Search documents and images stored in Object Storage using OpenSearch, OCI Vision, Text Recognition
For Big Data solutions, users prefer storing documents in a low-cost storage system like Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. When there are a large number of documents with Terrabytes of data, users require an easy, scalable option to search and find the relevant information. These users can also have requirements for indexing custom documents with specific steps for better search results.
This reference architecture describes how to use low code tools for developing a program to search documents and images stored in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage using a search engine designed with Oracle Visual Builder. You can add security on the file level based on OpenSearch security, or labels associated with the documents.
This reference architecture provides the following features.
- Supports most files types:
- Word, Excel, Powerpoint, pdf, xml, and so on
- Images with text using Text Recognition. You can search for text in an image.
- Images without text using Image Labeling. You can find objects in images.
- Custom documents
- Supports multi-language (Hebrew, Arabic, and so on)
- Provides an easy user interface
- Works with low code tools which makes any change in process easy to implement. You can, for example, add additional file types or additional steps in the parsing process easily.
- Runs in High Availability mode and is scalable.
Architecture
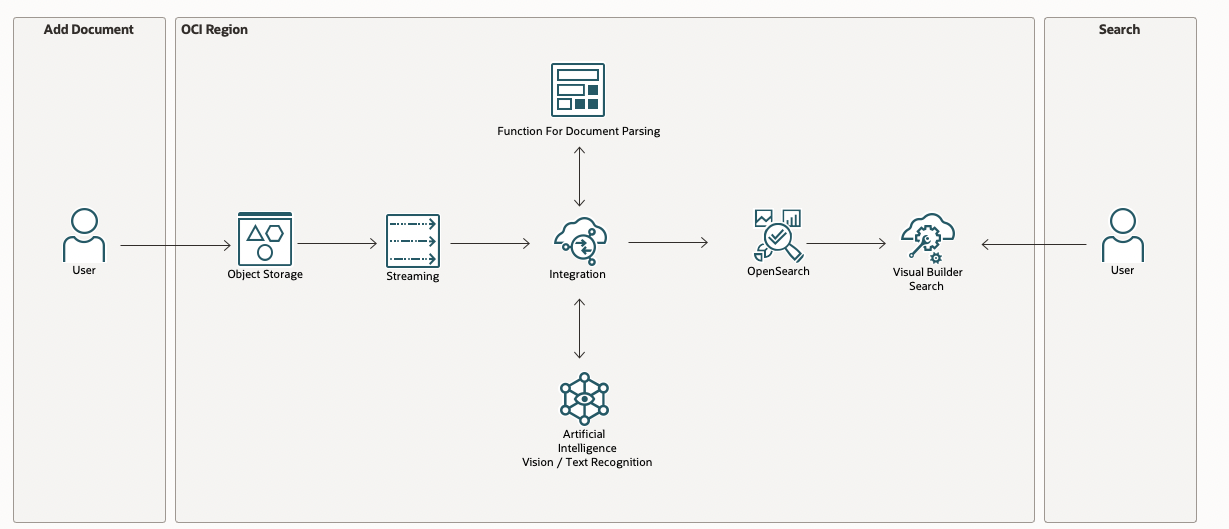
The following diagram illustrates the logical flow for this reference architecture.
oci_opensearch_vision_flow-oracle.zip
- A document is uploaded to Object Storage
- An event is raised and queued in Streaming (Kafka)
- The event is processed by Oracle Integration Cloud Service (OIC) based on the file type
- The result is uploaded to OpenSearch
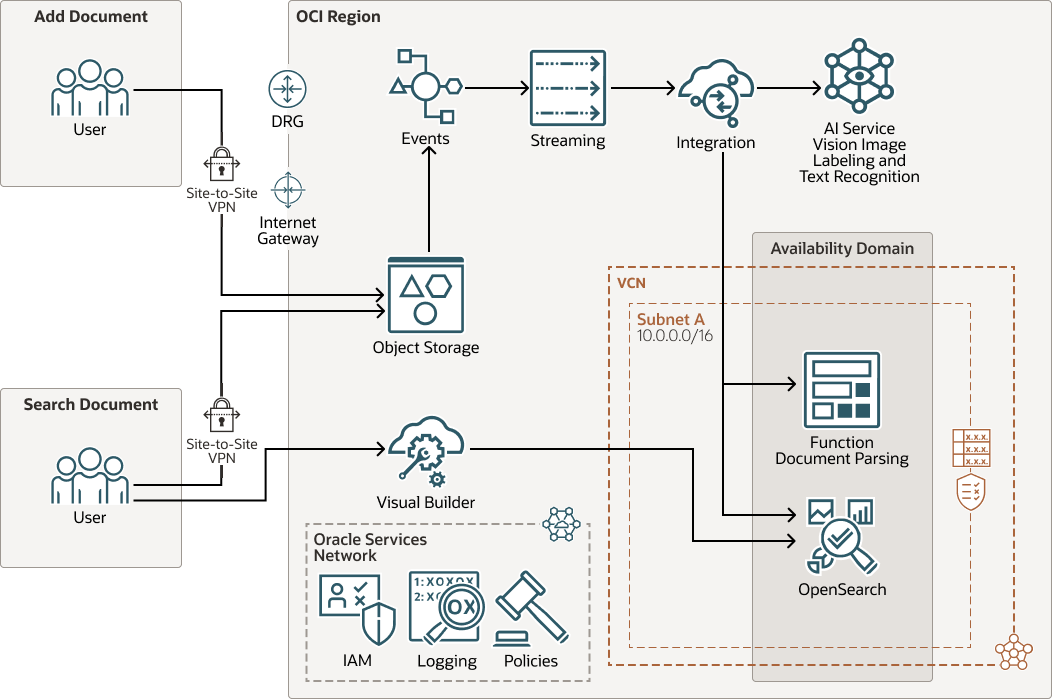
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
oci_opensearch_vision_arch-oracle.zip
An end-user can search for these documents in a search page designed with Visual Builder.
The internal processing is designed with a low code tool, OIC.
The application detects the changes in Object Storage (file creation, update, deletion) and sends them to OIC for processing.
OIC connects all the pieces together:
- Receives events from Object Storage using a Streaming Queue (Kafka)
- Detects the type of document
- Processes based on the document type:
- Sends images to OCI AI Vision for labeling or text recognition
- Sends document to a Java Function to parse the documents (Word, PDF, ...)
- For custom documents (like ID cards), it detects the name, the birth date and ID of the card.
- The document is converted and the result is stored in Opensearch for indexing.
The end-user search interface is built with Visual Builder. When an end-user searches, the result comes from OpenSearch and the document link points to Object Storage.
When viewing a document, the document comes from Object Storage using short lived pre-authenticated requests created on the fly.
This processing pipeline can be extended by additional steps to invoke any custom code using a function (or REST services on a compute instance) to enhance the metadata that will be stored in the index of the OpenSearch instance.
The architecture has the following components:
- OCI Search Service with OpenSearch
OCI Search Service with OpenSearch is an insight engine offered as an Oracle managed service. Without any downtime, Oracle automates patching, updating, upgrading, backing up, and resizing the service. Customers can store, search, and analyze large volumes of data quickly and see results in near real time.
- Oracle Integration
Oracle Integration is an enterprise connectivity and automation platform for quickly modernizing applications, business processes, APIs, and data. Developers and cloud architects can connect SaaS and on-premises applications six times faster with a visual development experience, prebuilt integrations, and embedded best practices. Oracle Integration gives you native access to events in Oracle Cloud ERP, HCM, and CX. Connect app-specific analytic silos to simplify requisition-to-receipt, recruit-to-pay, lead-to-invoice, and other critical processes. Finally, give your IT and business leaders end-to-end visibility.
- Object storage
Object storage provides quick access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store and then retrieve data directly from the internet or from within the cloud platform. You can seamlessly scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability. Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
- OCI Vision
OCI Vision is an AI service for performing deep-learning–based image analysis at scale. With prebuilt models available out-of-the-box, developers can easily build image recognition and text recognition into their applications without machine learning (ML) expertise. For industry-specific use cases, developers can automatically train custom Vision models with their own data. These models can be used to detect visual anomalies in manufacturing, extract text from documents to automate business workflows, and tag items in images to count products or shipments. In addition to gaining access to pre-trained models, developers can create custom models without data science expertise or managing custom model infrastructure.
- Streaming
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Streaming service provides a fully managed, scalable, and durable solution for ingesting and consuming high-volume data streams in real-time. Use Streaming for any use case in which data is produced and processed continually and sequentially in a publish-subscribe messaging model.
- Events
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services emit events, which are structured messages that describe the changes in resources. Events are emitted for create, read, update, or delete (CRUD) operations, resource lifecycle state changes, and system events that affect cloud resources.
- Functions
Oracle Functions is a fully managed, multitenant, highly scalable, on-demand, Functions-as-a-Service (FaaS) platform. It is powered by the Fn Project open source engine. Functions enable you to deploy your code, and either call it directly or trigger it in response to events. Oracle Functions uses Docker containers hosted in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Registry.
- Tenancy
A tenancy is a secure and isolated partition that Oracle sets up within Oracle Cloud when you sign up for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. You can create, organize, and administer your resources in Oracle Cloud within your tenancy. A tenancy is synonymous with a company or organization. Usually, a company will have a single tenancy and reflect its organizational structure within that tenancy. A single tenancy is usually associated with a single subscription, and a single subscription usually only has one tenancy.
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Compartment
Compartments are cross-region logical partitions within an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy. Use compartments to organize your resources in Oracle Cloud, control access to the resources, and set usage quotas. To control access to the resources in a given compartment, you define policies that specify who can access the resources and what actions they can perform.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
Recommendations
- Maintenance and High Availability
The design uses nearly only PaaS services, maintained by the cloud. There is no need to install, patch, update, or upgrade the software using this solution. This is valid for: Object Storage, Events, Streaming, OCI Vision, Oracle Integration, Visual Builder, and Functions.
The only component that requests attention is the Oracle Integration Cloud agent installed in a compute instance to access the OpenSearch cluster that resides in a private network. Follow the guidelines in the OIC documentation to make the OIC agent easy to maintain and highly available.
- Scalability and size
This reference architecture uses PaaS service and it is scalable out-of-the-box for most services. Note that the OpenSearch cluster does not scale up and down automatically (only manually). So, a right scaling of the solution is needed based on the your use case.
Considerations
Consider the following points when deploying this reference architecture.
- Performance
OCI Search Service with OpenSearch has an unparalleled level of configuration. You are not locked into specific shapes or SKUs; instead, you can use flex shapes that allow you to configure the precise number of compute cores and amount of memory and storage based on your exact requirements.
OCI Search Service with OpenSearch manages the work involved in setting up your cluster, including provisioning infrastructure. Once your cluster is running, OCI Search Service with OpenSearch handles common administrative tasks, such as performing backups, monitoring instances, and patching software. OCI Search Service with OpenSearch integrates with OCI metrics to produce metrics that provide information about the state of the clusters. OCI Search Service with OpenSearch also offers the ability to modify cluster configuration and total data size without a service disruption.
- Security
The documents are stored in private Object Storage. A temporary link with a short life is created when a user clicks on the document.
The implementation returns the same result for all users and is described in detail in the LiveLabs workshop linked in the Explore More section. There is no security implemented at the document level. You can implement it based on OpenSearch security and/or on the label associated with documents and users.
- Cost
This reference architecture uses Object Storage and OpenSearch which are low cost products. It uses also a Standard version of OIC. OIC is used very efficiently with indexing, it uses only the reference to files, and not the files themselves.
Explore More
Links to additional information that can help you learn about, modify, use, or implement this architecture.
- Oracle LiveLabs Workshop: Search Documents and Images stored in Object Storage using OpenSearch, AI Vision, Text Recognition
- Best practices framework for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Aggregate logs using OCI Search Service with OpenSearch
- Use OCI Vision to extract data from images and scanned documents
- Oracle Integration Documentation