Deploy Exadata Database Service with Oracle Data Guard in Multiple Regions
Deploy secure, high-performance computing in multiple Oracle Cloud regions using Oracle Exadata Database Service and Oracle Data Guard.
Maintaining business continuity and ensuring IT resiliency is a top priority for IT leaders today. Instead of maintaining replicated disaster recovery environments in data centers, companies are increasingly looking at the cloud to avoid up-front infrastructure costs and for the ability to scale to their needs.
If a large-scale outage affects your production applications, you need the ability to restore the workloads quickly. Oracle Data Guard ensures high availability, data protection, and disaster recovery for enterprise data. If the production database becomes unavailable because of a planned or an unplanned outage, Oracle Data Guard can switch any standby database to the production role regardless of its region, minimizing the downtime associated with the outage.
Architecture
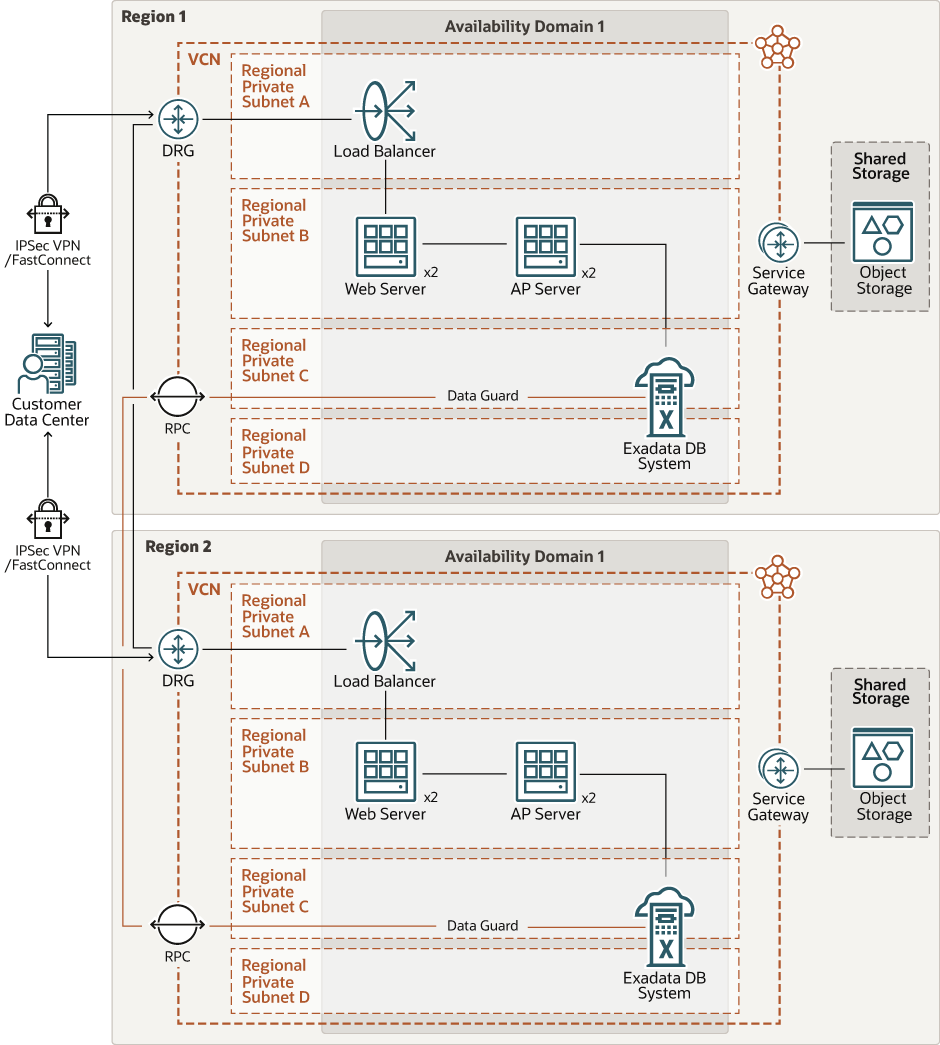
This architecture shows a secure, high-performance computing environment in multiple regions using Oracle Exadata Database Service and Data Guard.
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
exadb-cg-multi-region-arch-oracle.zip
The architecture has the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
All the resources in this architecture are deployed in a single region.
- Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
All the resources in this architecture are deployed in a single availability domain.
- Fault domains
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
To ensure high availability, the middle-tier resources in this architecture are distributed across all the fault domains in the availability domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- FastConnect
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect provides an easy way to create a dedicated, private connection between your data center and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
- IPSec VPN
Site-to-Site VPN provides IPSec VPN connectivity between your on-premises network and VCNs in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. The IPSec protocol suite encrypts IP traffic before the packets are transferred from the source to the destination and decrypts the traffic when it arrives.
- Load balancer
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancing service provides automated traffic distribution from a single entry point to multiple servers in the back end.
This architecture includes a public load balancer.
- Security lists
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Route tables
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between VCNs in the same region, between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
The VCN that's used for the data tier in this architecture has a DRG to enable private connectivity to your on-premises data center using FastConnect or VPN Connect.
- Service gateway
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and never traverses the internet.
The VCN that's used for the data tier in this architecture has a service gateway.
- Remote Peering Gateway
Remote peering allows the VCNs' resources to communicate using private IP addresses without routing the traffic over the internet or through your on-premises network. Remote peering eliminates the need for an internet gateway and public IP addresses for the instances that need to communicate with another VCN in a different region.
- Object storage
Object storage provides quick access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store and then retrieve data directly from the internet or from within the cloud platform. You can seamlessly scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability. Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
- Exadata DB systems
Oracle Exadata Database Service enables you to leverage the power of Exadata in the cloud. You can provision flexible X8M systems that allow you to add database compute servers and storage servers to your system as your needs grow. X8M systems offer RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) networking for high bandwidth and low latency, persistent memory (PMEM) modules, and intelligent Exadata software. You can provision X8M systems by using a shape that's equivalent to a quarter-rack X8 system, and then add database and storage servers at any time after provisioning.
- Data Guard
Oracle Data Guard provides a comprehensive set of services that create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby databases to enable production Oracle databases to remain available without interruption. Oracle Data Guard maintains these standby databases as copies of the production database. Then, if the production database becomes unavailable because of a planned or an unplanned outage, Oracle Data Guard can switch any standby database to the production role, minimizing the downtime associated with the outage.
Recommendations
Your requirements might differ from the architecture described here. Use the following recommendations as a starting point.
- VCN
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks.
When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.
Use regional subnets.
- Cloud Guard
Clone and customize the default recipes provided by Oracle to create custom detector and responder recipes. These recipes enable you to specify what type of security violations generate a warning and what actions are allowed to be performed on them. For example, you might want to detect Object Storage buckets that have visibility set to public.
Apply Cloud Guard at the tenancy level to cover the broadest scope and to reduce the administrative burden of maintaining multiple configurations.
You can also use the Managed List feature to apply certain configurations to detectors.
- Security Zones
For resources that require maximum security, Oracle recommends that you use security zones. A security zone is a compartment associated with an Oracle-defined recipe of security policies that are based on best practices. For example, the resources in a security zone must not be accessible from the public internet and they must be encrypted using customer-managed keys. When you create and update resources in a security zone, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure validates the operations against the policies in the security-zone recipe, and denies operations that violate any of the policies.
Considerations
When you design the topology for Exadata with Data Guard in multiple regions, consider the following factors:
- Performance
Organizations need to know what types of traffic traverses the environment, determine the appropriate risk levels, and then apply proper security controls as needed. Different combinations of security controls impact performance. Consider adding dedicated interfaces for FastConnect or VPN services. Finally, run performance tests to validate the design can sustain the required performance and throughput.
- Security
Use policies to restrict who can access the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources that your company has, and how they can access them.
Encryption is enabled for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage by default and can’t be turned off.
- Availability
For best high availability practice, evaluate which failover option best meets your business and application requirements when your primary database or primary site is inaccessible or lost due to a disaster.