63 Using REST Resources with the WEM Framework
You can manage assets using the WebCenter Sites REST API if you grant privileges on applications' resources to perform REST operations.
Topics:
63.1 Authentication for REST Resources
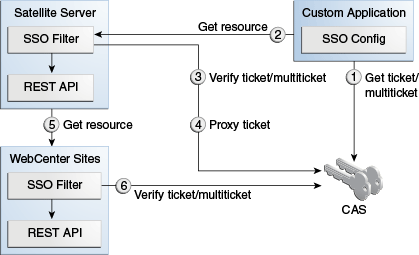
The WEM Framework uses the SSO mechanism built on top of CAS for authentication purposes. The system behaves differently when you use the REST API from a browser or programmatically.
When accessing the REST API from a browser, the user is redirected to the CAS login page and, upon successful login, back to the original location with the ticket parameter, which is validated to establish the user's identity. When accessing the REST API programmatically, the developer must supply either the ticket or multiticket parameter.
Both the ticket and multiticket parameters could be acquired by using either the Oracle SSO API if making calls from Java, or simply by using the HTTP protocol if making calls from any other language. The difference between ticket and multicket is that a ticket is acquired per each REST resource and can be used only once (as the name implies, think of a train or a theater ticket, which is valid for one ride or one play), while a multiticket could be used multiple times for any resource. Both the ticket and multiticket parameters are limited in time, but the typical usage pattern differs. As a ticket is acquired per each call, there is no expiration time. However, reusing the same multiticket will eventually lead to its expiration and getting an HTTP 403 error. The application must be able to recognize such behavior and fall back to the multiticket re-acquisition procedure in such a case. The decision to use either ticket or multiticket is up to the application developer.
Topics:
63.1.1 Acquiring Tickets from Java Code
The Oracle SSO API is implemented in an authentication provider-independent manner. Users are not able to register their own SSO authentication providers. Support for a new authentication provider can be implemented only by Oracle. Switching between providers involves only changing the SSO configuration files.
All SSO calls originate at the SSO front-end class SSO. It is used to get the SSOSession object. SSOSession is acquired per each SSO configuration. It is a single configuration in the web application case, which is loaded using the Spring Web application loader or a configuration loaded from a configuration file in the case of a standalone application.
-
To acquire a ticket in a Web application:
SSO.getSession().getTicket(String service, String username, String password) SSO.getSession().getMultiTicket(String username, String password)
-
To acquire a ticket in a standalone application:
SSO.getSession(String configName).getTicket (String service, String username, String password) SSO.getSession(String configName).getMultiTicket (String username, String password)
63.1.2 Acquiring Tickets from Other Programming Languages (Over HTTP)
The CAS REST API is used to acquire a ticket, or a multiticket, or both in the delivery environment. Two HTTP POST calls should be performed to acquire either ticket or multiticket. The difference between ticket and multiticket is that the service parameter is * (asterisk) for multiticket, while it is an actual REST resource you are trying to access for the ticket parameter.
The example below demonstrates the calls to be made to the CAS server to get a ticket to the http://localhost:8080/cs/REST/sites service with fwadmin/xceladmin credentials:
The protocol is fairly straightforward. First a call to get Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) is made by passing the user name and password parameter in application/x-www-form-urlencoded POST request. The Response will contain the Location HTTP header, which should be used to issue a second application/x-www-form-urlencoded POST request with service parameter. The response body will contain the actual ticket.
63.1.3 Using Tickets and Multitickets
To use the generated ticket/multiticket, supply the ticket/multiticket URL query parameter. For example:
http://localhost:8080/cs/REST/sites?ticket=ST-1-7xsHEMYR9ZmKdyNuBz6W-cas http://localhost:8080/cs/REST/sites?multiticket=ST-2-Bhen7VnZBERxXcepJZaV-cas
By default the communication channel between WebCenter Sites and Remote Satellite Server is not trusted. The proxyTickets parameter in the SSOConfig.xml file on Remote Satellite Server is set to true, which forces Remote Satellite Server to proxy the ticket supplied by the application that is being accessed.
For optimal performance, the system can be configured for authentication by Satellite Server alone. The security check should be disabled on the WebCenter Sites side by excluding the REST and WebCenter Sites elements used by the REST API from the SSO filter. The proxyTickets parameter in the SSOConfig.xml file on Remote Satellite Server should be set to false. In this mode it is possible to leverage multitickets. Note that the WebCenter Sites installation should be hosted inside a private network in this mode, and the communication channel between WebCenter Sites and Remote Satellite Server should be trusted.
63.1.4 SSO Configuration for Standalone Applications
The single sign-on module relies on the Spring configuration. The only required bean is ssoprovider, which references the ssoconfig bean.
This section includes the following topics:
63.1.4.1 Beans and Properties
The following table describes ssolistener beans and properties.
id="ssolistener", class="com.fatwire.wem.sso.cas.listener.CASListener"
Table 63-1 id="ssolistener"
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| No properties for this bean. | n/a |
The following table describes ssofilter beans and properties.
id="ssofilter", class="com.fatwire.wem.sso.cas.filter.CASFilter"
Table 63-2 id="ssofilter"
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Required. SSO configuration reference. Sample Value: |
|
|
Required. SSO provider reference. Sample Value: |
The following table describes provider beans and properties.
id="provider", class="com.fatwire.wem.sso.cas.CASProvider"
Table 63-3 id="provider"
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
SSO configuration reference. Sample Value: |
The following table describes config beans and properties.
id="config", class="com.fatwire.wem.sso.cas.conf.CASConfig"
Table 63-4 id="config"
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Proxy callback path, relative to Sample Value: |
|
|
Use this property to specify the default behavior on unauthenticated access to protected pages. Sample Value: |
|
|
Login page path, relative to Can accept additional query parameters:
Sample Value: |
|
|
CAS REST servlet path, relative to Sample Value: |
|
|
Logout page path, relative to Sample Value: |
|
|
Required property. CAS URL prefix. The URL must resolve both internally and externally. Example: |
|
|
If |
|
|
Be careful when enabling the redirect behavior to occur by default. Ensure the clients are able to follow the redirects. Otherwise, Default value: |
|
|
Multiticket timeout in msecs. Default value: The CAS multiticket timeout is based on |
|
|
List of mappings that should be excluded. Regular expressions are allowed. Allowed value: |
|
|
List of protected mappings. Regular expressions are allowed. Allowed value: path is a URL path part. It may contain asterisks ( Example
Parameters may contain only Example
|
|
|
To make custom REST resources in an application available through remote Satellite Server, specify the following value:
Example
|
|
|
Specifies whether to proxy tickets. Set this property to Set this property to Default value: |
|
|
Specifies whether to use multitickets. Default value: |
63.1.4.2 Query Parameters Processed by SSO Filter
This table describes query parameters that are processed by SSO filter.
Table 63-5 Query Parameters Processed by SSO Filter
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Used to verify user identity. Can be used only during some limited period of time for one resource and only once. Type: Value: |
|
|
Used to verify user identity. Can be used only during some limited period, multiple times for any resource. Type: Value: |
|
|
If this property is set to Type: Value: |
|
|
Used to specify the default behavior on unauthenticated access to protected pages. If this property is set to Type: Value: |
63.2 About Configuring CAS
Here are some sources for information on CAS clustering.
-
For information about CAS architecture, use the following link:
-
For information about configuring CAS clustering during the WebCenter Sites installation, see Setting Up a CAS Cluster in Oracle Fusion Middleware Installing and Configuring Oracle WebCenter Sites.
-
For information about configuring CAS with LDAP providers, use the following link:
http://www.jasig.org/cas/server-deployment/authentication-handler
63.3 REST Authorization
REST authorization is the process of granting privileges to perform REST operations on applications' resources (which map to objects in WebCenter Sites). REST authorization uses the deny everything by default model. A privilege is denied when it is not explicitly granted to a particular group.
Topics:
63.3.1 Security Model
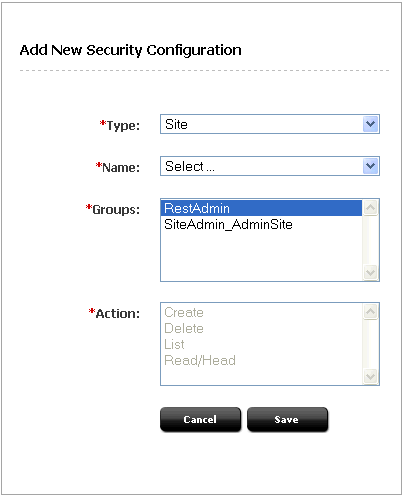
The WEM security model is based on objects, groups, and actions. Security must be configured per object type in the Admin interface. Objects of a given type are accessible to a user only if the user belongs to at least one group with privileges to perform specified actions on the objects of the given type.
Figure 63-2 Add New Security Configuration
Description of "Figure 63-2 Add New Security Configuration"
-
Object is a generic term that refers to any entity in the WEM Framework such as a site, a user, or an asset. Protected objects are of the following types:
-
Asset Type
-
Asset
-
Index
-
Site
-
Role
-
User
-
User Locale
-
ACL
-
Application
-
-
Security groups are used to gather users for the purpose of managing their permissions (to operate on objects) simultaneously.
-
An action is a security privilege:
LIST,READ,UPDATE,CREATE,DELETE.LISTprovidesGETpermission on services that list objects (such as/types), whereasREADprovidesGETpermission on services that retrieve individual objects in full detail (such as/types/{assettype}).Privileges are assigned to groups to operate on allowed objects. Some objects, such as ACLs, are read-only (they can be created directly in WebCenter Sites, but not over REST).
A security configuration is an array, such as shown above, which specifies:
-
The protected object type and object(s)
-
Groups that are able to access the objects
-
Actions that groups (and their members) can perform on the objects
For more information about possible security configurations and the Web Experience Management Framework, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle WebCenter Sites.
63.3.2 Use of the Security Model to Access REST Resources
Object types and objects in WebCenter Sites map to REST resources in the WEM Framework. For example, the Asset Type object maps to:
-
<BaseURI>/types/resource (which lists all asset types in the system) -
<BaseURI>/types/<assettype>resource (which displays information about the selected asset type), and so on
Actions in WebCenter Sites map to REST methods in the WEM Framework. For example, granting the READ privilege to group Editor to operate on asset type Content_C gives users in the Editor group permission to use GET and HEAD methods on the REST resource /types/Content_C.
-
The
LISTaction allows group members to useGETmethods on REST resources. -
TheREADaction allows group members to useGETandHEADmethods on REST resources. -
The
UPDATEaction allows group members to usePOSTmethods on REST resources. -
The
CREATEaction allows group members to usePUTmethods on REST resources. -
The
DELETEaction allows group members to useDELETEmethods on REST resources.
For comprehensive information, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware REST API Resource Reference for Oracle WebCenter Sites.
63.3.3 About Configuring REST Security
See Using REST Security in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle WebCenter Sites.
63.3.4 Privilege Resolution Algorithm
When configuring a security privilege, specify that the privilege applies to all objects of a certain type or a single object of a certain type. For example, granting the privilege to UPDATE (POST) any site allows users in the group to modify the details of all sites in the WEM Framework.
The Asset object type requires you to specify the site to which the security setting applies, as assets are always accessed from a particular site. The AssetType object can be extended by specifying a subtype, which is used to make the security configuration more granular. For example, setting the DELETE privilege on asset type Content_C allows a DELETE request to be performed on the REST resource /types/Content_C (that is, to delete the Content_C asset type from the system).
Because privileges can be granted only to groups, a user's total privileges are not obvious until they are computed across all of the user's groups. The WEM Framework provides a privilege resolution algorithm. Its basic steps are listed below:
-
REST finds the groups in which the user has membership.
-
REST determines which groups can perform which REST operations on which REST resources. If site or subtype is specified, each is taken into account.
-
REST compares the results of steps 1 and 2. Access is granted if at least one of the groups from step 1 is in the list of groups from step 2. Otherwise, access is denied.
63.4 Management of Assets Over REST
Sample code that illustrates how you can manage assets with the WebCenter Sites REST API is available in your WebCenter Sites installation directory.
See the following locations:
Misc/Samples/WEM Samples/REST API samples/Basic Assets/com/fatwire/rest/samples/basic/ Misc/Samples/WEM Samples/REST API samples/Basic Assets/com/fatwire/rest/samples/flex/
The subfolders basic and flex each contain the following set of files:
-
CreateAsset.java -
DeleteAsset.java -
ReadAsset.java -
UpdateAsset.java.
The code is richly documented with step-by-step instructions.