C MAF Application and Project Files
This appendix provides a reference for the files that OEPE generates when you create a MAF application using the Mobile Application Framework Application template.
This appendix includes the following section:
C.1 Introduction to MAF Application and Project Files
By default. OEPE creates a MAF application with three projects:
-
Assembly project, which contains application-wide resources such as a login page if you configure security for your MAF application.
-
Application project, which contains the Data Control Manager.
-
View project, which contains application feature resources such as HTML, AMX, or task flow files that render the content of an application feature.
OEPE also generates files within these projects that you use to configure your MAF application and application features or files that your MAF application needs when you deploy it to the targeted platform. In almost every case, you do not work with the generated files directly. Instead you use the editors, such as the MAF Application Editor, the MAF Features Editor and the Data Control Manager.
C.2 About the Assembly-Level Resources
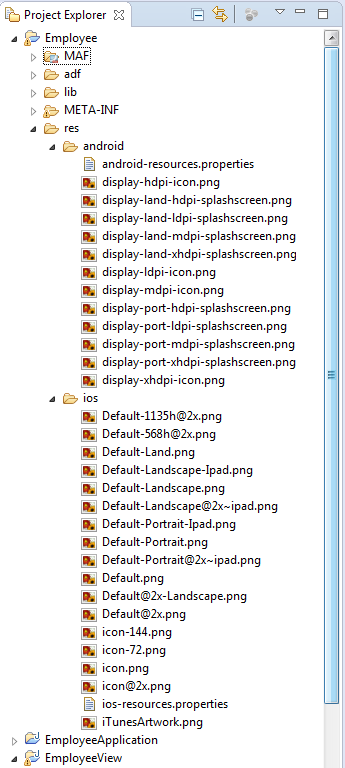
Oracle Enterprise Pack for Eclipse generates the files for the MAF application in the assembly project. These files contain configuration files for describing the metadata of the MAF application. You access these files from the res node under the assembly project in the Project Explorer, shown in Figure C-1.
The assembly project (which is generated with the default name, application), which contains the application-wide resources, provides the presentation layer of the MAF application in that it includes metadata files for configuring how the application will display on a mobile device. This project dictates the security for the MAF application and can include the application's login page, an application-wide resource. The application controller project is essentially a consumer of the view controller project, which defines the application features and their content.
Tip:
Place code that supports application-wide functionality, such as an application-level lifecycle listener, in the application controller project.Table C-1 Mobile Application-Level Artifacts Accessed Through Top_Level Project
| Artifact(s) | File Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
For example:
|
A stub XML application descriptor file that enables you to define the MAF application. Similar to the application descriptors for ADF Fusion Web applications, this enables you to define the content for an application, its navigation behavior, and its user authentication requirements. |
|
|
For example:
|
Use to configure the default skin used for MAF applications. |
|
Application images |
For example:
|
A set of images required for the deployment of iOS and Android applications. These include PNG images for application icons and splash screens. Deployment to an iOS-powered device, such as an iPhone, requires a set of images in varying sizes. The default iOS images provided with the project include:
To override these images, see Section 27.2.4.5, "How to Add a Custom Image to an Android Application." |
|
|
For example:
|
The |
|
|
For example:
|
Enables you to set the application error logging, such as the logging level and logging console. For more information, see Section 30.4, "Using and Configuring Logging." |
|
|
For example:
|
The configuration file for the Java virtual machine, JVM 1.4. Use this file to configure the application startup and heap space allotment, as well as Java and JavaScript debugging options. For more information, see Section 30.3.5, "How to Enable Debugging of Java Code and JavaScript." |
|
|
For example:
|
Used to configure application-level settings, including the Configuration Service parameters. See also Chapter 17, "Configuring End Points Used in MAF Applications." |
|
|
For example:
|
The repository for all of the connections defined in the MAF application. |
|
|
For example:
|
The configuration file for the offline cache of data returned from REST web services. Caching not only improves the user experience by boosting performance, but allows users to read and view data when they are working in an off-line mode. |
Within the application project itself (which is generated with the default name, applicationApplication) OEPE creates the following artifacts, listed in Table C-2.
Table C-2 Application Project Artifacts
| Artifact(s) | File Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
For example:
|
The default application lifecycle listener (ALCL) for the MAF application. |
|
|
For example:
|
Defines the available skins and also enables you to define new skins. For more information, see Chapter 8, "Skinning MAF Applications." |
|
|
For example:
|
Maintains the paths (and relative paths) for the |
|
|
For example:
|
The data controls registry. For information on using the DeviceFeatures data control, which leverages the services of the device, see Chapter 14, "Using Bindings and Creating Data Controls in MAF AMX." For information on the ApplicationFeatures data control, which enables you to create a springboard page that calls the embedded application features, see Section 5.1.5, "What You May Need to Know About Custom Springboard Application Features with MAF AMX Content." |
C.3 About the View Project Resources
The view project (which is generated with the default name, applicationView), as illustrated in Figure C-3) houses the resources for the application features. Unlike the application project the view project's metadata files describe the resources at the application feature-level, in particular the various application features that can be aggregated into a MAF application so that they can display on a mobile device within the springboard of the MAF application itself or its navigation bar at runtime. Further, the application feature metadata files describe whether the application feature is comprised of HTML or MAF AMX pages. In addition, the view controller project can include these application pages as well as application feature-level resources, such as icon images to represent the application feature on the springboard and navigation bar defined for the MAF application.
Tip:
Store code specific to an application feature within the view controller project. Use the application controller project as the location for code shared across application features, particularly those defined in separate view controller projects.The view controller project can be decoupled from the application controller project and deployed as an archive file for reuse in other mobile applications as described in Section 9.1, "Working with Feature Archive Files." In rare cases, an application controller project can consume more than one view controller project.
Note:
Adding a MAF view controller project as a dependency of another MAF view controller project, or as a dependency of a MAF application controller project, prevents the deployment of a MAF application.These resources include the configuration file for application features called maf-feature.xml, which you edit using the MAF Feature Editor.
Table C-3 View Controller Artifacts
| Artifact(s) | File Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
For example:
|
A stub XML descriptor file that enables you to define application features. After you have configured the Mobile Preferences as described in Oracle Enterprise Pack Installing Oracle Enterprise Pack for Eclipse you can deploy this application using the default deployment configuration settings. For more information, see Chapter 27, "Deploying Mobile Applications." |
|
Application-Specific Content |
For example:
|
The application features defined in |