Trinus Co: Financial Services and Real Estate Solutions Workload Deployment on Oracle Cloud
To help individuals better manage their investment portfolios, Trinus deployed the back-end systems that are used to run its broker management platform on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
With help from its cloud implementation partner, 3DB, the Brazil-based brokerage firm can now provide investors with a secure environment for self-service access to their stocks, mutual funds, real estate investments, and more. When users access their accounts to make trades or to sell stocks on the Trinus investment portal, their requests are sent to OCI through a FortiGate firewall, and then distributed to various applications that run on OCI instances.
Individual investors can access their accounts by logging into the investment portal, which is provided by a third-party software-as-a-service (SaaS) application. When an investor makes a transaction, such as buying a stock or selling a mutual fund, the information is sent to Trinus's backend systems on OCI.
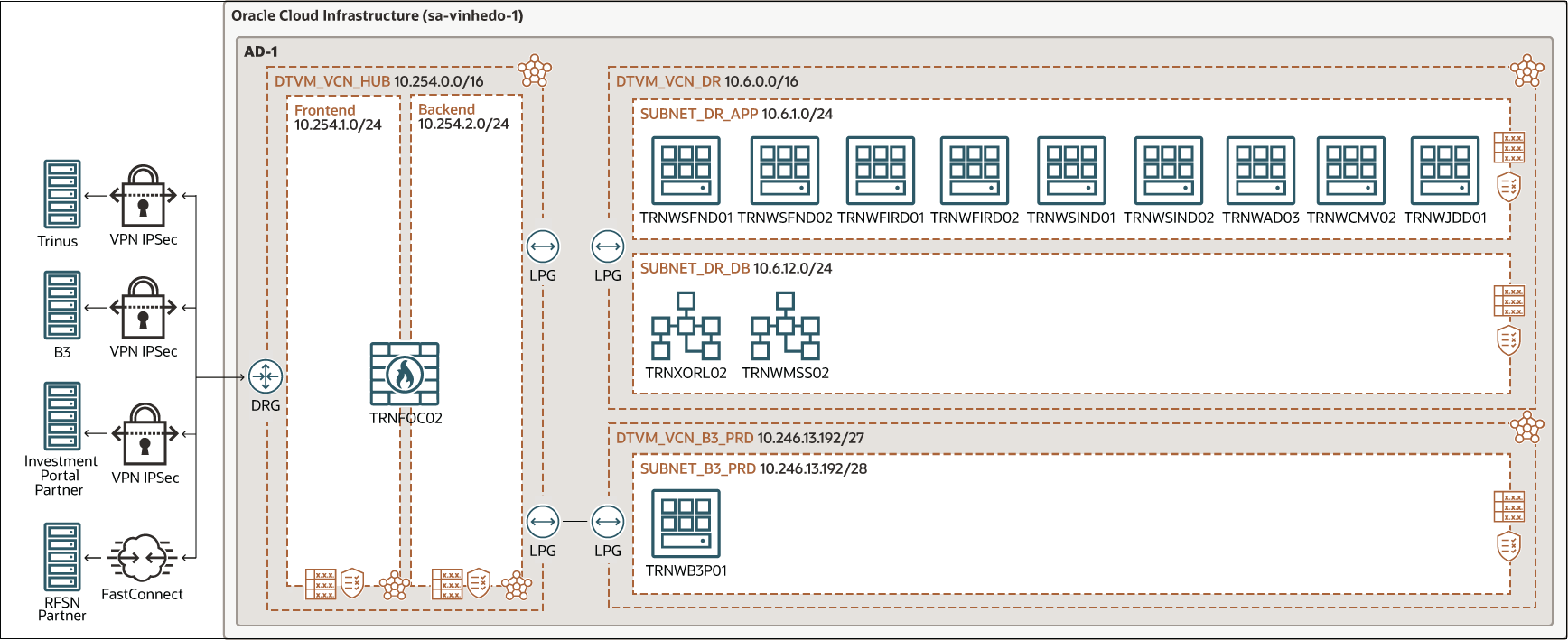
To prevent data loss and to ensure a fast recovery in case of an outage, Trinus has its primary tenancy in the Oracle Cloud region in São Paulo, Brazil and its disaster recovery site in Vinhedo.
Architecture
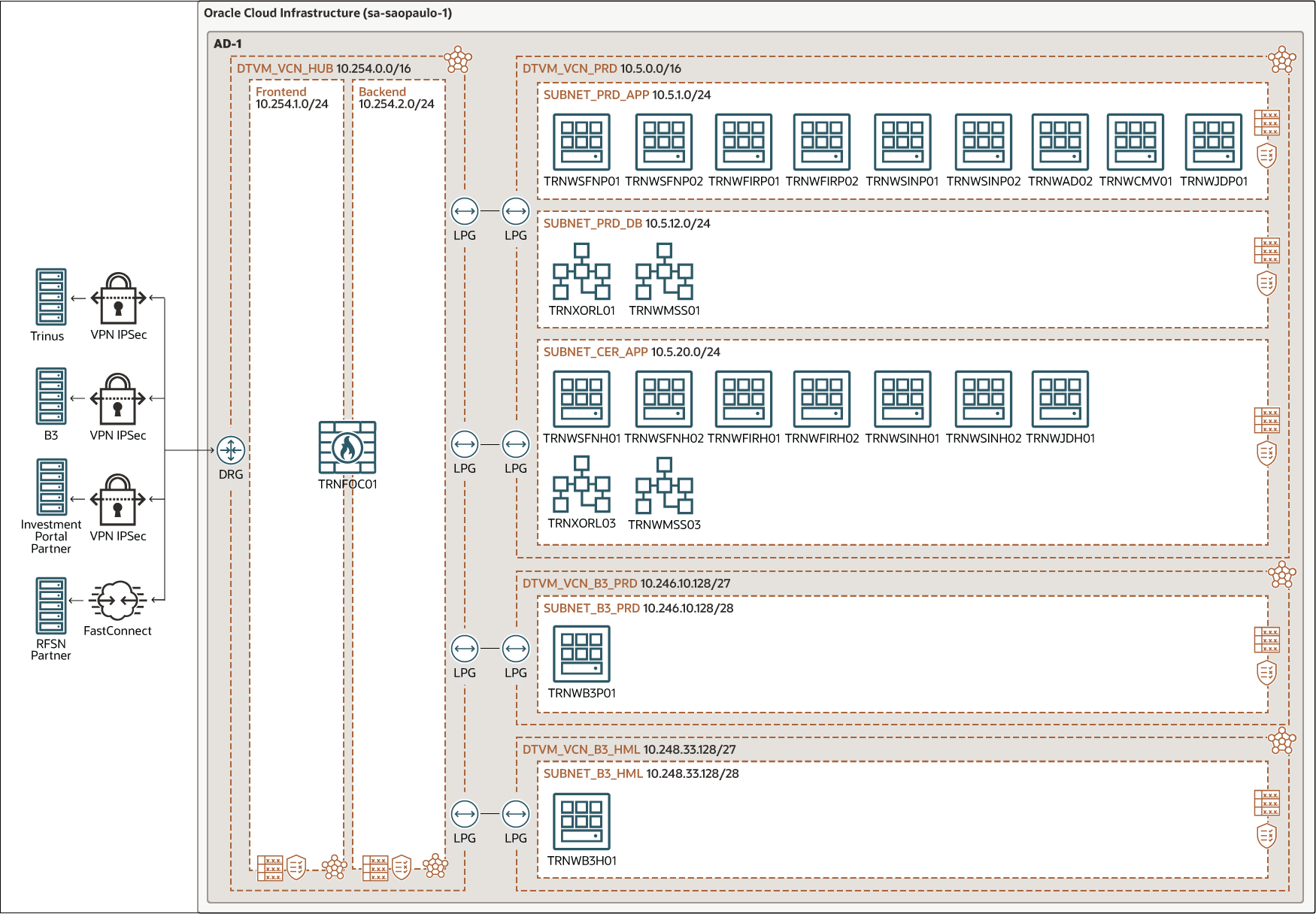
When a transaction is made, a request is generated, encrypted, and then sent to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure through a site-to-site VPN.
This request enters the FortiGate firewall virtual cloud network (VCN) through a dynamic routing gateway. The request is then sent to the production application VCN by using local peering.
In the production application VCN, Trinus runs multiple business-critical applications on OCI virtual machines (VMs). The VCN also includes an Oracle Enterprise Database and an MS SQL Server database.
Depending on the type of investment transaction, requests are routed to the application running on the appropriate VM instance. Also depending on the kind of transaction, validation and registration requests are sent to the Brazil Stock Exchange (B3) and to RFSN (National Financial System Network), which gives access to the main payment and market operation systems in Brazil (SPB, SELIC, CETIP, among others). Communications with B3 use site-to-site VPN. Data transfer with RFSN uses a dedicated, high-bandwidth FastConnect connection, which can be scaled up or down depending on ever-changing traffic and data transfer requirements.
Trinus uses the B3 Integrated Broker Administration System (SINACOR) application as one of its main engines. SINACOR is the official stock exchange system that interconnects all brokers and manages all stock exchange transactions. Trinus installed the SINACOR application on OCI virtual machines (in the diagram: TRNWSINP01, TRNWSINP02, TRNWSINH01, TRNWSINH02). Each of the environments (production, homologation) has two OCI virtual machines dedicated to SINACOR for redundancy.
SINACOR stores user requests, transactions, and other data in an Oracle Enterprise Database. The remaining business applications, such as judicial controlling and anti-money laundering systems, store data in either an Oracle Enterprise Database or on the MS SQL Server.
In the primary region in São Paulo, Trinus's architecture features three distinct OCI compartments and VCNs, one each for the production, certification, and homologation environments. Trinus also runs a replica of the production networking,VM instances, databases, and firewall in a disaster recovery region in Vinhedo. The Oracle Enterprise Database is replicated to Vinhedo region using Oracle Data Guard technology.
The architecture diagram below illustrates Trinus's workload as implemented in the primary OCI region - Brazil East (São Paulo).
trinus-oci-principal-oracle.zip
The following diagram illustrates the disaster recovery setup Trinus runs on Brazil South East (Vinhedo).
The architecture has the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Tenancy
A tenancy is a secure and isolated partition that Oracle sets up within Oracle Cloud when you sign up for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. You can create, organize, and administer your resources in Oracle Cloud within your tenancy. A tenancy is synonymous with a company or organization. Usually, a company will have a single tenancy and reflect its organizational structure within that tenancy. A single tenancy is usually associated with a single subscription, and a single subscription usually only has one tenancy.
- Identity and access management (IAM)
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (IAM) enables you to control who can access your resources in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and the operations that they can perform on those resources.
- Policy
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management policy specifies who can access which resources, and how. Access is granted at the group and compartment level, which means you can write a policy that gives a group a specific type of access within a specific compartment, or to the tenancy.
- Availability domain
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Compartment
Compartments are cross-region logical partitions within an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy. Use compartments to organize your resources in Oracle Cloud, control access to the resources, and set usage quotas. To control access to the resources in a given compartment, you define policies that specify who can access the resources and what actions they can perform.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Route table
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- Local peering gateway (LPG)
An LPG enables you to peer one VCN with another VCN in the same region. Peering means the VCNs communicate using private IP addresses, without the traffic traversing the internet or routing through your on-premises network.
- Compute
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute service enables you to provision and manage compute hosts in the cloud. You can launch compute instances with shapes that meet your resource requirements for CPU, memory, network bandwidth, and storage. After creating a compute instance, you can access it securely, restart it, attach and detach volumes, and terminate it when you no longer need it.
- Data Guard
Oracle Data Guard provides a comprehensive set of services that create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby databases to enable production Oracle databases to remain available without interruption. Oracle Data Guard maintains these standby databases as copies of the production database. Then, if the production database becomes unavailable because of a planned or an unplanned outage, Oracle Data Guard can switch any standby database to the production role, minimizing the downtime associated with the outage.
Get Featured in Built and Deployed
Want to show off what you built on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure? Care to share your lessons learned, best practices, and reference architectures with our global community of cloud architects? Let us help you get started.
- Download the template (PPTX)
Illustrate your own reference architecture by dragging and dropping the icons into the sample wireframe.
- Watch the architecture tutorial
Get step by step instructions on how to create a reference architecture.
- Submit your diagram
Send us an email with your diagram. Our cloud architects will review your diagram and contact you to discuss your architecture.