About Setting Up an OCI Observability and Management Solution for AWS RDS Databases
The complexity of managing databases across multiple clouds necessitates a comprehensive approach to address various aspects such as observability, performance optimization, security, and compliance. Organizations must navigate through the intricacies of different cloud provider architectures, database services, and data consistency challenges to ensure a seamless and efficient multi-cloud database ecosystem.
This solution sets the stage for exploring the intricacies of multicloud Observability and Management with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Observability and Management (O&M) solution, delving into the challenges it addresses, the benefits it provides, and the strategies required to navigate the complexities of databases distributed across diverse cloud service providers.
Architecture
This architecture shows the Oracle databases running on AWS RDS and the OCI region hosts the O&M services.
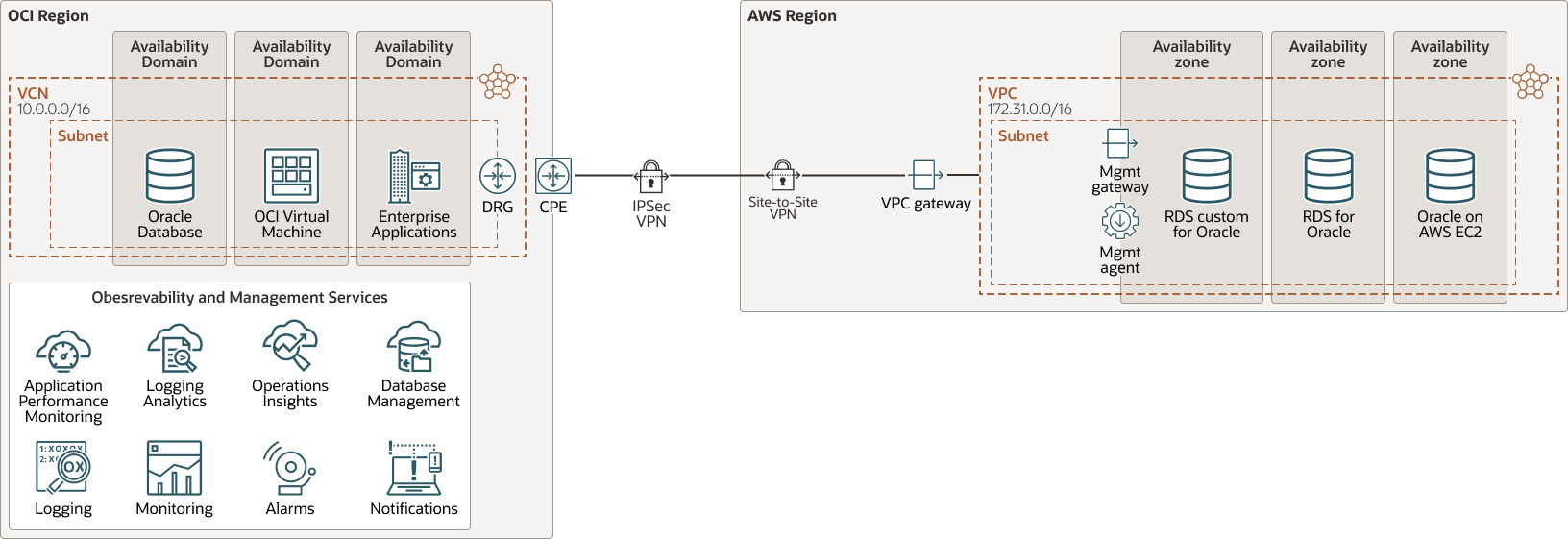
Description of the illustration multicloud-om-oci-aws.png
multicloud-om-oci-aws-oracle.zip
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domains
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Site-to-Site VPN
Site-to-Site VPN provides IPSec VPN connectivity between your on-premises network and VCNs in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. The IPSec protocol suite encrypts IP traffic before the packets are transferred from the source to the destination and decrypts the traffic when it arrives.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between VCNs in the same region, between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- Service gateway
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and never traverses the internet.
- Observability and Management Services
OCI Observability and Management is an integrated set of OCI services that enables Oracle customers to proactively monitor and manage multicloud and on-premises environments. Customers can improve performance, rapidly detect, and remediate availability and security anomalies, and accurately forecast resource needs. The solution is completely built on open technologies and AI/machine learning, offering modern observability and complete freedom of choice and co-existence with other popular monitoring tools.
- Management Gateway
Management Gateway provides a single egress point for management agents and other clients to connect to OCI services.
- Management Agent
Management Agent is a cloud service that offers a versatile collection of log and metrics data from anywhere and enables monitoring of all resources. It receives metric and log data by using REST and protocol-based collection mechanisms, including Files, JMX, SQL, JDBC, OS, and Prometheus.
- Database Management
OCI Database Management provides DBAs a unified console for managing databases, on-premises or in the cloud, with comprehensive capabilities for monitoring, performance diagnostics, tuning, and administration. It uses advanced database fleet diagnostics and tuning to troubleshoot issues and optimize database and SQL performance.
- Ops Insights
OCI Ops Insights enables administrators to uncover performance issues, forecast consumption, and plan capacity using AI based analytics on historical system and SQL performance data. Organizations can use these capabilities to make data-driven decisions to optimize resource use, proactively avoid outages, and improve performance.
- Stack Monitoring
OCI Stack Monitoring enables comprehensive monitoring of all components of your application infrastructure. It discovers the full stack including hosts, databases, application servers and more. Its interactive UI enables easy troubleshooting and uses machine learning to identify performance anomalies. It has an extensible framework which supports custom metrics and monitoring of any type of resource.
Considerations for the Setup
When setting up your environment, consider the following points:
- The user has the AWS tenancy and has set up the basic networking and deployed the databases.
- The user has OCI access with networks created.
About Required Services for Observability and Management
The services you require to complete this solution depends upon your role. The Database Administrator should have access to the database instances and the cloud connectivity to the agent and gateway instances. Users should have platform access and these applications:
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Access
- Amazon AWS access
- RDS Database details
The user also needs details of the network infrastructure access for OCI and AWS cloud environments.