11 Batching Messages
This chapter describes how to use the Oracle B2B interface to batch, schedule, and send outbound EDI X12 and EDI EDIFACT messages for outbound messages (Inbound messages to Oracle B2B are automatically debatched.)
The chapter contains the following topics:
See the following for more information about EDI:
11.1 Setting Up a Batch for EDI Messages
Batching is often used to group messages by document type; for example, you may want to send out a batch of purchase orders or a batch of invoices, to one or more trading partners. You can also batch multiple document types, sent to one or more trading partners.
When batching more than 1000 documents, where the payload size is greater than 30 KB, specific settings are required. See "Settings for Batching a Large Number of Documents" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Performance Guide.
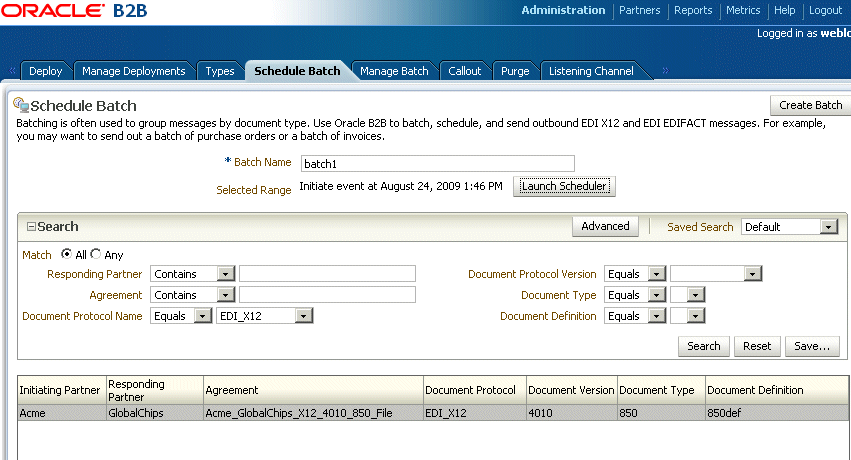
Figure 11-1 shows where you set up a batch transmission of EDI messages.
To set up a batch, do the following:
- Task 1 Search for Agreements to Batch
-
-
Click the Administration link.
-
Click the Schedule Batch tab under the Batch tab.
-
Use the search parameters described in Table 11-1 to identify which agreements you want to batch.
Use the document search parameters as follows: Select a document protocol name first to populate the list of document protocol versions; next select a document protocol version to populate the list of document types; and then select a document type to populate the list of document definitions.
Table 11-1 Search Parameters for Creating a Batch
Parameter Description Match All or Any
If you select All, then fields with values are matched using an and condition. If you select Any, then fields with values are matched using an or condition.
Responding Partner
Select Starts With, Contains, Equals, or Ends With, and type the appropriate portion of the name of the responding trading partner.
Agreement
Select Starts With, Contains, Equals, or Ends With, and type the appropriate portion of the name of the agreement.
Document Protocol Name
Select EDI_EDIFACT or EDI_X12.
Document Protocol Version
Select a document protocol version that you previously created.
Document Type
Select a document type that you previously created.
Document Definition
Select a document definition that you previously created.
-
Click Search.
Active, deployed agreements (outbound) that meet your search criteria are displayed.
-
Go to Task 2, "Create the Batch".
-
- Task 2 Create the Batch
-
-
Enter a unique name for the batch.
-
Select the agreements you want to batch.
-
Click Create Batch.
-
Go to Task 3, "Schedule the Batch".
-
- Task 3 Schedule the Batch
-
-
Click Launch Scheduler.
-
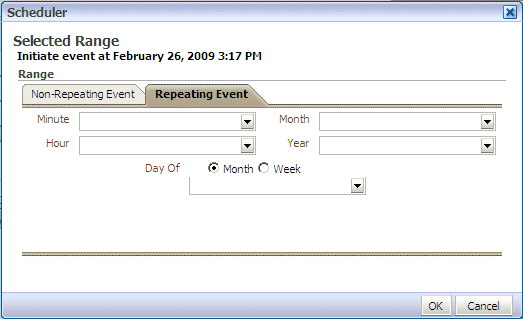
Select the Non-Repeating Event tab or the Repeating Event tab.
-
For a nonrepeating event, do one of the following:
-
Enter the date in the format shown in the Scheduler dialog and click OK.
-
Or, click the Calendar button, specify a date and time, and click OK.
For a repeating event (see Figure 11-2), enter details on the interval to trigger the event by specifying the minutes, hour, month, year, and date details. Then click OK.
-
-
You can see the batches you create on the Manage Batch tab.
Note:
If any one of the documents in a batch has the validation flag set to "on", the whole batch is validated.11.1.1 Creating a Batch Based on Max Count and Max Size
This feature allows you to batch outbound EDI messages based on "Allowed Number Of Transactions" (Max Count) in batched messages or the "Allowed Size" (Max Size) of batched messages.
To batch messages based on Max Count and Max Size, do the following:
-
Task 1, "Search for Agreements to Batch" in Setting Up a Batch for EDI Messages.
-
Create the batch:
-
Enter a unique name for the batch in the Batch Name field.
-
Select the agreements you want to batch based on "Search for Agreements to Batch".
-
In the case of creating Batch based on "Number Of Transactions" or "Maximum Size", Schedule Range is optional. However, you can click Launch Scheduler to schedule an event (Non-Repeating or Repeating) as specified in Task 3, "Schedule the Batch".
-
Enter a value for the size of outbound payload in KBs in the Max Size (KB) field if you want batching to occur based on size of the outbound EDI messages.
-
Enter a value in the Max Count field if you want batching to occur based on the number of transaction of outbound EDI messages.
-
Click Create Batch.
-
11.1.2 Understanding Batching Based on Batch Setup
For performance improvements there is a change introduced in 121.3.0 B2B Batching; a Batch monitoring thread has been added to the engine. This thread (by default) sleeps for 1 minute and when it wakes, it looks for pending messages to be batched and then processes these to find if count or size criteria are met. The tread sleep time is controlled by the property b2b.batchMonitorSleepInterval.
Note that the size referred to in this discussion is the xml payload size.
This change also introduces a new option b2b.batchMonitorStragglerTimeLag, (specified in minutes) for forcing batch processing to occur despite count and size not matching for a certain specified time limit.
For example, if the time lag is set to 60 minutes, count as 50 and size as 10Mb, then when the batch monitor thread wakes up and finds that the first message in pending messages table has crossed the one hour wait period, it forces a batch to be created even if the size and count criteria have not been met.
This feature uses two properties, b2b.batchMonitorStragglerTimeLag and b2b.batchMonitorStragglerBatchName.
Further details on their functionality can be seen in the Section E.1 Properties To Set in Fusion Middleware Control, Table E-1 Oracle B2B Properties in Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control
The following are the different cases of batching based on batch setup:
-
Case 1: When creating the batch, only Max Count is specified: Batching occurs in based on the specified number of transactions.
For example, if you specify Max Count as 4, when you enqueue four outbound EDI messages, a batched message having four transactions is created when the Batch monitoring thread wakes up from sleep. In case you enqueue less than four messages, the messages will not get batched. In case you enqueue more than four messages (less than 8), then it will batch 4 messages and the remaining will be kept in the pending table.
-
Case 2: When creating the batch, only Max Size (KB) is specified: Batching occurs based on the size of the messages to be batched including the size of last message.
For example, if you specify Max Size as 4 KB, when you enqueue four outbound EDI messages of 1 KB each, a batched message of 4KB size is created when the Batch monitoring thread wakes up from sleep. In case you enqueue messages such that the size criteria is not met, then messages will not get batched. In case you enqueue messages that add to more than 4 KB, say 6 msgs, then also only 4 messages will be batched and the remaining 2 messages will be kept in the pending table.
-
Case 3: When creating the batch, both Max Count and Max Size are specified: Batching occurs based on whichever criteria is met first.
-
Case 4: When creating the batch, you also schedule an event for the batch (using Launch Scheduler) along with Max Count and Max Size, messages are batched in the sequence of Case1, Case 2, and Case 3. However when the Timer Event occurs, it batches all the messages available for batching at that point in time (irrespective of the values provided for Max Count and Max Size.)
-
Case 5: When creating the batch, only Max Count is specified and "b2b.batchMonitorStragglerTimeLag" and "b2b.batchMonitorStragglerBatchName" are set for the Batch:
Condition 5.1: The Time lag has not exceeded, but the max count exceedsFor example, if you specify Max Count as 4, and time lag as 10 minutes, when you enqueue four outbound EDI messages, a batched message having four transactions is created when the Batch monitoring thread wakes up from sleep. In case you enqueue less than four messages, the messages will not get batched (time lag has not exceeded). In case you enqueue more than four messages (less than 8), then it will batch 4 messages and the remaining will be kept in the pending table.
Condition 5.2: Time lag has exceeded, max count does not exceedFor example, if you specify Max Count as 4, and time lag as 10 minutes, when you enqueue three outbound EDI messages, a batched message having three transactions is created when the Batch monitoring thread wakes up from sleep and finds that the first message in the pending list has exceeded the 10 minute time lag criteria.
Condition 5.3: Time lag has exceeded, max count exceeds
For example, if you specify Max Count as 4, and time lag as 10 minutes, when you enqueue 10 outbound EDI messages in such a manner that when the Batch monitoring thread wakes up from sleep and finds that the first message in the pending list has exceeded the 10 minute time lag criteria, two batched messages having 4 transactions each and another with just 2 transactions are created.
-
Case 6: When creating the batch, only Max Size (KB) is specified and "b2b.batchMonitorStragglerTimeLag" and "b2b.batchMonitorStragglerBatchName" are set for the Batch:
Condition 6.1: Time lag has not exceeded, max size exceeds
For example, if you specify Max Size as 4 KB, and time lag as 10 minutes, when you enqueue four outbound EDI messages of 1 KB each, a batched message of 4KB size is created when the Batch monitoring thread wakes up from sleep. In case you enqueue messages such that the size criteria is not met, then messages will not get batched (time lag has not exceeded). If you enqueue messages that add to more than 4 KB, say 6 messages, only 4 messages are batched and the remaining 2 messages are kept in the pending table.
Condition 6.2: Time lag has exceeded, max size does not exceed
For example, if you specify Max Size as 4 KB, and time lag as 10 minutes, when you enqueue three outbound EDI messages, a batched message having three transactions is created when the Batch monitoring thread wakes up from sleep and finds that the first message in the pending list has exceeded the 10 minute time lag criteria.
Condition 6.3: Time lag has exceeded, max size exceeds
For example, if you specify Max Size as 4 KB, and time lag as 10 minutes, when you enqueue 10 outbound EDI messages in such a manner that when the Batch monitoring thread wakes up from sleep and finds that the first message in the pending list has exceeded the 10 minute time lag criteria, two batched message having 4 transactions each and another with just 2 transactions are created.
-
Case 7: When creating the batch, both Max Count and Max Size are specified and
b2b.batchMonitorStragglerTimeLagandb2b.batchMonitorStragglerBatchNameare set for the Batch.When the batch monitor sleep thread wakes up, the criteria that is met first will trigger a batch to be created.
When lag has exceeded, batches are grouped/limited to the number based on count or size criteria if the size is found to be exceeding specified limits and, additionally, the pending set of remainder messages are batched.
Note:
Batching messages based on Max Count and Max Size works following the assumptions:-
Enqueued Outbound EDI Payload (XML) has only one transaction.
-
The size of enqueued Outbound EDI Payload (XML) is considered for the batching criteria.
11.2 Managing Batched Messages
Figure 11-3 shows where you can search for batches that you previously created, view details of a batch, and disable, update, or delete a batch.
Figure 11-3 Managing Batched EDI Messages
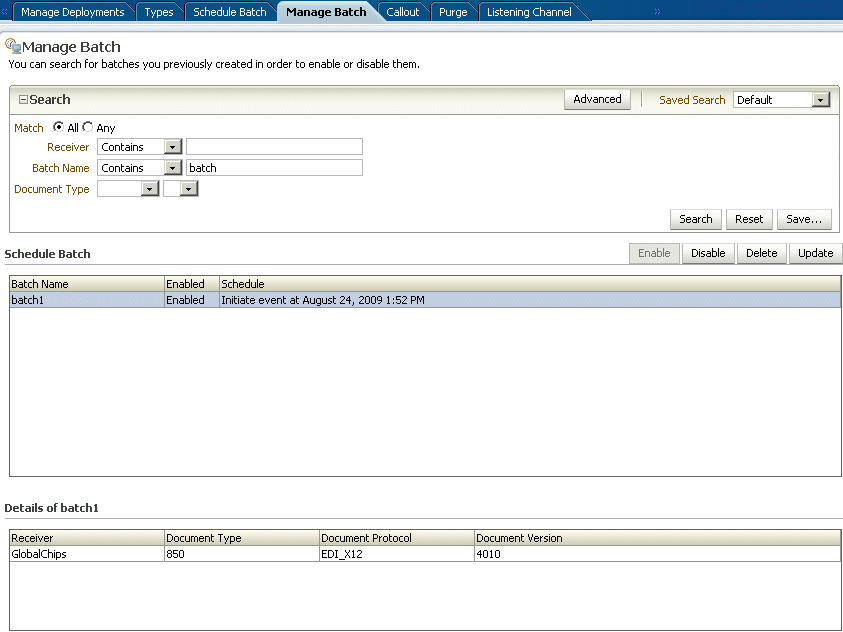
Description of "Figure 11-3 Managing Batched EDI Messages"
For the Update batch action, only the documents definitions selected can be updated. Ensure that you reselect all the documents that are to be part of the batch and not just the new ones.
In some cases, B2B may not pick up the batched messages when you update the batching schedule. If you see that batched messages are not being picked up, delete the batch and create a new batch schedule with the same name as the previous batch. The same name must be used so that B2B picks up the previous messages in WAIT_BATCH status.
11.3 Support for Sequencing Inbound Batched Messages
Oracle B2B provides support for sequencing of inbound batched messages.
When Oracle B2B receives a batched message:
-
Oracle B2B makes only one entry in the Sequence Manager table, and the state of the message in the Sequence Manager table is set to
PROCESSING. -
While de-batching, the messages are inserted into the Business Message table as well as the
B2B_PENDING_MESSAGEtable with the Sequence Number of the messages stored in an attribute column (Attribute4) of theB2B_PENDING_MESSAGEtable. -
after the last message of a batch is processed by Oracle B2B, it changes the state of the Sequenced Message to
PROCESSED, and indicates the message as a batch message by marking the messageID asBATCH_MESSAGE. -
After dispatching a message from a batch, Oracle B2B changes the state of the Business Message to
MSG_COMPLETEand deletes the corresponding entry in theB2B_PENDING_MESSAGEtable. If the Oracle B2B stops working in the middle of batch processing, on recovery, Oracle B2B sends only the messages that are present in theB2B_PENDING_MESSAGEtable.
Note:
The limitation of this approach is that the batch delivery does not resume until the complete batch is processed by Oracle B2B.Note:
Batching with sequencing is supported at the inbound side only.11.4 Batching Custom Documents
Custom documents can be used to leverage the batching feature to batch the outgoing custom documents. The batch can be triggered based on:
Note:
To enable batching of custom documents, you must set the EM property b2b.batchCustoDocument to true-
Time - To trigger the batch at a scheduled time
-
Count - To trigger when the number of messages received matched the configured count
-
Size - To trigger when the size of total number of messages reach the configured one
Figure 11-4 Scheduling a Batch for Custom Documents
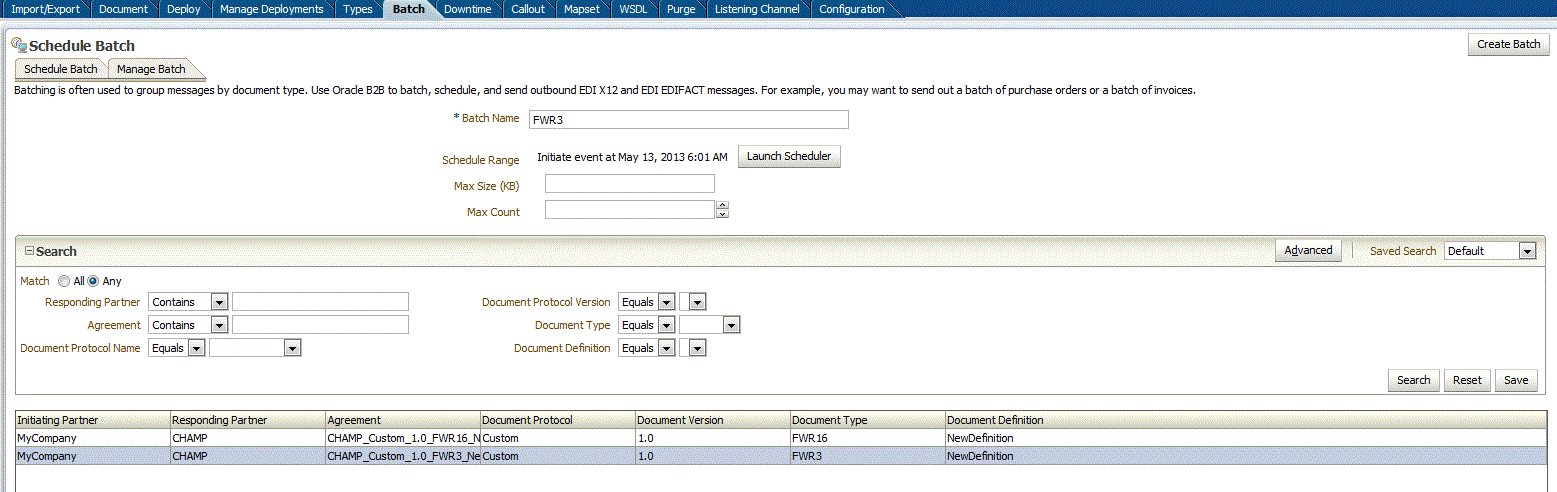
Description of "Figure 11-4 Scheduling a Batch for Custom Documents"
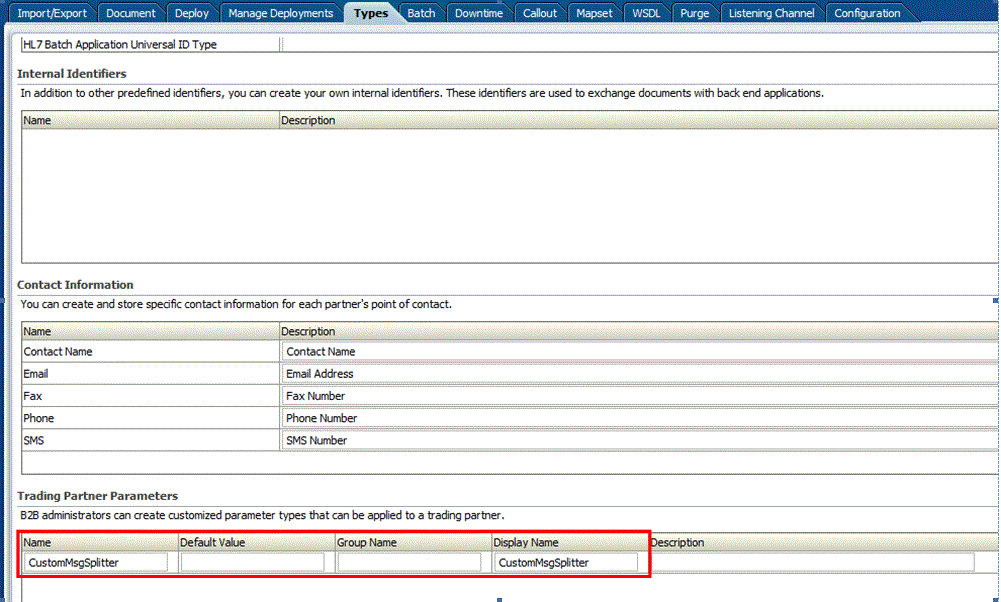
The messages that are batched together are separated by a configurable delimiter. This is configured as part of trading partner parameter. In order to achieve this, set the trading partner parameter name in Administration -> types. The parameter name is: CustomMsgSplitter
The value for the custom message splitter can be configured in profile screen, see Figure 11-5.
The same delimiter is used for inbound as well as outbound functions. This can be retrieved using the public API for trading partner parameters.
You can also arrive at the delimiter by providing the delimiter for a specific document of a particular trading partner. The delimiter provided in Figure 11-6 is available as part of the callout argument.
Figure 11-6 Documents Specific to a Trading Partner Details
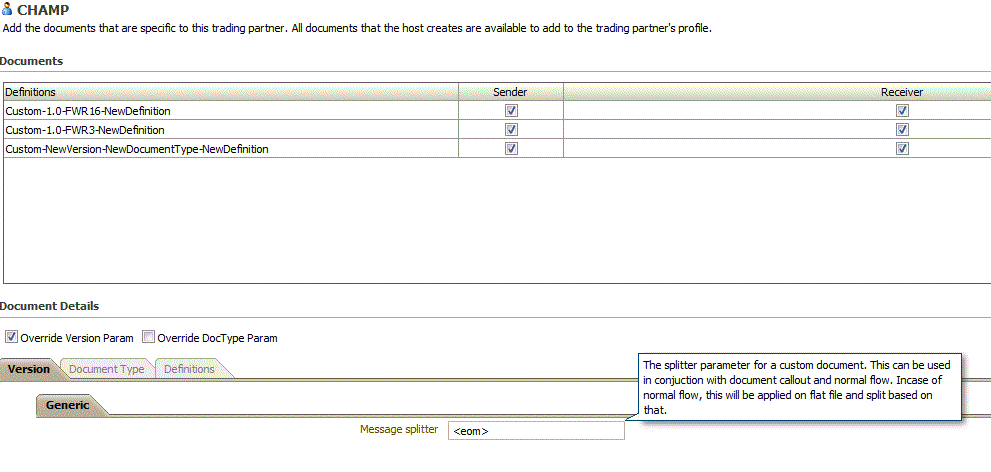
Description of "Figure 11-6 Documents Specific to a Trading Partner Details"