3 Deploying Dataspaces
This chapter describes how to deploy dataspaces to an Administration Server, a Managed Server, and a cluster. It also describes how to migrate dataspaces from development to production.
The chapter contains the following sections:
3.1 Introduction
Oracle Data Service Integrator Administration Console provides you the ability to deploy, export and import dataspaces. Using the console, you can export, import, and delete dataspaces that are deployed on a WebLogic Server without interrupting other running dataspaces. In addition, you can import artifacts to an existing dataspace without interrupting existing requests running against that dataspace
During development, you can deploy dataspaces to a WebLogic Server directly from the eclipse-based IDE. After development, you can deploy dataspaces to production WebLogic Servers using the Oracle Data Service Integrator Administration Console or the IDE.
3.2 Creating a New Dataspace
You can create a new dataspace using the Oracle Data Service Integrator Administration Console and associate a JAR file with it. This enables you to create and manage the dataspace on the server directly.
Only a domain user has the ability to create a new dataspace. For more information about domain users, refer to Section 5.6, "Working with Administrative Access Control Policies" in Chapter 5, "Securing Oracle Data Service Integrator Resources."
To create a new dataspace in the Oracle Data Service Integrator-enabled WebLogic domain:
-
Click the System Administration category from the navigation pane.
-
Select the domain node.
-
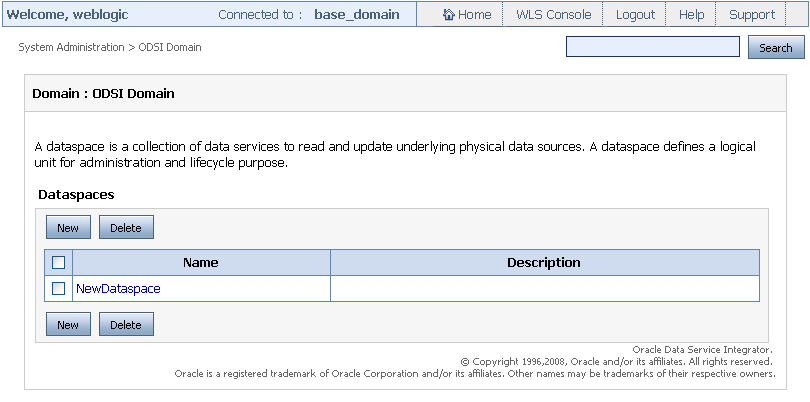
From the workspace content area, click New as shown in Figure 3-1.
-
On the Create Dataspace page shown in Figure 3-2, specify the following:
-
Name: Name of the new dataspace that you want to create.
-
Description: An optional description of the dataspace.
-
Resource File: A JAR file that you want to import in the dataspace. This is optional.
Figure 3-2 Specifying the New Dataspace Details
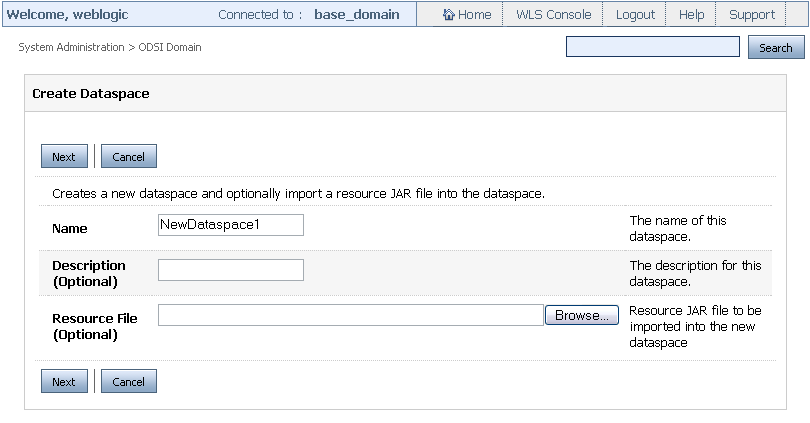
Description of ''Figure 3-2 Specifying the New Dataspace Details''
-
-
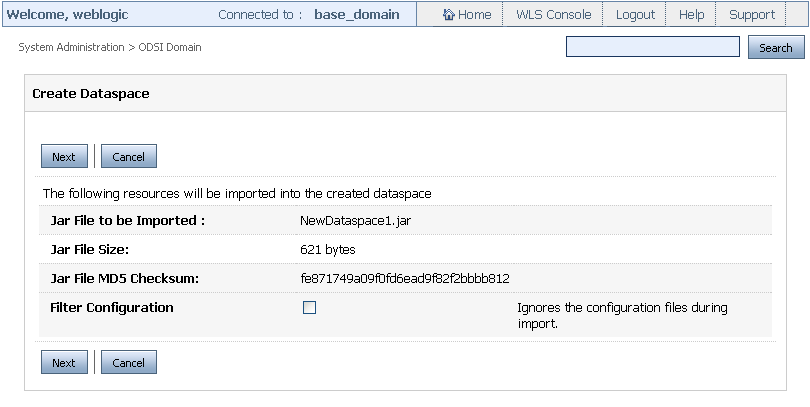
Click Next. This displays details such as the file size and checksum information about the resource file being imported as shown in Figure 3-3.
-
On this page, select the Filter Configuration checkbox if you do not want to import the resource file configuration. To retain the resource file configurations, make sure that you do not select the Filter Configuration checkbox.
Each dataspace contains one .space file that contains all the global dataspace properties. For example, for a dataspace my_dspace_DS there is a corresponding file named My_DSpace.space. The dataspace also contains one file, named My_DSpace.sources, that contains all the properties pertaining the physical sources used by the dataspace My_DSpace.
For each dataservice (.ds) file contained in the dataspace, there is a .service file named after the dataservice and located within the same folder as the data service, that carries the data service configuration properties.
Finally, a dataspace may contain one or more .xml files under the folder
DSP-INF/service-accounts, which carry service account information details. -
Click Next. This displays the page where you can select the state and targets for the dataspace as shown in Figure 3-4.
Figure 3-4 Selecting the State and Target Server for a Dataspace
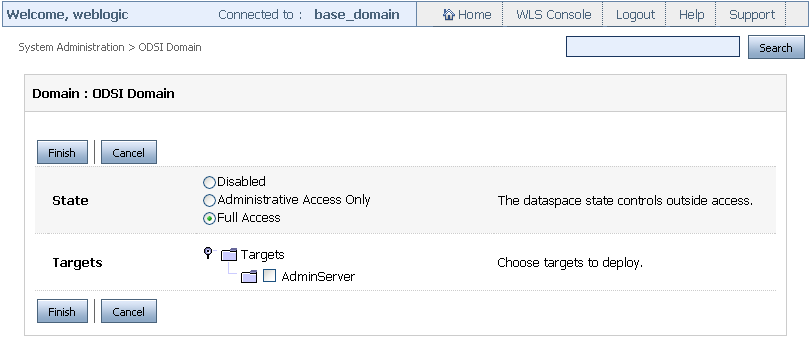
Description of ''Figure 3-4 Selecting the State and Target Server for a Dataspace''
A deployed dataspace can be in one of the following states:
-
Disabled: The dataspace is not live and cannot be administered from the console.
-
Administrative Access Only: The dataspace is accessible only to the Administrator.
-
Full Access: This dataspace is accessible to all authorized users.
-
-
Specify the state and target server and click Finish to create and deploy the new dataspace.
Note:
You may need to wait for sometime before the new dataspace is deployed successfully depending on the size of the dataspace.
3.3 Deleting a Dataspace
Only a domain user can delete a deployed dataspace. To delete a dataspace:
-
Navigate to the ODSI Domain level.
-
Select the dataspace that you need to delete as shown in Figure 3-5.
Figure 3-5 Selecting the Dataspace to Delete
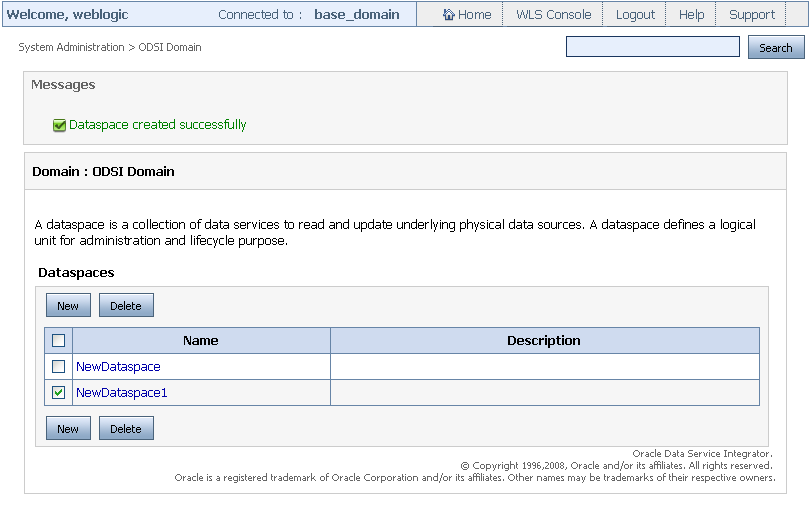
Description of ''Figure 3-5 Selecting the Dataspace to Delete''
-
Click Delete. The next page confirms if you want to delete the dataspace. Select Yes to delete the dataspace.
Note:
If you delete the target Managed Server on which your dataspace is deployed, the dataspace deletion will fail.
3.4 Deploying Dataspaces on a Target Server
Deployment is done through the System Administration category in the Oracle Data Service Integrator Administration Console. Oracle Data Service Integrator dataspaces can only run in an Oracle Data Service Integrator-enabled WebLogic domain. You can create a new WebLogic domain using the Configuration Wizard.
This chapter discusses how to deply dataspaces on a target server. It includes the following topics:
For more information about using the Configuration Wizard to set up an Oracle Data Service Integrator-enabled WebLogic domain, refer to Section 1.2.1.1, "Creating a New Domain" in Chapter 1, "Overview of Oracle Data Service Integrator Administration."
The Configuration Wizard automatically transfers the required items to the target server. These include the Oracle Data Service Integrator dataspace artifacts, with the corresponding configuration and binary files, as well as WebLogic components such as data source connections and pools. When you move a dataspace from the development to production, you need to make sure that these items are transferred to the target production server.
Note:
A target server can be an Administration Server, a Managed Server, or a cluster. The steps to deploy dataspaces on any of these targets are the same.An Administration Server is the central configuration repository for the set of WebLogic Servers in a domain.
You can deploy a dataspace on multiple Managed Servers and clusters depending on your requirement. To deploy dataspace artifacts on a Managed Server or a cluster, you must first create a Managed Server or cluster using the Configuration Wizard.
If you need to deploy a Web Service Map on a cluster, then you need to specify the cluster address. For details, refer to Section 3.4.2, "Deploying a Web Service Map on a Cluster."
For more information about creating Managed Servers, refer to the Create Managed Servers topic in WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help at http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E12840_01/wls/docs103/ConsoleHelp/taskhelp/domainconfig/CreateManagedServers.html.
For more information about creating clusters, refer to the Create a Cluster topic in the WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help at http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E12840_01/wls/docs103/ConsoleHelp/taskhelp/clusters/CreateCluster.html.
This section includes the following topics:
3.4.1 Deploying a Dataspace
To deploy a dataspace on WebLogic Server using Oracle Data Service Integrator Administration Console:
-
Start the Oracle Data Service Integrator Administration Console.
For more information, see Section 2.2, "Launching Oracle Data Service Integrator Administration Console" in Chapter 2, "Getting Started with Oracle Data Service Integrator Administration."
-
Select the System Administration category and then select the Targets tab from the workspace content area as shown in Figure 3-6.
Figure 3-6 Deploying a Dataspace on a Target Server
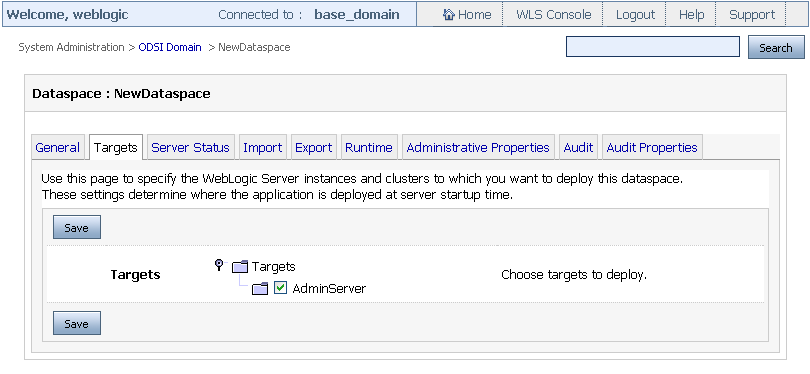
Description of ''Figure 3-6 Deploying a Dataspace on a Target Server''
-
Select the target server on which you want to deploy the dataspace.
-
Click Save. This set the target server for your Oracle Data Service Integrator dataspace.
-
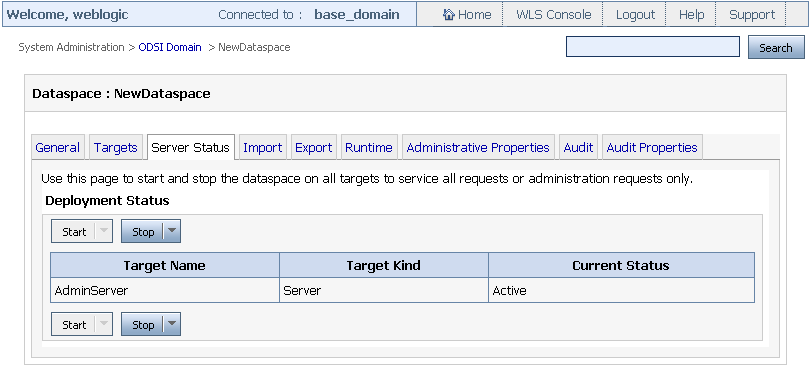
To view or change the deployment status, click the Server Status tab as shown in Figure 3-7.
The options to start and stop the target servers are mentioned in the following table:
Table 3-1 Options for Starting and Stopping Server
State Option Description Start
Servicing Administration Requests
Select this option when the dataspace is accessible only at the Administration level. This usually happens when the dataspace project is deployed on the production server and is yet to go live.
Start
Servicing All Requests
Select this option when the dataspace is ready to service all client requests.
Stop
Servicing Non-Administration Requests
Select this option when you need to stop servicing requests from clients but continue servicing administration requests.
Stop
Servicing All Requests
Select this option if you need to stop servicing requests from all clients including administration requests.
3.4.2 Deploying a Web Service Map on a Cluster
Before you deploy a web service map on a cluster you need to specify the cluster address using the WebLogic Server Administration Console. If you do not specify the cluster address then the WSDL creation for the web service map fails.
To specify the cluster address on WebLogic Server, specify the cluster address in the Configuration > General tab for the cluster as shown in Figure 3-8.
Figure 3-8 Specifying Cluster Address on WebLogic Server
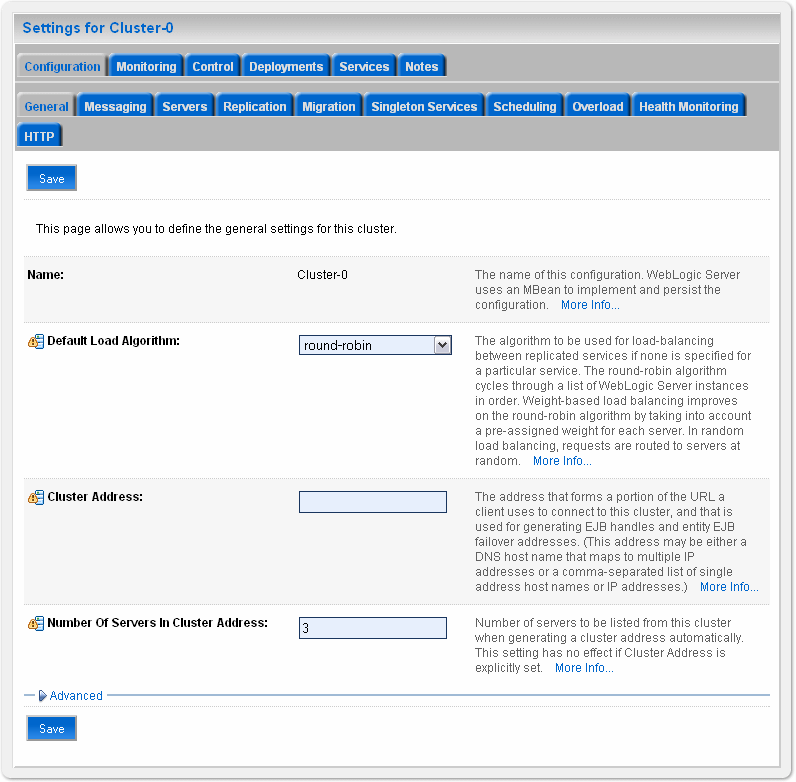
Description of ''Figure 3-8 Specifying Cluster Address on WebLogic Server''
For detailed information about configuring clusters on WebLogic Server, refer to Create and Configure Clusters at http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E12840_01/wls/docs103/ConsoleHelp/taskhelp/clusters/ClusterRoadmap.html.
3.5 Importing Dataspace Artifacts
Oracle Data Service Integrator Administration Console allows you to perform incremental and full deployment of resource JAR files. This section describes the steps to perform incremental and full deployment through the Oracle Data Service Integrator Administration Console.
Note:
You can also import the data service configuration settings from ALDSP 2.5. This enables you to use the same configurations that you used in the ALDSP 2.5 environment, while continuing to work with Oracle Data Service Integrator.To perform incremental or full deployment of resource files:
-
Acquire the lock by selecting Lock & Edit.
-
From the Navigation pane, select the System Administration category and then select the dataspace in which you want import configuration or artifacts.
-
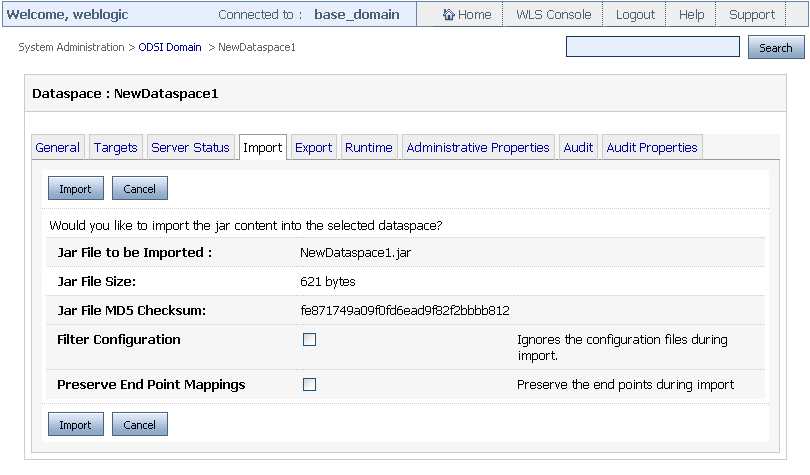
Click the Import tab as shown in Figure 3-9.
Figure 3-9 System Administration Category: Import Tab
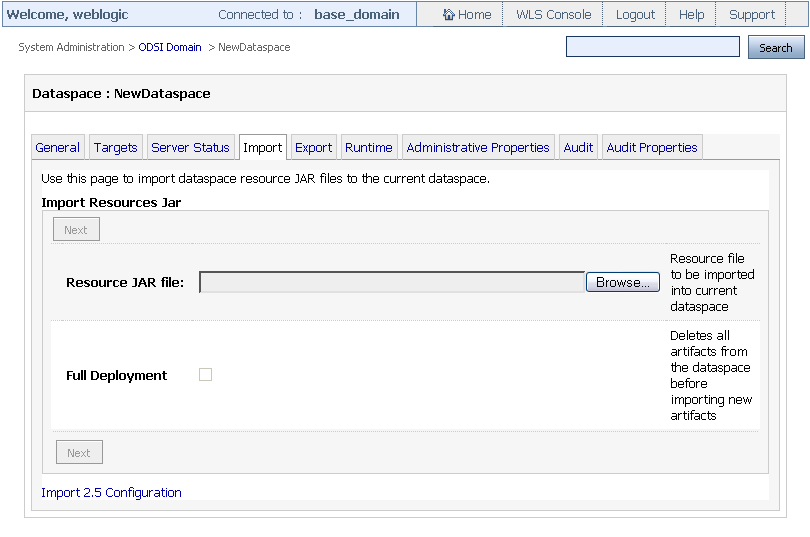
Description of ''Figure 3-9 System Administration Category: Import Tab''
-
Browse and specify the resource file path in the Resource JAR File box.
-
If you want to perform full deployment, select the Full Deployment check box from the Import Resource Jar section. If you select this option, then the system deletes all the artifacts from the dataspace and then imports the new artifacts.
-
If you want perform incremental deployment, do not select the Full Deployment check box. In case of incremental deployment, Oracle Data Service Integrator updates only those dataspace artifacts that have changed and adds any new artifacts.
As part of incremental deployment, if you need to delete any artifacts, you can provide an additional delete.list file in the import JAR under the META-INF folder. An example of a delete.list file is shown here:
<del:DeleteList xmlns:del='http://www.bea.com/dsp/management/deployment'> <Entry>test/RDBMS/RTL-ALL/CUSTOMER.ds</Entry> <Entry>test/RDBMS/RTL-ALL/schemas/CUSTOMER.xsd</Entry> </del:DeleteList>
Each entry in the list is deleted from the dataspace.
-
Click Next to move to the page that displays the resource JAR file details, which include file checksum details and file size as shown in Figure 3-10. In addition, this page provides the following options:
-
Filter Configuration: Select this option if you do not want to import the configurations of the resource file.
-
Preserve End Point Mappings: Select this option if you want import all the configuration and the resources (artifacts) but keep the old endpoint mappings intact.
This option is useful when you move configurations from the staging server to a live production server. On the staging server, you configure and test the configurations. If the testing is successful, move the configurations from the staging to the production server.
However, the endpoints used during staging and production would not be the same as you would not be testing directly on production server. So, when you import mappings from the staging server, you may want to retain the mappings that already exist in the production database. In that case, select the Preserve Endpoint checkbox.
-
-
After selecting options on this page, click Import. When the import is completed, the message "Import operation was successful" is displayed.
Note:
Depending on the size of the files and the topology of your domain, the import operation may take time, therefore you may need to wait for import to complete. -
Click Activate Changes from the change center to activate the import.
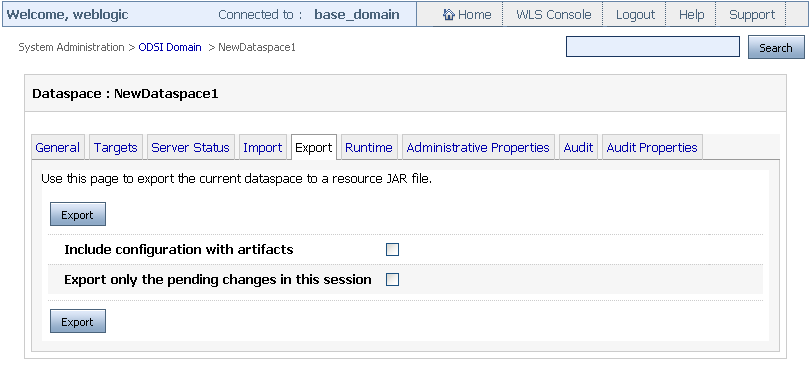
3.6 Exporting Dataspace Artifacts
You can export dataspace artifacts with or without retaining the configuration settings. To export dataspace artifacts:
-
Click the System Administration Category and the dataspace that you want to export as a JAR.
-
Click the Export tab.
-
Select the Include configuration artifacts check box as shown in Figure 3-11, if you want to export the configuration along with all the artifacts.
-
If you are already in a session and want to export changes that have occurred within that session then select the Export only the pending changes in this session check box.
Note:
The Export only the changes in this session check box is enabled only when the lock is acquired. -
Click Export
-
Specify the location where you want to save the dataspace artifacts and the file is saved as a JAR file at the specified location.