Migrate to Oracle SOA Suite in the Cloud Using a Stack from Oracle Cloud Marketplace
The rapid adoption of cloud-based applications by organizations, along with the need to integrate applications with mobile technologies, is dramatically increasing the complexity of integrating applications.
Oracle SOA Suite in the cloud provides a PaaS (Platform as a Service) computing platform solution for running the following applications in the cloud:
- Oracle SOA Suite
- Oracle Service Bus
- Oracle B2B
- Oracle Managed File Transfer (MFT)
- Oracle Business Activity Monitoring (BAM)
Architecture
The following diagram shows an on-premises deployment of Oracle SOA Suite and a cloud topology after migrating Oracle SOA Suite to Oracle Cloud.
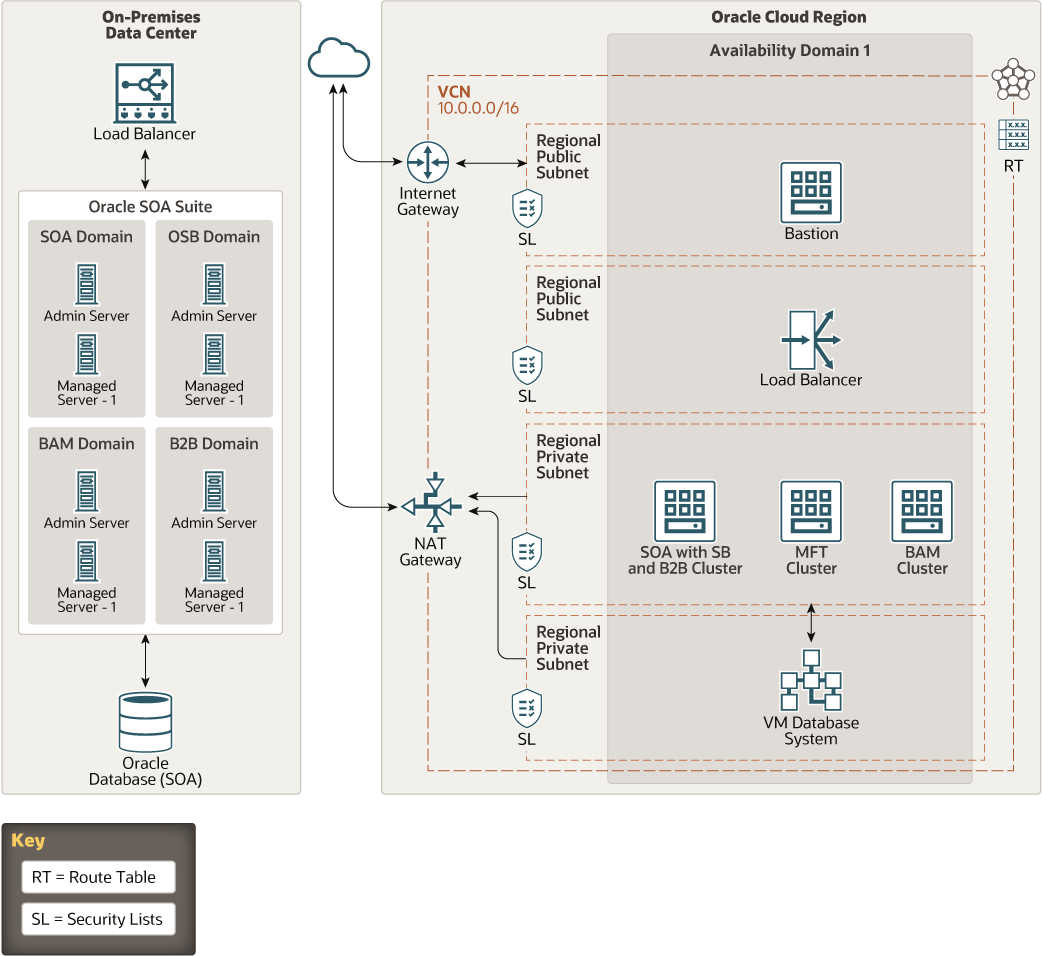
Description of the illustration migrate-soa-marketplace.png
Oracle SOA Suite in the cloud supports Oracle SOA Suite 12c (12.2.1.4) and its constituent components. Marketplace is an online store that's available in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console. When you launch an Oracle SOA Suite application from the marketplace, it prompts you for some basic information, and then directs you to Resource Manager to complete the configuration of your Oracle SOA Suite instance.
This architecture supports the following components:
- On-premises components
- Load balancer
Load balancer provides automated traffic distribution from a single entry point to multiple servers in the back end.
- Oracle SOA Suite
Oracle SOA Suite provides a comprehensive suite of components for developing, securing, and monitoring service-oriented architecture (SOA).
- SOA Domain
SOA Domain is the domain for the topology that you create and configure after you install Oracle SOA Suite.
- Oracle Service Bus (OSB) Domain
Oracle Service Bus is a component of Oracle SOA Suite. Oracle Service Bus connects, mediates, and manages interactions between heterogeneous services, not just Web services, but also Java and .Net, messaging services and legacy endpoints.
- Oracle Business Activity Monitoring (Oracle BAM) Domain
Oracle BAM is a component of Oracle SOA Suite used to monitor business processes for making tactical and strategic decisions. You can create dashboards that contain graphical views of data updated either in real time as streams or on a scheduled basis. Oracle BAM also supports alerting capabilities for business users to monitor business events, manage business exceptions, and continuously optimize their processes.
- Oracle B2B Domain
Oracle B2B is a component of Oracle SOA Suite that is an e-commerce gateway that enables the secure and reliable exchange of business documents between an enterprise and its trading partners. Oracle B2B supports business-to-business document standards, security, transports, messaging services, and trading partner management. With Oracle B2B used as a binding component within an Oracle SOA Suite composite application, end-to-end business processes can be implemented.
- Oracle Database
Oracle Database on-premises to store SOA information and data objects.
- Load balancer
- Oracle Cloud components
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability domain
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnet
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Route table
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Internet gateway
The internet gateway allows traffic between the public subnets in a VCN and the public internet.
- NAT gateway
The NAT gateway enables private resources in a VCN to access hosts on the internet, without exposing those resources to incoming internet connections.
- Bastion host
The bastion host is a compute instance that serves as a secure, controlled entry point to the topology from outside the cloud. The bastion host is provisioned typically in a demilitarized zone (DMZ). It enables you to protect sensitive resources by placing them in private networks that can't be accessed directly from outside the cloud. The topology has a single, known entry point that you can monitor and audit regularly. So, you can avoid exposing the more sensitive components of the topology without compromising access to them.
- Load balancer
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancing service provides automated traffic distribution from a single entry point to multiple servers in the back end.
- SOA with SB and Oracle B2B
Oracle Service Bus (SB) and Oracle B2B are service types of Oracle SOA Suite.
Oracle Service Bus connects, mediates, and manages interactions between heterogeneous services, not just Web services, but also Java and .Net, messaging services and legacy endpoints.
Oracle B2B is an e-commerce gateway that enables the secure and reliable exchange of business documents between an enterprise and its trading partners. Oracle B2B supports business-to-business document standards, security, transports, messaging services, and trading partner management. With Oracle B2B used as a binding component within an Oracle SOA Suite composite application, end-to-end business processes can be implemented. Note that Oracle B2B with Oracle SOA Suite in the cloud does not support Health Level 7, which enables health care systems to communicate with each other.
You can provision Oracle B2B with the SOA with SB & B2B Cluster service type.
- Oracle Managed File Transfer (MFT)
Oracle MFT is a high performance, standards-based, end-to-end managed file gateway. It features design, deployment, and monitoring of file transfers using a lightweight web-based design-time console that includes transfer prioritization, file encryption, scheduling, and embedded FTP and sFTP servers.
You can provision Oracle MFT with the MFT Cluster service type.
- Oracle Business Activity Monitoring (BAM)
Oracle BAM is used to monitor business processes for making tactical and strategic decisions. Oracle SOA Suite in the cloud supports multinode BAM clusters, providing high availability for Oracle BAM Composer and dashboards.
- Oracle VM DB System
Oracle VM DB System is an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure database service that enables you to build, scale, and manage full-featured Oracle databases on virtual machines. A VM DB System uses Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Block Volumes storage instead of local storage and has the ability to run Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) to improve availability.
- Region
Oracle Service Bus is not shown in the architecture, but you can provision Oracle Service Bus with the SOA with SB & B2B Cluster service type. Oracle Service Bus provides standards-based integration for high-volume SOA environments. It connects, mediates, and manages interactions between heterogeneous services, legacy applications, packaged applications, and multiple enterprise service bus (ESB) instances across an enterprise-wide service network. Oracle Service Bus is deployed on the Administration Server and one non-clustered (stand-alone) Managed Server. Management features are deployed on the Administration Server, and runtime features are deployed on the Managed Server.
Recommendations
- VCN
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks.
When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.
- Network security groups (NSGs)
You can use NSGs to define a set of ingress and egress rules that apply to specific VNICs. We recommend using NSGs rather than security lists, because NSGs enable you to separate the VCN's subnet architecture from the security requirements of your application.
- Security Zones
For resources that require maximum security, Oracle recommends that you use security zones. A security zone is a compartment associated with an Oracle-defined recipe of security policies that are based on best practices. For example, the resources in a security zone must not be accessible from the public internet and they must be encrypted using customer-managed keys. When you create and update resources in a security zone, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure validates the operations against the policies in the security-zone recipe, and denies operations that violate any of the policies.
- Cloud Guard
Clone and customize the default recipes provided by Oracle to create custom detector and responder recipes. These recipes enable you to specify what type of security violations generate a warning and what actions are allowed to be performed on them. For example, you might want to detect Object Storage buckets that have visibility set to public.
Apply Cloud Guard at the tenancy level to cover the broadest scope and to reduce the administrative burden of maintaining multiple configurations.
You can also use the Managed List feature to apply certain configurations to detectors.
Considerations
When migrating from Oracle SOA Suite, consider the following requirements and options:
- Scalability
- Application tier:
You can scale the application server vertically by changing the shape of the compute instance. A shape with a higher core count provides more memory and network bandwidth as well. If more storage is required, increase the size of the block volumes attached to the application server.
- Database tier:
You can scale the database vertically by enabling additional cores for the database. Both the cores and storage can be scaled up without any database downtime.
- Application tier:
- Resource limits
- Consider the best practices, limits by service, and compartment quotas for your tenancy.
- Security
- Use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies to control who can access your cloud resources and what operations can be performed.
- To protect the database passwords or any other secrets, consider using the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Vault service.
- Performance and cost
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers compute shapes that cater to a wide range of applications and use cases. Choose the shapes for your compute instances carefully. Select shapes that provide optimal performance for your load at the lowest cost. If you need more performance, memory, or network bandwidth, you can change to a larger shape.
- Availability
Consider using a high-availability option based on your deployment requirements and your region. The options include distributing resources across multiple availability domains in a region, and distributing resources across the fault domains within an availability domain.
Fault domains provide the best resilience for workloads deployed within a single availability domain. For high availability in the application tier, deploy the application servers in different fault domains, and use a load balancer to distribute client traffic across the application servers.
- Monitoring and alerts
Set up monitoring and alerts on CPU and memory usage for your nodes, so that you can scale the shape up or down as needed.
Deploy
An Oracle LiveLabs workshop is available for you to run a demo in your tenancy or you can launch a free trial workshop. To access the workshop, see Migrate SOA Applications to OCI Workshop.