Deploy an Oracle API Gateway Service in a Hybrid Environment
Architecture
This architecture depicts an on-premises customer data center and an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) region with a compartment and two availability domains that use an API Gateway server to provide a public internet access environment.
The on-premises customer data center leverages the API gateway for planning, creating, prototyping, deploying, and managing API's in an secure and scalable environment. The on-premises environment can be a private API environment or can be part of a public API environment where API's can be shared with the public Internet.
The API Gateway serves as an API Designer portal and an Developer portal. The API Designer is where API designers create, test, deploy, and manage their API's, the Developer portal is where API consumers can view the API's, API documentation, and try APIs.
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.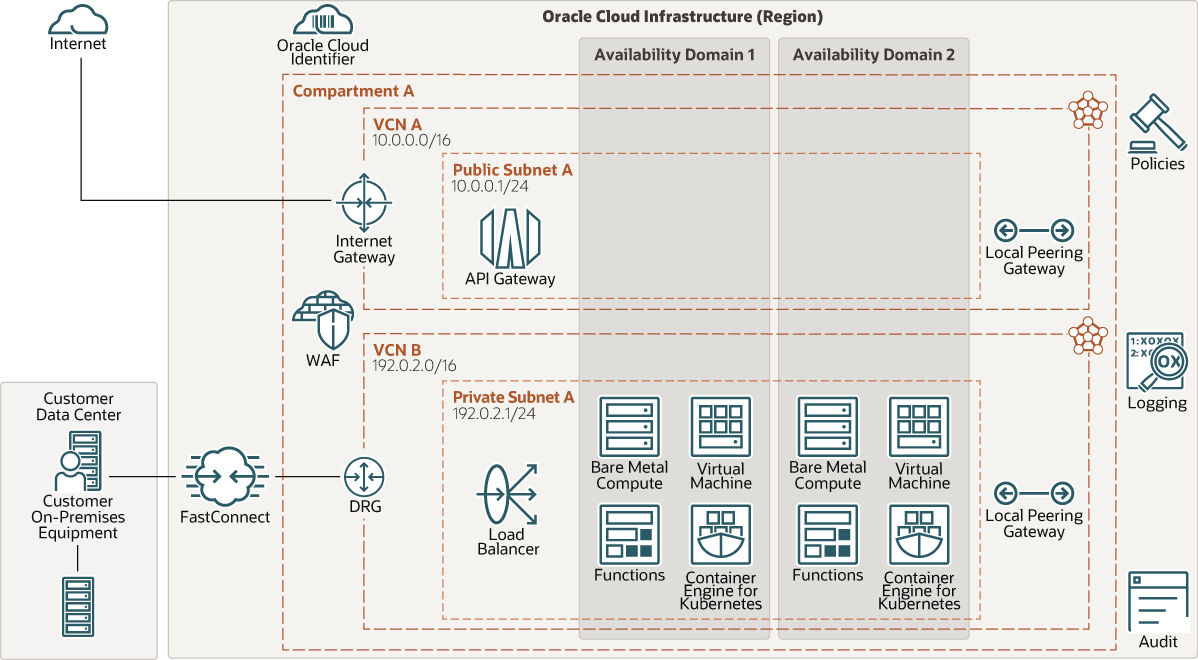
Description of the illustration api-gateway-hybrid.png
The architecture has the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domains
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- FastConnect
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect provides an easy way to create a dedicated, private connection between your data center and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Web
Application Firewall (WAF)
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Web Application Firewall is a cloud-based, Payment Card Industry (PCI) compliant, global security service that protects applications from malicious and unwanted internet traffic. WAF can protect any internet- facing endpoint, providing consistent rule enforcement across a customer's applications.
- Internet gateway
The internet gateway allows traffic between the public subnets in a VCN and the public internet.
- Load balancer
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancing service provides automated traffic distribution from a single entry point to multiple servers in the back end.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- Local peering gateway (LPG)
An LPG enables you to peer one VCN with another VCN in the same region. Peering means the VCNs communicate using private IP addresses, without the traffic traversing the internet or routing through your on-premises network.
- API gateway
The API Gateway service enables you to publish APIs with private endpoints that are accessible from within your network, and which you can expose to the public internet if required. The endpoints support API validation, request and response transformation, CORS, authentication and authorization, and request limiting.
Recommendations
- VCN
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks.
When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.
Use regional subnets.
- Security
Use Oracle Cloud Guard to monitor and maintain the security of your resources in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure proactively. Cloud Guard uses detector recipes that you can define to examine your resources for security weaknesses and to monitor operators and users for risky activities. When any misconfiguration or insecure activity is detected, Cloud Guard recommends corrective actions and assists with taking those actions, based on responder recipes that you can define.
For resources that require maximum security, Oracle recommends that you use security zones. A security zone is a compartment associated with an Oracle-defined recipe of security policies that are based on best practices. For example, the resources in a security zone must not be accessible from the public internet and they must be encrypted using customer-managed keys. When you create and update resources in a security zone, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure validates the operations against the policies in the security-zone recipe, and denies operations that violate any of the policies.
Considerations
When deploying an Oracle API Gateway, consider the following:
- Performance
You can optimize API Gateway performance using various configuration options. For example, general performance tuning options include tracing, monitoring, and logging. More advanced performance tuning options include database pooling, HTTP keep alive, chunked encoding, client threads, and Java memory.
- Security
Use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management policies to control who can access your cloud resources and what operations can be performed.
To protect the passwords or any other secrets, consider using the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Vault service.
- Availability
Consider using a high-availability option based on your deployment requirements and your region. The options include distributing resources across multiple availability domains in a region, and distributing resources across the fault domains within an availability domain.
Fault domains provide the best resilience for workloads deployed within a single availability domain. For high availability in the application tier, deploy the application servers in different fault domains, and use a load balancer to distribute client traffic across the application servers.