Deploy a Cross-Region Disaster Recovery Solution Using RackWare
If a large-scale outage affects your production applications, you need the ability to restore the workloads quickly. RackWare Management Module (RMM) is an automated disaster recovery (DR) tool that handles the process of migrating existing workloads across different data centers and clouds, creating an exact duplicate of a running image without needing to rebuild or recreate template images and applications.
Your business continuity plan should include a strategy that meets your recovery point, recovery time, and budget objectives. Maintaining business continuity and ensuring IT resiliency is a top priority for IT leaders today. Instead of maintaining replicated DR environments in data centers, companies are increasingly looking at the cloud to avoid up-front infrastructure costs and ability to scale as per their needs.
RMM’s software platform delivers a suite of intuitive and automated services that provide IT resiliency and simplified migration to the cloud, while reducing capital and operating expenses. RMM decouples the application stack from the underlying platform allowing it to be ported to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. RMM includes discovery, analysis and automation features allowing all processes to be fast, easy and error-free.
Architecture
This architecture implements a disaster revovery strategy based on RackWare Management Module.
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
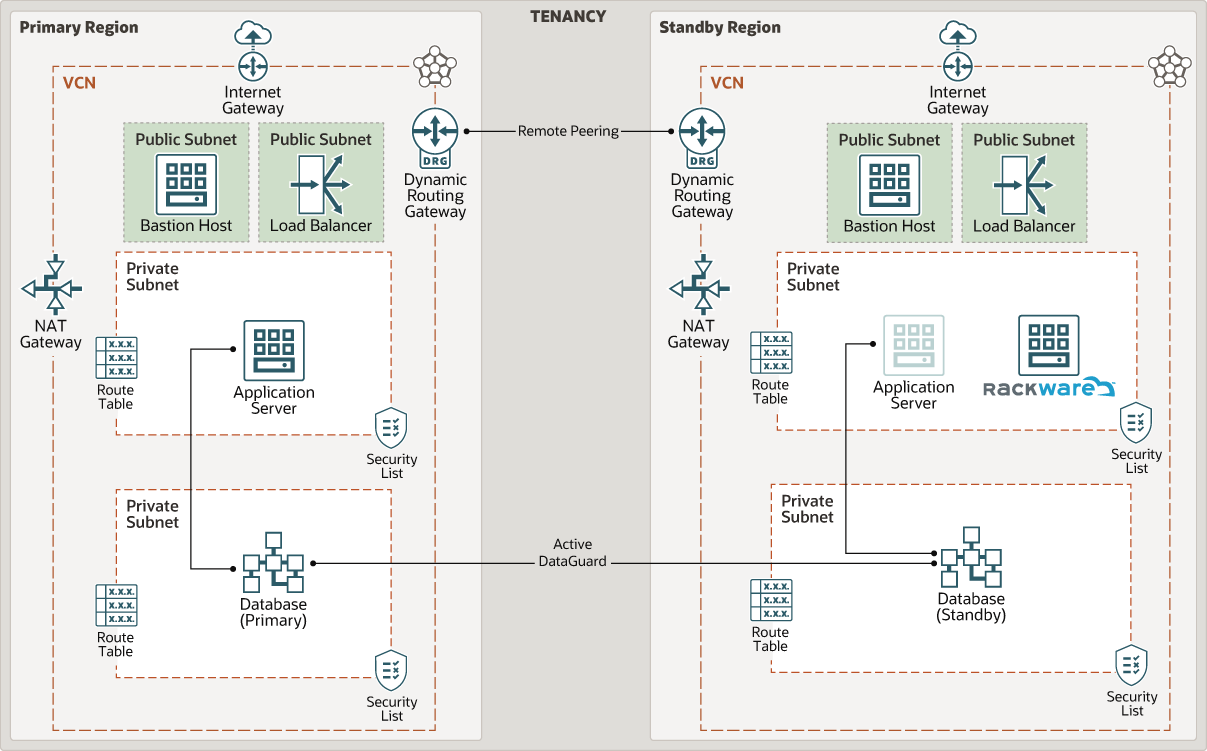
Description of the illustration rackware_oci_architecture.png
The architecture has the following components:
- Tenancy
A tenancy is a secure and isolated partition that Oracle sets up within Oracle Cloud when you sign up for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. You can create, organize, and administer your resources in Oracle Cloud within your tenancy.
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Bastion host
The bastion host is a compute instance that serves as a secure, controlled entry point to the topology from outside the cloud. The bastion host is provisioned typically in a demilitarized zone (DMZ). It enables you to protect sensitive resources by placing them in private networks that can't be accessed directly from outside the cloud. The topology has a single, known entry point that you can monitor and audit regularly. So, you can avoid exposing the more sensitive components of the topology without compromising access to them.
- Load balancer
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancing service provides automated traffic distribution from a single entry point to multiple servers in the back end.
- Internet Gateway
The internet gateway allows traffic between the public subnets in a VCN and the public internet.
- NAT Gateway
The NAT gateway enables private resources in a VCN to access hosts on the internet, without exposing those resources to incoming internet connections.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- Route table
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Rackware
In this architecture, RMM discovers application server VM in the primary region and provisions an exact replica in the standby region.
- Active DataGuard
DataGuard provides the management, monitoring, and automation software to create and maintain one or more synchronized copies of a production database to protect Oracle data from failures, disasters, human error, and data corruptions while providing high availability for mission critical applications.
Considerations
When deploying a cross-region disaster recovery solution using Rackware, consider these options.
- RPO/RTO/Cost Options and Tradeoffs
Use this table to determine which provisioning option best meets your requirements:
Option Tradeoff Dynamic Provisioning - Target VMs NOT pre-provisioned
- Provisioned at DR event
Lowest cost
Longest RTO
Pre-Provisioned at Reduced Footprint - Pre-provision some/all VMs at smaller HW spec
Medium cost
Better RTO
Pre-Provisioned – Images Kept Offline - Sync’ing storage in VM
- Does not incur OS licensing costs
Medium cost
Even Better RTO
Pre-Provisioned – Production Equivalent Pre-provision some/all VMs at full HW spec
Highest cost
Best RTO
- DeploymentUpon deployment, the following occurs:
- RackWare replicates production environment to the DR site.
- RMM discovers hosts.
- RMM performs live capture of workload.
- RMM assigns applications in the DR site.
- The sync policy is set.
- The policy is configurable: hourly, daily, weekly, etc. or per defined schedule.
- Multiple policies can be configured and applied.
- The policies allow Automatic sync and alerts.
- Provisioning options are determined; you can either:
- Pre-provision VMs (hot stand-by).
- Dynamically provision VMs – Sync to storage (low cost).
- RackWare replicates production environment to the DR site.
Recommendations
- VCN
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks.
When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.
- Infrastructure
Use Terraform to set up a similar infrastructure (VCN, Subnet, Security Lists, Route Table, Gateways) in both the source and destination regions.
- Data replication Set up Oracle database data replication from the production site to the DR site with Oracle Data Guard or Active Data Guard. Oracle recommends that you do not use storage replication technology to provide disaster protection for Oracle databases. Data Guard and Active Data Guard provide greater data protection and availability than you can obtain by using storage technologies alone. Many enterprises have been replacing array mirroring with Active Data Guard for their business critical databases because it provides:
- Superior Isolation and is bandwidth efficient
- Continuous Oracle Data validation
- Automatic repair
- Lower Cost, higher ROI
- Rackware Storage methods
Choose one of these two storage methods for DR:
- Store and forward—This method creates an image of
your source workload in storage on the RMM’s database. To take advantage
of point-in-time snapshots for backup functionality, you must choose
this method. Store and forward requires block storage on RMM, as
described in the following example:
- Source Host01: 100 GB used data across all disks
- Source Host02: 200 GB used data across all disks
- Source Host03: 50 GB used data across all disks
Total used data = 350 GB
The typical compression ratio for storage is 1.5x to 2x.
In this scenario, as a starting point, we recommend that you create a 350 / 1.5 = 234GB datastore on the RMM. You can add additional storage to the storage pool at any time.
- Passthrough—This method does not require additional block storage. With the Passthrough method, RMM does not store a copy of the used data from source hosts but acts as a passthrough proxy to sync the source workload data through itself and onto the target DR instances.
- Store and forward—This method creates an image of
your source workload in storage on the RMM’s database. To take advantage
of point-in-time snapshots for backup functionality, you must choose
this method. Store and forward requires block storage on RMM, as
described in the following example:
Explore More
Learn more about RackWare Management Module.
Review these additional resources:
- To learn how to leverage RMM technology on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure to create disaster recovery solutions, try the Disaster Recovery RackWare Deployment on OCI Workshop.
- To deploy RMM for the first time, see Rackware RMM Getting Started for Oracle Marketplace 2.0.