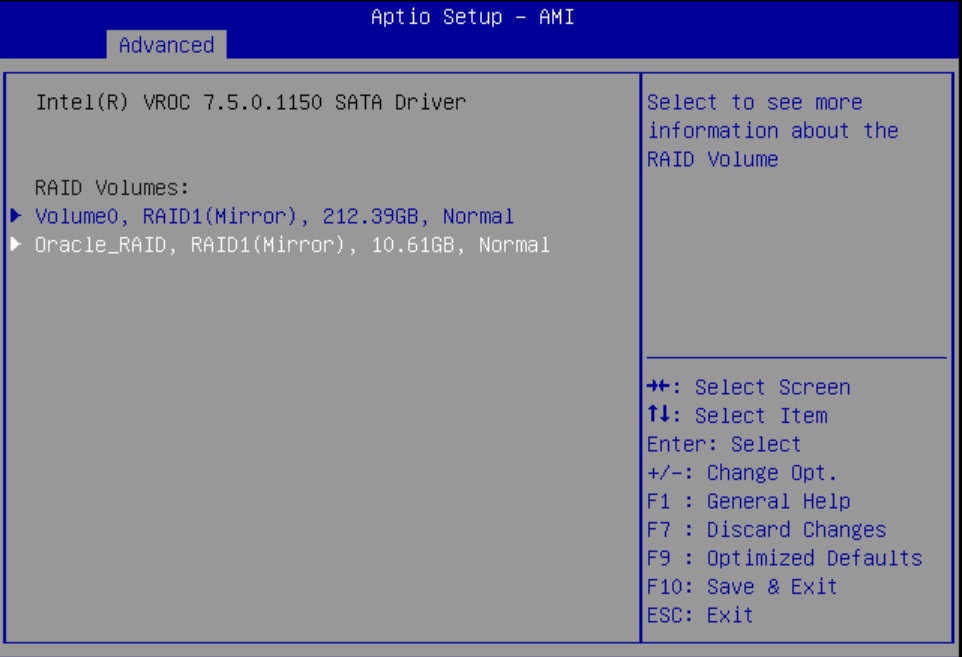
Configure SATA RAID Using VROC
This procedure configures a RAID volume so that you can install an operating system. You can create and manage RAID arrays on Oracle Server X9-2 and Oracle Server X9-2L SATA M.2 SSDs using Intel Virtual RAID On CPU (VROC), which provides the following benefits:
-
Use SATA drives to their full potential
-
Fewer hardware queues
-
Bootable RAID
-
Hot Insert/Surprise removal
Note:
This procedure applies only to Oracle Server X9-2 and Oracle Server X9-2L with Oracle Linux and installed SATA M.2 SSD boot devices. Microsoft Windows, VMware ESXi, and Oracle Solaris do not support VROC on Oracle Server X9-2 and Oracle Server X9-2L.
Intel VROC (SATA RAID) provides an enterprise RAID solution for SATA devices connected to the Intel Platform Control Hub (PCH) configured for RAID mode. Virtual RAID on CPU (Intel VROC) is an enterprise, hybrid RAID solution, specifically designed for SATA SSDs connected directly to the CPU. Intel VROC is made possible by the new CPU feature Intel Volume Management Device, Intel VMD, a new hardware architecture on Intel Xeon Scalable Processors.
Identifying Installed Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Cards in BIOS Setup Utility
You can install an operating system on an Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Cards without any additional configuration. All installed Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Card controllers (two per card) are visible to an OS installer program.
This task uses the BIOS Setup Utility to list all installed Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Cards.
Note:
Each Oracle Flash Accelerator F640 PCIe Card supports two 3.2TB drives, each with its own controller. These appear in the BIOS Setup Utility, and in OS installation programs as two separate 3.2TB drives.