Learn About Disaster Recovery to Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer
A disaster recovery architecture requires a distributed deployment. A topology where applications, databases, and object storage, are deployed across Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer, or between two OCI on-premises (same or remote data centers).
In an OCI to on-premises architecture, the cloud portion of a distributed deployment serves as the production environment or active site, and the on-premises deployment as a failover or secondary site or passive or standby site for production continuity. In an on-premises to on-premises solution, you must configure one OCI on-premises as the active site, and the second on-premises OCI as a passive or standby site.
This solution enables architects and system administrators to implement disaster recovery from OCI to Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer or between Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer racks using Oracle tools and Rackware.
Note:
This content is provided for informational purposes and self-supported guidance only. Consultancy or other assistance related to the content is not covered under the Oracle Support contract or associated service requests. If you have questions or additional needs, then please reach out to your Oracle Sales contact directly.About Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer
Use Compute Cloud@Customer to deploy Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services on-premises to meet data sovereignty and regulatory requirements, while using OCI's identity and governance services to manage access to them. Maintain absolute control over your data while leveraging the capabilities of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) managed by Oracle.
Identical APIs and management tools as OCI enable you to create a consistent development experience across environments while retaining complete control over data to meet evolving data residency and latency requirements. Compute Cloud@Customer enables workload consolidation and operation streamlining at a low cost with a flexible consumption model like the public cloud.
Before You Begin
Review the Configure a standby database for disaster recovery solution to configure Oracle Data Guard for any of the three disaster recovery methods and use it to automate most of these actions. You will learn to configure Data Guard by setting up a standby database for an existing primary database and make use of the restore from service Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) feature and Data Guard Broker.
Then, download Oracle Cloud Marketplace Rackware Migration Manager.
Additionally, review these resources:
- Oracle Database Installation Guide for Linux.
-
If you would like to use Oracle GoldenGate, then see the Oracle GoldenGate installation and configuration documentation to setup replication from Oracle Autonomous Database running on OCI to on-premises environment.
Depending on your Oracle support plan, you can download Oracle Database from the following locations:
Architecture
The three most popular disaster recovery strategies are Backup and Restore, Pilot Light, and Warm Standby.
The following is the architecture for a disaster recovery from OCI to Compute Cloud@Customer that can be used for the three strategies: Backup and Restore, Pilot Light, and Warm Standby:
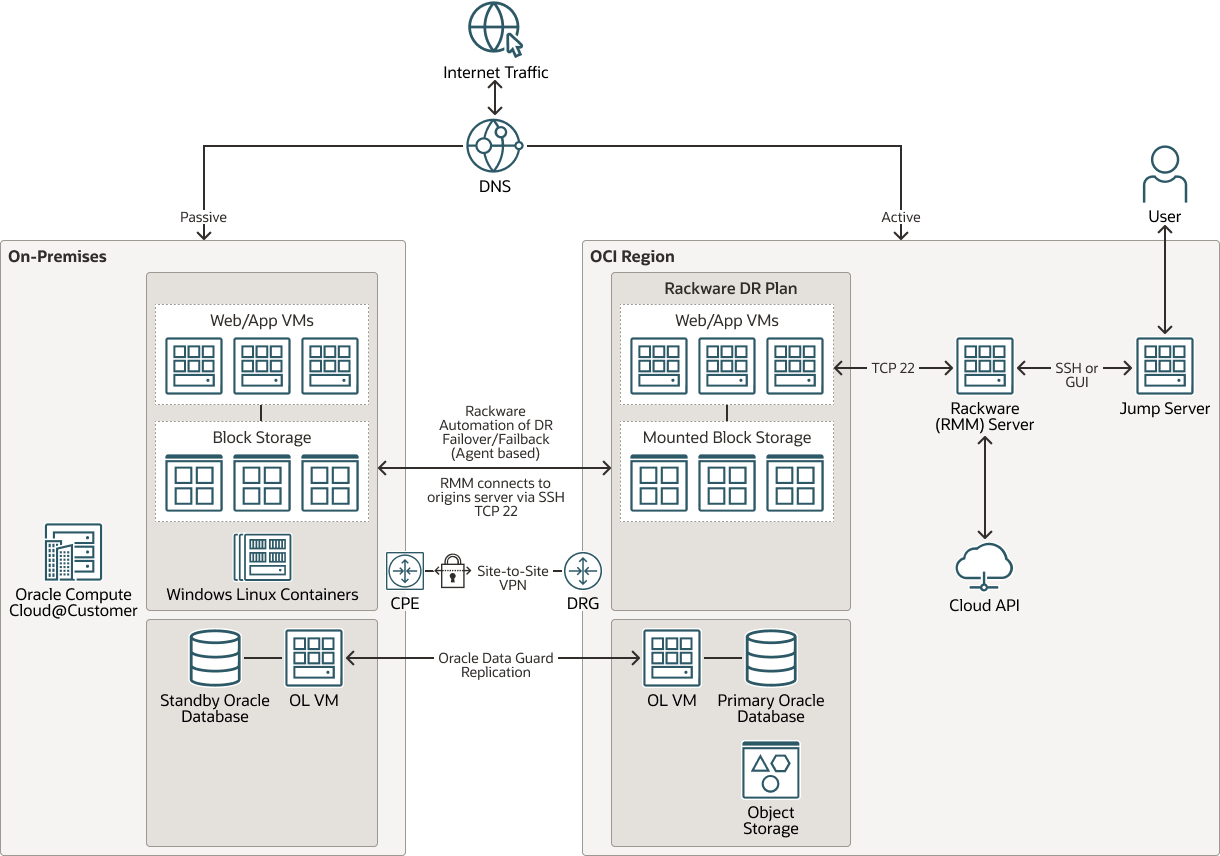
Description of the illustration dr-oracle-compute-cloud-customer-oci.png
dr-oracle-compute-cloud-customer-oci-oracle.zip
The following is the architecture for a disaster recovery between Compute Cloud@Customer racks.
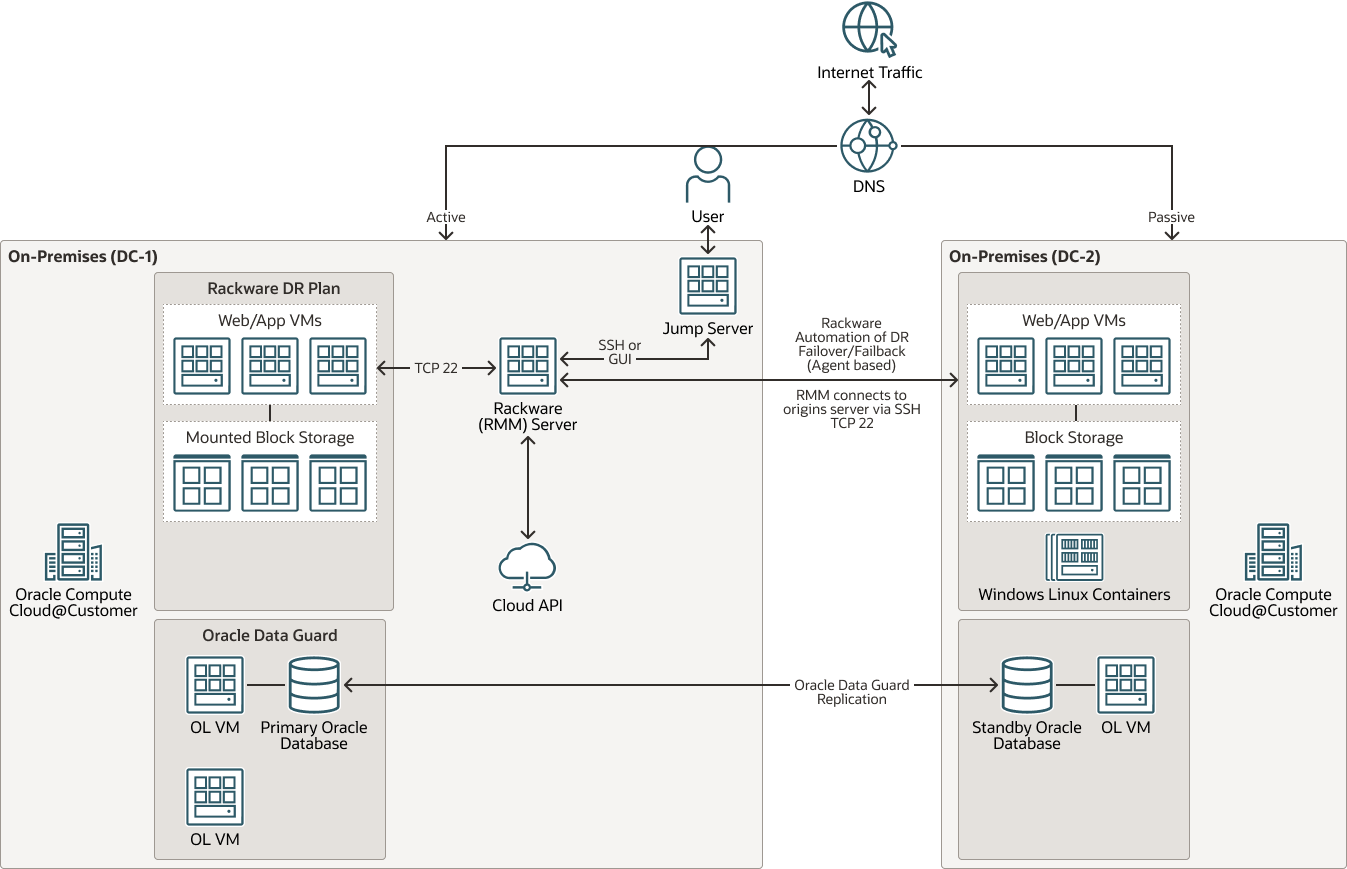
Description of the illustration dr-compute-cloud-customer-racks.png
dr-compute-cloud-customer-racks-oracle.zip
These architectures support the following components:
- OCI Site-to-Site VPN
OCI Site-to-Site VPN provides IPSec VPN connectivity between your on-premises network and VCNs on OCI. The IPSec protocol suite encrypts IP traffic before the packets are transferred from the source to the destination and decrypts the traffic when it arrives.
- OCI Object Storage
OCI Object Storage provides access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store data directly from applications or from within the cloud platform. You can scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability.
Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
- Oracle Data Guard
Oracle Data Guard and Active Data Guard provide a comprehensive set of services that create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby databases and that enable production Oracle databases to remain available without interruption. Oracle Data Guard maintains these standby databases as copies of the production database by using in-memory replication. If the production database becomes unavailable due to a planned or an unplanned outage, Oracle Data Guard can switch any standby database to the production role, minimizing the downtime associated with the outage. Oracle Active Data Guard provides the additional ability to offload read-mostly workloads to standby databases and also provides advanced data protection features.
- Dynamic routing gateway
(DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between VCNs in the same region, between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another OCI region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
Considerations
When configuring disaster recovery from Compute Cloud@Customer to OCI, consider these strategies:
- Backup and Restore
Compute Cloud@Customer can be deployed as a backup and restore solution for your workload running in OCI. This strategy is recommended for low priority workloads, development, and test environments where Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) can support hours. Since all resources such as instances and block volumes can be provisioned after the disaster recovery, in this architecture, a backup and restore solution is considered a lowest cost solution for disaster recovery.
- Pilot Light
If a large-scale outage affects your production applications, you will need the ability to restore the workloads quickly. Your business continuity plan should include a disaster recovery strategy that meets your recovery point, recovery time, and budget objectives. A pilot-light topology offers a balance between cost and recovery requirements.
The term pilot light refers to a small flame that is always lit in devices such as gas-powered heaters and can be used to start the devices quickly when required. In the context of disaster recovery, a pilot-light environment contains the core components of a given workload, with the latest configuration and critical data, running at a minimal scale at a location that's remote from the primary site. In the event of a disaster at the primary site, you can use the pilot-light components at the remote location to restore a production-scale environment quickly.
- Warm Standby
Configure the same configuration, version, and quantity of virtual machines running in the production environment as the disaster recovery site. The virtual machines are constantly replicated by a Rackware Oracle Database in continuum from OCI to Compute Cloud@Customer, and Oracle Database Sync configured with continuum replication.
About Required Services and Roles
This solution requires the following services and roles:
-
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
-
Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer
-
Oracle Data Guard
-
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage
- Oracle Linux 7.x and 8.x
- Oracle Database 19C
- Rackware Management Module (RMM)
These are the roles needed for each service.
| Services Name: Role | Required to... |
|---|---|
Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure: sysdba |
Close, shutdown, and unmount the standby database in the cloud. |
Oracle Data Guard: SYS, SYSDG, or SYSDBA |
Run the Oracle Data Guard command-line interface (DGMGRL) to convert the standby to a snapshot standby and switch the primary and standby database roles.
|
| OCI: Administrator | Complete access to resources such as compute, network, observability and management services, including the configuration of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage utilized by this solution. |
| OCI: Security administrator | Inspect access to resources such as compute, network, and complete access to observability and management services. |
Oracle Database: root |
Configure the primary and standalone database, instantiate and configure the standby database. |
| Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer: Administrator | User on Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer with Administrator permissions to configure and deploy Oracle Linux Instances, complete access to resources such as compute, network, observability and management services. |
See Oracle Products, Solutions, and Services to get what you need.