Prepare Your Environment to Use Web Application Firewall
Prepare your environment to be able to use the Web Application Firewall (WAF) service of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure to secure your application.
Before You Begin
employee-helidon-lb load balancer already been deployed. See Deploy a microservices-based RESTful Java
application to Oracle Cloud.
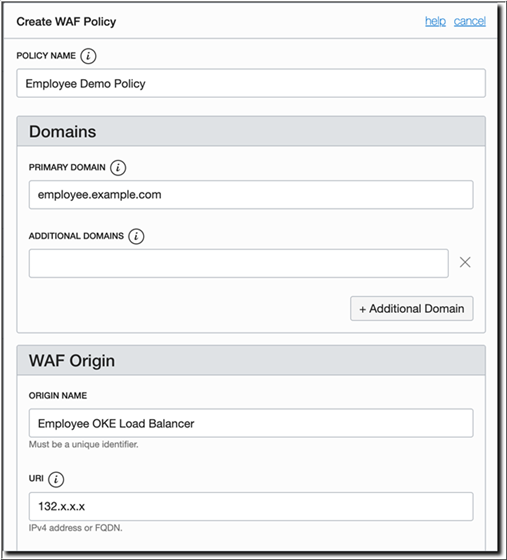
Obtain and note the EXTERNAL-IP address of the load balancer of the sample Employee application. This will be required to create the WAF policy later.
kubectl get service employee-helidon-lbThe preceding command should return an output similar to the following:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
employee-helidon-lb LoadBalancer 10.X.X.X 132.X.X.X 80:31437/TCP 5mEXTERNAL-IP displayed by Kubernetes is the same as the public IP address, which is displayed when you navigate to Core > Networking > Load Balancers in the Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure console.
Route Application Traffic Using WAF
To route traffic through WAF, the specified primary domain and any additional domains must resolve to the CNAME Target listed in the WAF policy information. This is presented as a notice when the policy is first created.
If the application is actually configured in a DNS zone, you would normally create a CNAME or ALIAS record for employee.example.com using WAF_Target as its value.
example.com host name for the sample Employee application, you need to configure your machine (from which you'll access the application) to resolve the host.
The application now runs over WAF.