12 Implementing Application Feature Content Using Remote URLs
This chapter describes how application features with content from remote URLs can access (or be restricted from) device services.
This chapter includes the following sections:
-
Section 12.2, "Creating Whitelists for Application Components"
-
Section 12.3, "Enabling the Browser Navigation Bar on Remote URL Pages"
12.1 Overview of Remote URL Applications
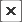
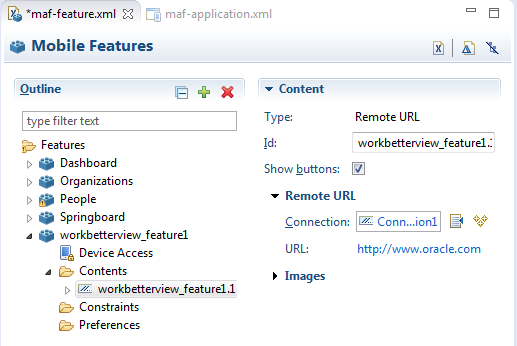
By configuring the content type for an application feature in the MAF Feature Editor as Remote URL, as shown in Figure 12-1, you create a browser-based application that is served from the configured URL. Such server-hosted applications differ from the client applications written in MAF AMX, local HTML, or a platform-specific language such as Objective-C in that they are intended for occasional use and cannot directly access the device's memory or services (such as the camera, contacts, or GPS). These interactions are instead contingent upon the capabilities of the device's browser. Remote applications that open within the MAF web view, however, access device features using Apache Cordova JavaScript APIs (and the MAF JavaScript API to access the MAF container services). The Apache Cordova JavaScript API libraries are platform-specific, which means you must ensure that the content used for a remote URL application references the Apache Cordova library appropriate to the target platform. See Section B.1, "Using MAF APIs to Create a Custom HTML Springboard Application Feature."
12.1.1 Enabling Remote Applications to Access Device Services through Whitelists
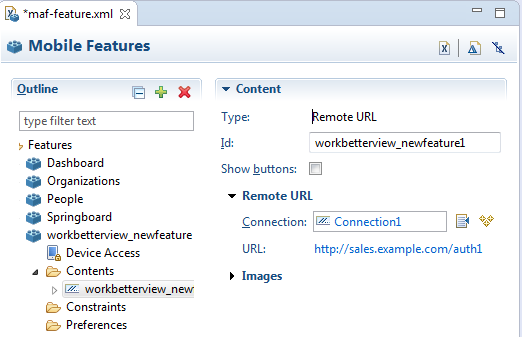
To ensure security for remotely served content, MAF supports the concept of whitelists, a registry of URLs that opens within the application web view to access various device services, such as GPS, a camera, or a file system. If a web page is not included on a whitelist (that is, it is not whitelisted), then MAF's Apache Cordova implementation opens a web page in the device browser (such as Safari) instead. Without whitelisting, a remote web page cannot open within the MAF web view, thereby limiting its access to the embedded device capabilities. As illustrated in Figure 12-2, a URL that opens within the MAF web view is presented as an application feature.
12.1.2 Enabling Remote URL Implementations to Access Apache Cordova
Remote URL implementations use Apache Cordova JavaScript APIs to access device features and the MAF JavaScript API to access the MAF container services. As described in Appendix B, "Application Container APIs," a JavaScript <script> tag that references the www/js/base.js libraries enables this access. These libraries are platform-specific, meaning that you must ensure that the content used for a remote URL application references the Apache Cordova library appropriate to the target platform. The Apache Cordova JavaScript API libraries are platform-specific, which means you must ensure that the content used for a remote URL application references the Apache Cordova library appropriate to the target platform. See Section B.1, "Using MAF APIs to Create a Custom HTML Springboard Application Feature."
12.1.3 How Whitelisted Domains Access Device Capabilities
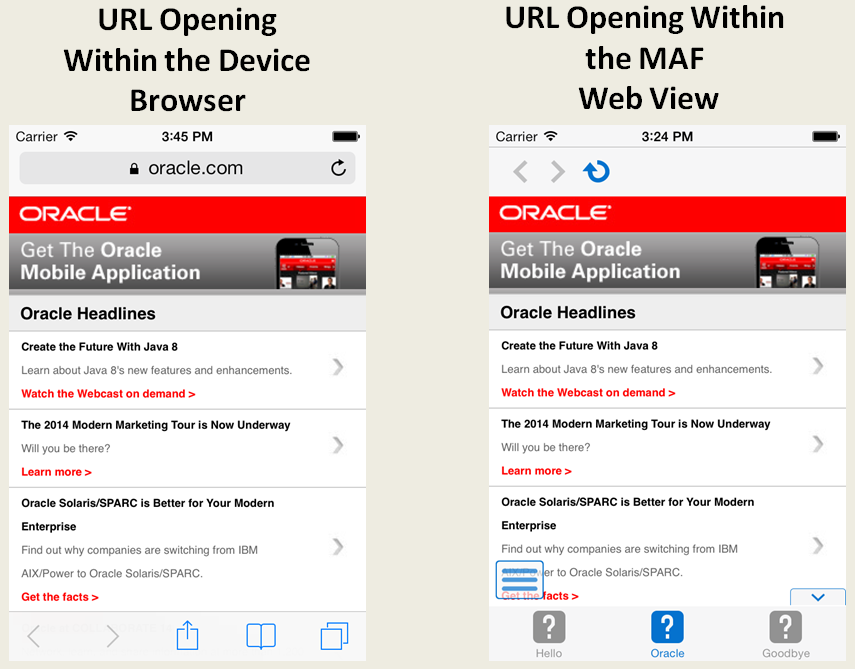
By default, the domains defined in the connections.xml file (the repository for all of the connections defined in the mobile application) are whitelisted automatically. These domains for the Remote URL content are created using the Create URL Connection dialog, shown in Figure 12-3. MAF parses the domain from each of the connection strings and adds these domains to the whitelist.
Oracle Enterprise Pack for Eclipse then populates the connections.xml file, located in the assembly project under adf > META-INF, with the connections information and also creates the connection resources.
In addition to the domains that MAF includes from the connections.xml file, you can enable (or restrict) remote URL content to open with the MAF web view by configuring the following in the MAF Application Editor:
-
One or more whitelisted domains
-
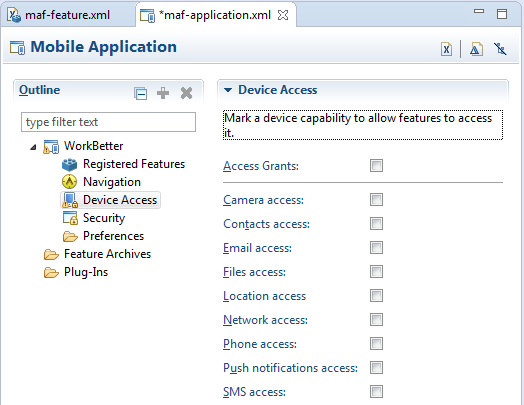
Device access permissions—As described in Section 21.6, "Allowing Access to Device Capabilities," an application feature only accesses the device capabilities that have been granted at the application level; by default, MAF applications do not allow any access to the Apache Cordova APIs. If an application's user interface is implemented using remotely hosted content, then it can only open within the MAF web view to access device features and services if the
maf-application.xmlfile's configuration includes theaccess="true"definition for the requested API.
Before you begin:
Using the MAF Feature Editor, designate the content for an application as Remote URL and then create the connection as described in Section 4.7.1, "How to Designate the Content for a Mobile Application."
To restrict access to device services:
-
Open the Device Access page in the MAF Feature Editor.
-
Clear the Granted option, as shown in Figure 12-4, or update the maf-application.xml with
access=false(for example,<adfmf:deviceCamera id="dc1" access="false"/>).
12.1.4 How to Create a Whitelist (or Restrict a Domain)
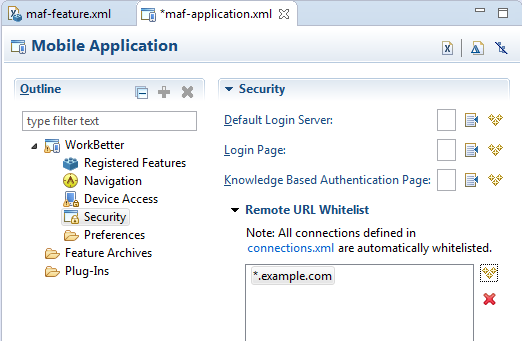
You configure the whitelist in the Security page of maf-application.xml, as shown in Figure 12-5.
Before you begin:
Be aware that some URLs configured in the mobile application may open to other domains.
To create whitelists:
-
Open MAF Application Editor and select Security in the outline.
-
Under Remote URL Whitelist, click Add and in the Add Whitelisted Domain dialog, enter a domain that can be called from within the web view of the application feature, and click OK. Continue to add the domains you want to be whitelisted.
These domains can include a wildcard (*). For example,
*.example.comis a valid domain entry as is*.example.*. You cannot enter a fully qualified path.Caution:
Entering only the wildcard allows the web view to request all domains and can pose a security risk; adding all domains to the whitelist not only enables all of them to open within the web view, but also enables all of them to access the device (whether or not it is intended for them to do so).
12.1.5 What Happens When You Add Domains to a Whitelist
When you add a domain, Oracle Enterprise Pack for Eclipse updates <adfmf:remoteURLWhiteList> element as illustrated in Example 12-1.
12.1.6 What You May Need to Know About Remote URLs
Some URLs are redirected to a URL that may not be part of the whitelist domain. These URLs may open in the device browser rather than the application web view. For example, if you whitelist www.oracle.com (<adfmf:domain>www.oracle.com<adfmf:domain>), MAF opens the mobile version of this site (www.m.oracle.com) in the device browser, because it does not pass the whitelist. Figure 12-6 shows a web page that has not been whitelisted and has opened within the device browser.
To enable www.oracle.com to open within the application web view, you must specify *.oracle.* or www.oracle.* as shown in Example 12-1.
Because the MAF whitelist is at the domain-level, you cannot restrict an individual page within a whitelisted domain from opening with an application feature web view; all pages are allowed.
12.2 Creating Whitelists for Application Components
Use a whitelist for pages that contain links to URLs that point to another domain. Such pages would otherwise open in the device browser instead of the MAF web view. In such a case, you can create an anchor tag or an <amx:goLink> component with a url attribute for the <amx:goLink> component that points outside of the application, such as the url attribute in <goLink2> in Example 12-2.
Example 12-2 <amx:goLink> with a url Parameter
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<amx:view xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:amx="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mf/amx"
xmlns:dvtm="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mf/amx/dvt">
<amx:panelPage id="pp1">
<amx:panelGroupLayout id="panelGroupLayout1">
<amx:goLink text="This opens in the device browser"
id="golink1"
url="http://www.example.com"
shortDesc="Opens in device browser"/>
<amx:goLink text="This opens in the web view"
id="golink2"
url="http://www.example2.com"
shortDesc="Accesses device services"/>
</amx:panelGroupLayout>
</amx:panelPage>
</amx:view>
12.3 Enabling the Browser Navigation Bar on Remote URL Pages
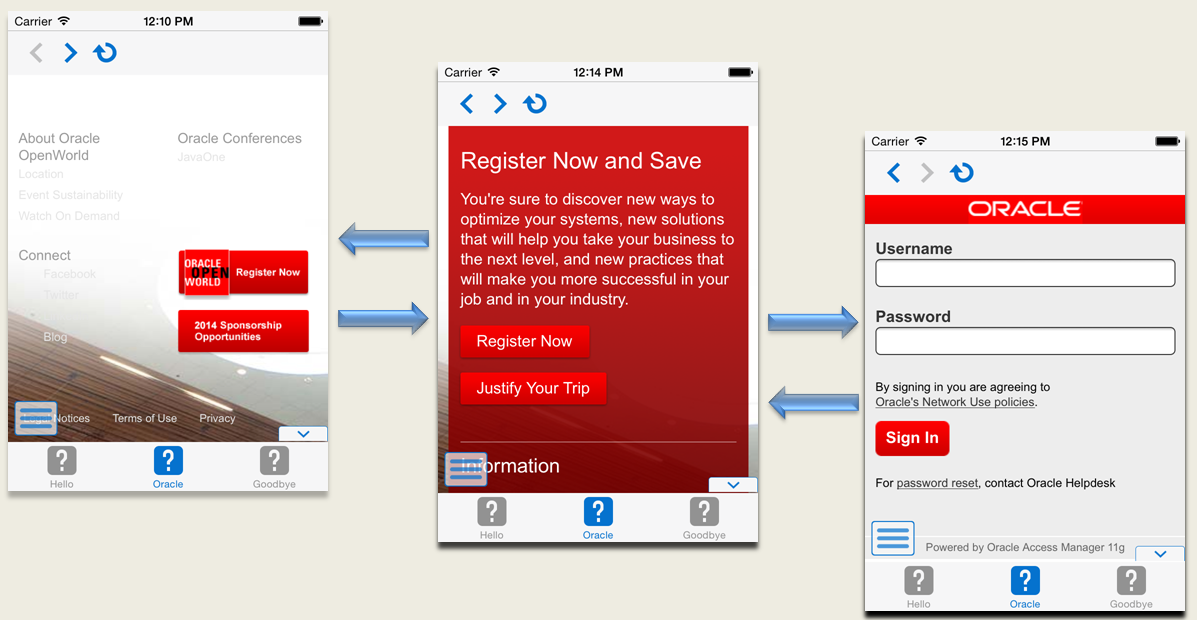
MAF enables you to add a navigation bar with buttons for back, forward, and refresh actions for application features implemented as remotely served web content that open within the MAF web view, as shown in Figure 12-7. The forward and back buttons are disabled when either navigation forward or back is not possible.
Note:
The back button is disabled on Android-powered devices.
12.3.1 How to Add the Navigation Bar to a Remote URL Application Feature
You enable users to navigate through, or refresh remote content through the Content tab of the overview editor for the maf-feature.xml file.
Before you begin:
Designate an application feature's content be delivered from a remotely hosted application by first selecting Remote URL and then by creating the connection to the host server, as described in Section 4.11, "Defining the Content Types for an Application Feature."
Ensure that the domain is whitelisted.
To enable a navigation bar:
-
Select the Remote URL application feature listed under Features in the MAF Feature Editor outline.
-
Expand Content and select the Remote URL content.
-
In the Content section, select Show buttons, as shown in Figure 12-8.
12.3.2 What Happens When You Enable the Browser Navigation Buttons for a Remote URL Application Feature
Oracle Enterprise Pack for Eclipse updates the adfmf:remoteURL element with an attribute called showNavButtons, which is set to true, as shown in Example 12-3.
Example 12-3 The showNavButtons Attribute
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<adfmf:features xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:adfmf="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mf">
<adfmf:feature id="oraclemobile" name="oraclemobile">
<adfmf:content id="oraclemobile.1">
<adfmf:remoteURL connection="connection1"
showNavButtons="true"/>
</adfmf:content>
</adfmf:feature>
</adfmf:features>
After you deploy the application, MAF applies the forward, back, and refresh buttons to the web pages that are traversed from the home page of the Remote URL application feature, as shown in Figure 12-9.
12.4 About Authoring Remote Content
The Browser-based user interface may be authored using Apache Trinidad components (described at http://myfaces.apache.org/trinidad/) because they display equally well within the browsers of either smartphones or feature phones. To accommodate recent smartphones and tablet devices, web applications may also be authored using ADF Rich Faces components as described in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing Web User Interfaces with Oracle ADF Faces.
Note:
Oracle recommends using ADF Mobile browser for application features that derive their content from remote URLs. ADF Mobile browser applications are comprised of JSF pages populated with Apache Trinidad components. For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing Oracle ADF Mobile Browser Applications.