Learn About Connecting Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Government Cloud to Microsoft Azure Over Megaport
As organizations expand their cloud infrastructure to meet growing demands, the need to securely connect and transfer data between different cloud environments becomes crucial. By utilizing ExpressRoute via Megaport Cloud Router (MCR) combined with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) FastConnect, customers can establish continuous connectivity, with dedicated bandwidth between Azure and OCI Government Cloud, enabling seamless migration, data copying, all while achieving speeds up to 10Gbps.
This Solution Playbook shows you how to connect OCI Government Cloud to Microsoft Azure by using OCI FastConnect, Megaport Cloud Router, and Azure ExpressRoute. It also helps address the compliance challenges that arise when dealing with data from non-FedRAMP regions.
Architecture
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
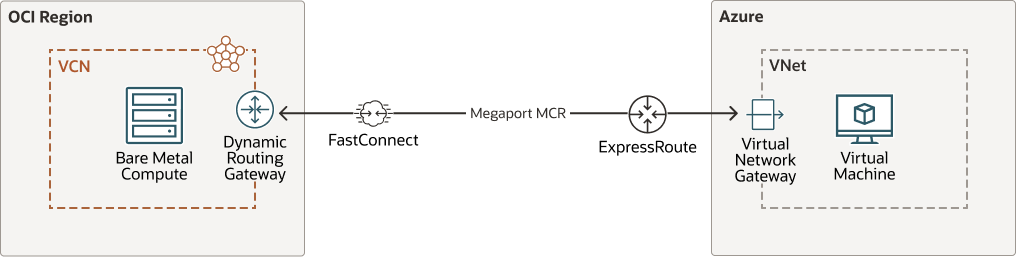
Description of the illustration connect-azure-oci-megaport.png
connect-azure-oci-megaport-oracle.zip
- Tenancy
A tenancy is a secure and isolated partition that Oracle sets up within Oracle Cloud when you sign up for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. You can create, organize, and administer your resources in Oracle Cloud within your tenancy. A tenancy is synonymous with a company or organization. Usually, a company will have a single tenancy and reflect its organizational structure within that tenancy. A single tenancy is usually associated with a single subscription, and a single subscription usually only has one tenancy.
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Compartment
Compartments are cross-region logical partitions within an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy. Use compartments to organize your resources in Oracle Cloud, control access to the resources, and set usage quotas. To control access to the resources in a given compartment, you define policies that specify who can access the resources and what actions they can perform.
- Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domains
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- NAT gateway
The NAT gateway enables private resources in a VCN to access hosts on the internet, without exposing those resources to incoming internet connections.
- FastConnect
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect provides an easy way to create a dedicated, private connection between your data center and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
About Microsoft Azure Components Used in this Architecture
In addition to these OCI components, this architecture also includes these Azure components:
- Azure Virtual Network
Azure Virtual Network allows you to build a private network in Azure. A virtual network that includes virtual machines (VMs) enables many types of resources to securely communicate with each other, the internet, and on-premises networks. Although a virtual network is similar to a traditional network that you'd operate in your own datacenter, it provides extra benefits such as scale, availability, and isolation.
- Azure VPN Gateway
Azure VPN Gateway uses a specific type of virtual network gateway to send encrypted traffic between an Azure virtual network and on-premises locations over the public Internet. You can also use it to send encrypted traffic between Azure virtual networks over the Microsoft network. You can create multiple connections to the same VPN gateway and all VPN tunnels share the available gateway bandwidth.
- Azure ExpressRoute
ExpressRoute enables you to create private connections between Azure data centers and those on your on-premises infrastructure or in a colocation environment. These connections avoid the public internet and offer greater reliability, faster speeds, lower latencies, and higher security than typical connections over the internet.
For more complete details on these components, see the official Microsoft Azure documentation listed in the Explore More topic, below.
About Megaport
- Ports
Ports are high-speed Ethernet interfaces (1 Gbps, 10 Gbps, and 100 Gbps) that connect to the Megaport network.
- Virtual Cross Connect (VXC)
A VCX connects any two endpoints on the Megaport network. Generally, these connections support capacities ranging from 1 Mbps to 10 Gbps, although some high-capacity ports within the same area can support connections of up to 20 Gbps .
- Megaport Cloud Router (MCR)
The MCR is a virtual router for on-demand, private, Layer 3 connectivity to service providers between key global routing zones.
Recommendations
- VCN
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks.
When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.