Understand Deployment Architecture
The following figure shows how Oracle Cloud VMware Solution is designed and deployed in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, and its integration with other services running natively in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
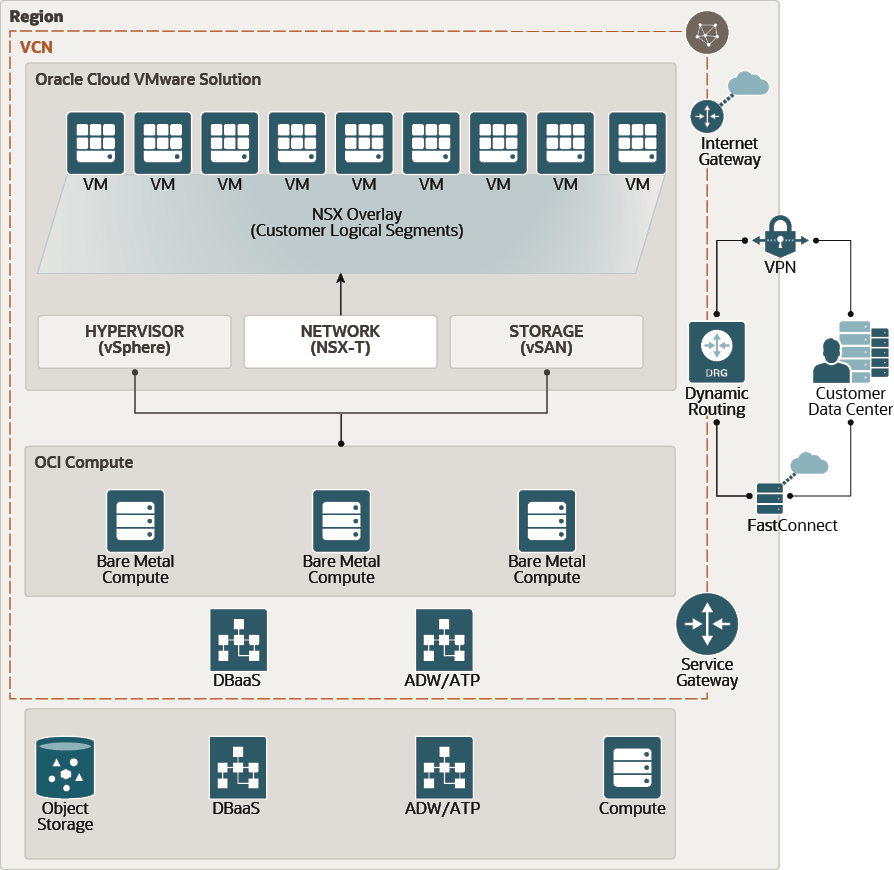
Description of the illustration ovcs_architecture.pngThe Oracle Cloud VMware Solution architecture comprises the following key components, discussed in detail below:
- Compute (vSphere and ESXi)
- Network (VCN and NSX-T)
- Storage (vSAN)
Understand Compute Architecture (vSphere and ESXi)
- 156–3328 OCPUs
- 2.25–48 TB memory
- 153–3264 TB raw storage
Understand Networking Architecture (VCN and NSX-T)
- NSX Manager and Controller
- NSX Edge
The bare metal instances used for the SDDC are backed by 2x25-Gbps network bandwidth and support 52 VNICS (26 per physical NIC), which ensures high throughput, low latency, and a fully redundant network.
Understand Storage Architecture (vSAN)
Oracle Cloud VMware Solution includes vSAN storage technology that provides a single shared datastore (vsanDatastore) for compute and management workloads (VMs). Each SDDC uses an “all flash” vSAN storage solution built on NVMe-backed bare metal instance storage that offers high performance, low latency, and robust block storage capability without the need of traditional SAN.
vSAN implements fault domains, which are different from Oracle Cloud Infrastructure fault domains. vSAN fault domains let vSAN group multiple hosts (typically within the same chassis or rack) into a logical boundary domain. The fault domains setting ensures that multiple replica copies of storage objects are distributed across the domains. If an entire domain (chassis or rack) fails, only one replica is affected.
vSAN storage policies are used to determine the high availability of individual VMs. You can configure different policies in Oracle Cloud VMware Solution to determine the number of host and device failures that a VM can tolerate.