1 Introduction to JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets
This chapter contains the following topics:
-
Section 1.1, "JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets Overview"
-
Section 1.2, "JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets Business Processes"
-
Section 1.3, "JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets Integrations"
-
Section 1.4, "JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets Implementation"
1.1 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets Overview
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets provides an effective way to track assets for your critical financial and reporting needs, enabling you to produce fixed asset reports, maintain purchase requests for assets, reconcile assets, and maintain tax information. With the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets system from Oracle, you can control the fixed asset accounting lifecycle, from acquisition and depreciation to revaluation and eventual disposal. For example, you can:
-
Add, depreciate, split, revalue, and dispose of fixed assets.
-
Ensure compliance with tax and accounting requirements.
-
Configure and maintain an unlimited number of depreciation methods.
-
Use predefined or custom depreciation methods.
-
Use the most advantageous depreciation method for each asset.
-
Value assets by using an unlimited number of currencies.
-
Maintain insurance and tax information by asset.
-
Automate asset definition and configuration.
-
Update asset information daily, monthly, quarterly, or annually.
1.2 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets Business Processes
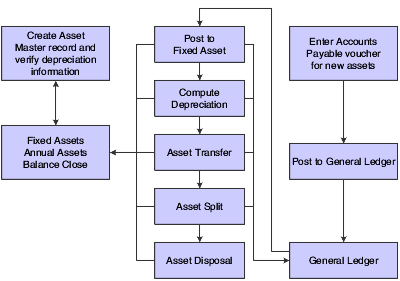
This process flow illustrates the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets business processes:
We discuss these business processes in the business process chapters in this implementation guide.
1.3 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets Integrations
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets system integrates with these JD Edwards EnterpriseOne systems from Oracle:
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Address Book
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Service Management
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Equipment Plant Maintenance
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Interoperability
System integration helps ensure that asset information and account transactions are consistent. You need to enter fixed asset and account information only once throughout the company. This one-time action saves considerable time and money, especially when you need to record numerous and complex business transactions daily, and update or revise asset information, such as depreciation rates and account numbers. We discuss integration considerations in the implementation chapters in this implementation guide. Supplemental information about third-party application integrations is located on the Customer Connection website.
1.3.1 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Address Book
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets accesses the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Address Book system from Oracle to retrieve up-to-date name and address information for:
-
Tax authorities.
-
Lessors, financiers, and insurers.
-
Employees who are responsible for the asset.
1.3.2 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting system systems from Oracle access and store detailed transaction information in the F0911 table. To maintain integrity between the two systems, process all transactions through both the general ledger (GL) and fixed assets.
1.3.3 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement systems from Oracle access and store information in both the F0911 table and the F1201 table to keep company purchases and asset records concurrent and up-to-date. When you purchase assets, you must create asset master records in the Asset Master File table to identify the new assets in the system. The system creates the necessary general ledger accounts in the Account Ledger.
1.3.4 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable systems from Oracle are integrated through the Account Ledger table (F0911). You can enter charges that are associated with fixed assets through JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable. The system automatically enters the asset number from the purchase order to the accounts payable voucher and updates table F0911.
1.3.5 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Service Management
In JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Service Management, an installed base record can be created to track products that you have sold or leased to customers. When these records are created, they are stored in the Asset Master File table (F1201). Before the records are created, the accounts that are used to track this information must be set up within the FX range of AAIs for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets system. These accounts must also have the default coding set up as regular cost accounts in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets system. Typically, installed base records are not depreciated; therefore, depreciation methods do not need to be created for these accounts.
Asset Master records for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Service Management can be segregated from the regular Asset Master File records (F1201) by using the warranty date field. The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Service Management system fills in the warranty date field as installed base records are created. Regular fixed asset master records do not use this field.
1.3.6 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Equipment Plant Maintenance
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Equipment Plant Maintenance system from Oracle shares information from many tables in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets system, including:
-
This table stores the equipment master and fixed asset master information.
-
Asset Account Balances File table (F1202).
This table stores the equipment account balance and asset account balance information.
-
Location Tracking Table (F1204).
This table stores the current, historical, and planned location information for fixed assets and equipment.
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Equipment Plant Maintenance system from Oracle also shares Fixed Assets Constants and automatic accounting instructions (AAIs). All accounts that are part of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Equipment Plant Maintenance system must be set up in the FX range of AAIs. Other AAIs are used in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Equipment Plant Maintenance system to track additional cost and statistical information that is not normally used on regular fixed assets.
Fixed assets items and equipment items share the same category codes. If you use the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Equipment Plant Maintenance system, you might want to reserve some of the category codes for equipment. For example, you could set aside the first ten category codes to use with equipment.
In addition to sharing tables and setup information, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Equipment Plant Maintenance and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets systems have other similar features. For example, when entering, inquiring, and running reports for equipment and fixed asset master items, you use many of the same programs, such as Cost Summary, Supplemental Data, Location Search and Transfer, Asset Master Revisions, and so on.
Equipment items are similar to fixed asset items; however, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Equipment Plant Maintenance system enables you to add and track maintenance issues through work orders and maintenance schedules. The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Equipment Plant Maintenance system tracks statistical information such as meter readings and other equipment-related detail.
1.3.7 Interoperability
To fulfill the information requirements of an enterprise, companies sometimes use products from different software and hardware providers. Interoperability among products is key to successfully implementing an enterprise solution. Full interoperability among different systems results in a flow of data among the different products that is seamless to the user.
You can access Interoperability programs from the Asset Interoperability menu (G1233).
For Fixed Assets interoperability transactions, enter JDEFA in the Transaction field and F1201Z1 in the File Name field.
1.4 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets Implementation
This section provides an overview of the steps that are required to implement the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets system.
In the planning phase of your implementation, take advantage of all JD Edwards EnterpriseOne sources of information, including the installation guides and troubleshooting information.
When determining which electronic software updates (ESUs) to install for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets, use the EnterpriseOne and World Change Assistant. EnterpriseOne and World Change Assistant, a Java-based tool, reduces the time required to search and download ESUs by 75 percent or more and enables you to install multiple ESUs at one time.
See JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Tools Software Updates Guide.
For information about the Oracle Business Accelerator solution for implementation of JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets, review the documentation available.
See http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E24705_01/index.htm
1.4.1 Global Implementation Steps
The suggested global implementation steps for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets system are:
-
Set up companies, fiscal date patterns, and business units.
-
Set up accounts, and the chart of accounts.
-
Set up the General Accounting constants.
-
Set up multicurrency processing, including currency codes and exchange rates.
-
Set up ledger type rules.
-
Enter address book records.
1.4.2 Core Implementation Steps
The core implementation steps for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Fixed Assets system are:
-
Set up Fixed Assets constants.
-
Define customized UDCs.
-
Set up depreciation rules. Specify rule conventions and set up life year rules, depreciation formulas and spread patterns, date pattern overrides, and short years in Fixed Assets.
-
Define AAIs when Fixed Assets interacts with General Accounting.
-
Set up next numbers for Fixed Assets.
-
Set up asset acquisition years.
-
Set up depreciation default values.
-
(COL) Set up cost accounts for depreciation inflation adjustments.
-
Map business unit category codes to specific asset category codes.
-
Set up ledger type rules.
-
Set up disposal account rules.
-
Set up beginning balances.
-
(RUS) Create a revaluation code.
-
(Optional) Set up supplemental data type categories.
-
Set up revaluation indexes.
-
(PER) Set up revaluation accounts and limits.
-
(CHL and PER) Set up the Fixed Asset ledger.
-
Set up units of production schedules.
1.5 Business Interface Integration Objects
A business interface is a set of components that implementation teams can use to create an integration between JD Edwards EnterpriseOne and an external system. Business interfaces can include one or more of these business interface components:
-
Business Services
-
Real-Time Events
-
Batch Import and Export Programs
For additional information about business interfaces, and the business objects available for this product area, see these topics in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Applications Business Interface Reference Guide: