Process Bulk Data Using OCI Data Integration and Oracle Integration Cloud Services
Process or integrate bulk data from external sources to targeted systems or applications.
Consider this scenario: You receive data in bulk from an external source (for example, customers, suppliers, employees, products). Before it reaches your end systems or applications, the data needs to be orchestrated, enriched, combined, or organized. As part of the flow to accomplish this, you need to integrate with two or more intermediate applications or services, or apply complex transformations to the data. This process may add additional attributes to the data after making calls or orchestrating with various third-party applications (based on, for example, REST, SOAP). This transactional data may also need complex transformations (JSON or XML), look-ups, or cross-references.
This scenario can be easily implemented with two cloud services: OCI Data Integration and Oracle Integration, where OCI Data Integration addresses all of your data integration or "Extract, Transform, Load" (ETL) needs and Oracle Integration addresses all of your application integration or enterprise-grade connectivity, regardless of the applications you are connecting or where they reside.
Architecture
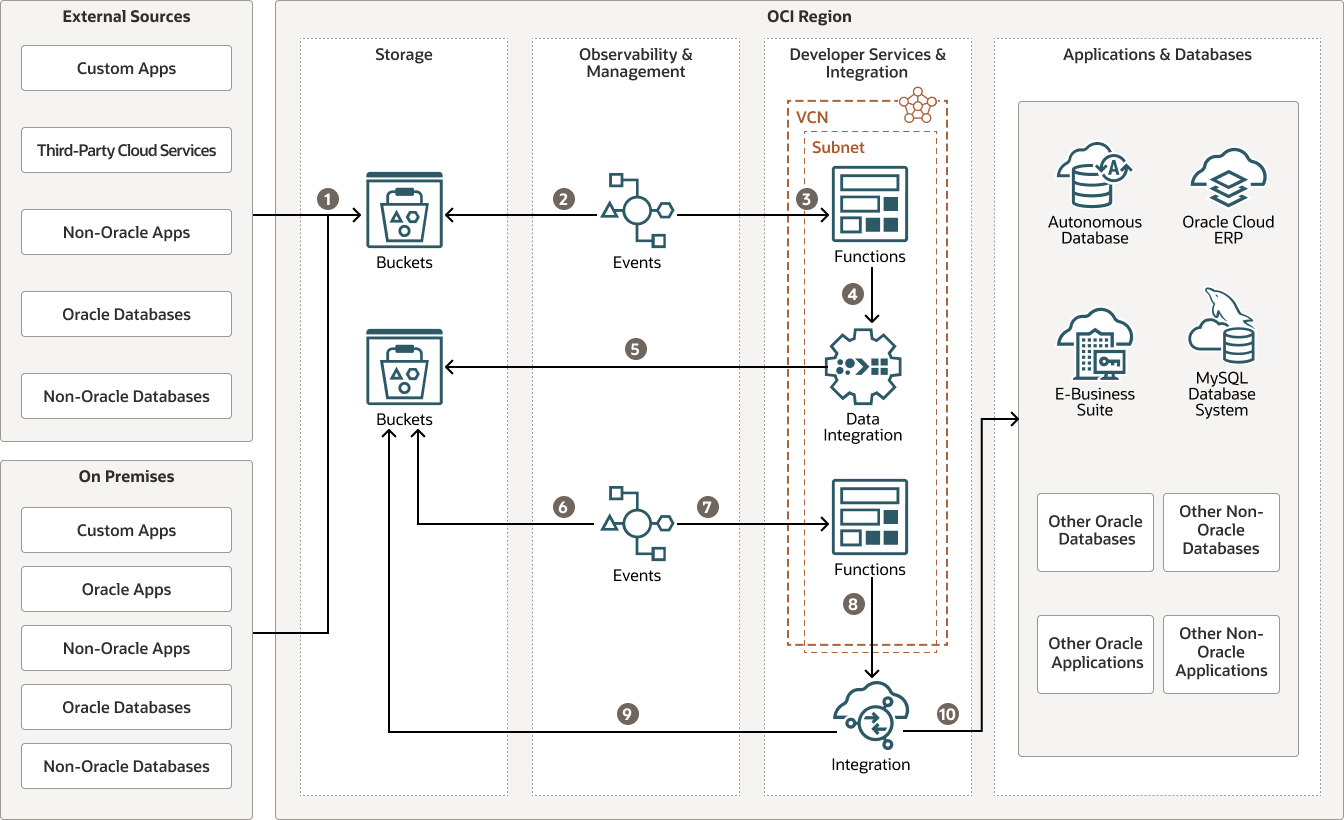
This reference architecture represents a use case for using OCI Data Integration and Oracle Integration to process bulk data.
This reference architecture also addresses the challenges of processing Apache Parquet, Apache Avro, and Microsoft Excel files in Oracle Integration through OCI Data Integration. For example, to process financial reporting data (for example, accounts payable, accounts receivable, GLs, cash flows, assets and liabilities, revenue) OCI Data Integration converts these file formats into comma-separated value (CSV) files, which are then processed by Oracle Integration.
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
oci-bulk-data-integration-architecture-diagram-oracle.zip
Here is an explanation of the steps shown in the above reference architecture:
- External sources (for example, custom applications, non-Oracle applications, Oracle databases running on third-party clouds, third-party cloud services, on-premises databases, and applications) upload or drop the bulk data load file into an OCI Object Storage bucket.
- OCI Observability & Management service: OCI Events looks for an object or file uploaded into the OCI Object Storage bucket.
- OCI Events triggers an action to invoke OCI Functions with a bucket and a file name.
- OCI Functions receives the event and invokes the OCI Data Integration pipeline with input parameters: bucket name and file name.
- OCI Data Integration pipeline reads the bulk data load file from the OCI Object Storage bucket and splits the single, large data file into numerous, smaller files. It then uploads the split files into the OCI Object Storage bucket.
- Another instance of OCI Events looks for split files uploaded into the OCI Object Storage bucket.
- OCI Events triggers an action to invoke OCI Functions with a bucket name and for each file name.
- OCI Functions receives the event and invokes Oracle Integration's flow with the input parameters of bucket name and each file name.
- Oracle Integration reads each file from the OCI Object Storage bucket.
- Oracle Integration, based on the requirement, orchestrates and enriches the data by making invocations to one or more intermediate applications or systems. It then performs complex functions (for example, transformations, look-ups, cross-references) and finally processes the data to downstream systems or applications.
The architecture has the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Data Integration
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Data Integration is a fully managed, serverless, cloud-native service that extracts, loads, transforms, cleanses, and reshapes data from a variety of data sources into target Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services, such as Autonomous Data Warehouse and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. Users design data integration processes using an intuitive, codeless user interface that optimizes integration flows to generate the most efficient engine and orchestration, automatically allocating and scaling the execution environment.
ETL (extract transform load) leverages fully-managed, scale-out processing on Spark, and ELT (extract load transform) leverages full SQL push-down capabilities of the Autonomous Data Warehouse in order to minimize data movement and to improve the time to value for newly ingested data.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Data Integration provides interactive exploration and data preparation, and helps data engineers protect against schema drift by defining rules to handle schema changes.
- Integration
Oracle Integration is a fully managed, preconfigured environment that allows you to integrate cloud and on-premises applications, automate business processes, and develop visual applications. It uses an SFTP-compliant file server to store and retrieve files and allows you to exchange documents with business-to-business trading partners by using a portfolio of hundreds of adapters and recipes to connect with Oracle and third-party applications.
- Events
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services emit events, which are structured messages that describe the changes in resources. Events are emitted for create, read, update, or delete (CRUD) operations, resource lifecycle state changes, and system events that affect cloud resources.
- Functions
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Functions is a fully managed, multitenant, highly scalable, on-demand, Functions-as-a-Service (FaaS) platform. It is powered by the Fn Project open source engine. Functions enable you to deploy your code, and either call it directly or trigger it in response to events. Oracle Functions uses Docker containers hosted in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Registry.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Route table
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.