19 Processing Fees and Interest
This chapter contains the following topics:
19.1 Understanding Fee and Interest Processing
If invoices remain unpaid after their due date or if you receive the payments late, you can assess fees on the invoices. These fees can be based on the invoice aging (the number of days past the due date) or a flat amount.
You can calculate interest on late payments in one of three ways:
-
Simple interest (per month or per year on outstanding balances).
-
Compound interest.
-
Interest on fees (simple or compound).
You set up bill codes and automatic accounting instructions (AAIs) that determine whether you charge a late fee or interest. This distinction is important because revenue collected from fees and interest is taxed differently than revenue received from rent. In some cases, you must differentiate the interest that you charge from the interest that you must pay on security deposits.
The system stores fee and interest information in the Fees and Interest table (F1525B).
19.2 Setting Up Fees and Interest
This section provides an overview of fee and interest search levels and discusses how to set up fees and interest.
19.2.1 Understanding Fee and Interest Search Levels
You can define up to 12 fee and interest tables that contain fee and interest information, such as timing, period, and frequency, that the system uses when you run the Fee & Interest Generation program (R15160). Using up to 12 search levels, you do not have to define the calculation of fees and interest for every lease, tenant, building, and bill code. Set up only the general policy and any exceptions within that policy. When you run the R15160 program, the system selects the most specific fee and interest table, based on its search level, and the key information of the invoice being generated. The search level identifies the level of detail with which a fee and interest table is associated.
You set up a search level by entering values in any combination of these four fields on the Fee and Interest Table form:
-
Lease
-
Tenant
-
Building
-
Bill Code
For example, you can define a late fee generally for all the leases and facilities-specifically for a lease, tenant, building, or bill code-or for any combination of those four items. You can also specify whether charges are general, such a 25.00 late fee that applies to all tenants, or specific, such as .5 percent per month after a five-day grace period for a specific lease.
This table lists the field combinations that comprise the 12 valid fee and interest search levels:
| Key Field | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 | Level 5 | Level 6 | Level 7 | Level 8 | Level 9 | Level 10 | Level 11 | Level 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lease | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Tenant | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| Building | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Bill Code | X | X | X | X | X | X |
Notice that as the level increases from 1 to 12, the level of detail becomes more general. With level 1, for example, the search is limited to a specific lease, tenant, building, and bill code (AR account). Level 10, however, limits the search only to a specific building.
19.2.1.1 Example: Determining the Number of Fee Tables to Set Up
For example, suppose you have the same late fee policy for all tenants in all buildings except one. In the one building, you have a second late fee policy for all tenants except one. For the one tenant, you have a third policy. That same tenant has another lease related to the first policy. The first two policies include all the bill codes, and the third policy is associated with heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (bill code HVAC).
In this example, set up only four fee tables (four levels of detail) to satisfy all of the late fee requirements:
-
Level 12 (all leases, tenants, buildings, and bill codes).
-
Level 10 (all leases, tenants, and bill codes for a specific building).
-
Level 2 (all bill codes for a specific lease, tenant, and building).
-
Level 1 (a specific lease, tenant, building, and bill code).
19.2.1.2 Example: Late Fees (Fixed Amount and Simple Interest)
If the rent is not paid within five days, the tenant is assessed a 50.00 one-time penalty. An additional five days grace period is allowed before a simple interest of 12.0 percent is charged on the last open unpaid rent balance. The interest is retroactive to the first day of the month, and it accrues daily. All the charges are based on the due date of the invoice, and the bill code LATE is used to record the income from such charges.
The bill code, plus the prefixes RC and PM, comprise the related AAIs RCLATE and PMLATE.
19.2.1.3 Example: Simple Interest on a Security Deposit
For the security deposit, a tenant is entitled to earn annual interest on a monthly basis. The interest is simple (noncompounding); and the rate varies, according to the prime rate. Although the lease begins on June 1, 2008, the interest calculation begins two months later on August 1. The interest is based on the general ledger date of the receipt for the security deposit, and the bill code INTR (interest) is used to record the interest.
You use the R15160 processing options to specify the interest rate because it is variable. The Rate Indc field identifies this rate. The Retr Code field is blank. This code is optional because no grace period exists.
The bill code, plus the prefixes RC and PM, comprise the related AAIs RCINTR and PMINTR.
19.2.1.4 Example: Compounding Interest
You can set up only one detail line associated with compounding interest in a fee and interest table. To set up compounded interest, you must:
-
Leave the Retro Code field blank because no grace period exists.
-
Enter a bill code for an adjustment in the BCd/AdjR field. During the generation, therefore, the system updates the AR Account Ledger table as an adjustment.
-
Enter 1 in the Cmp Flg field.
The adjustment reason, plus the prefix RA, comprise the related AAI RAIN.
19.2.2 Forms Used to Set Up Fee and Interest Tables
| Form Name | FormID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With Fee and Interest | W1525A | Fees & Interest (G1527), Fee & Interest Information | Review and select fee and interest table records. |
| Fee and Interest | W1525B | On the Work With Fee and Interest Table form, click Add. | Set up fees and interest. |
19.2.3 Setting Up Fees and Interest
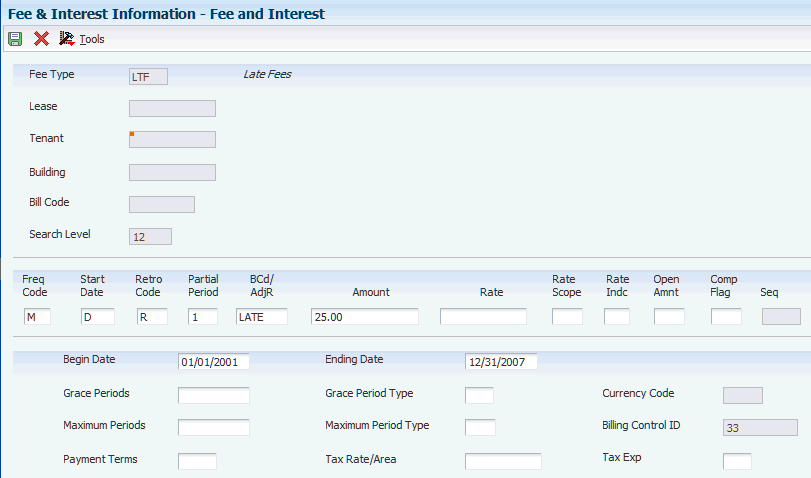
Access the Fee and Interest form.
Use the Fee & Interest Information program (P1525) to set up tables of charges, interest rates, and calculation patterns, which enables you to maintain information associated with the various fees and interest that applies to the organization.
- Fee Type
-
Enter the fee type from user-defined code (UDC) table 15/FY that specifies how to group fee tables together for items such as late or interest charges.
- Search Level
-
Displays the level, 1–12, of the fee and interest table based on the values in the Lease, Tenant, Building, and Bill Code fields.
- Freq Code (fee frequency code)
-
Enter a code from UDC table 15/FC that specifies the frequency with the system applies or compounds an amount or rate. Values are:
D or 1: Daily
M or 2: Monthly
Y or 3: Yearly
If you select monthly, then each month is a separate generation period. An individual table entry may be applied to an individual invoice only once per generation period. The R15160 program applies the rate or amount once for every generation period between the last date of generation and the current generation date.
- Start Date
-
Enter a code from UDC table 15/FI that specifies which date, associated with an invoice, the system uses as the starting point for generation. For instance, late fees would be based on the due date of an invoice, whereas interest accrual for security deposits would be based on the G/L date. Values are:
D or 1: Due Date
G or 2: G/L Date/Transaction Date
I or 3: Invoice Date
S or 4: Service/Tax Date
- Retro Code (retroactive start date code)
-
Enter a value that specifies whether the fee or interest is calculated as of the date after the grace period or retroactively as of the start date. Values are:
Blank: Fee or interest starts after grace period.
1 or R: Fee or interest is retroactive to start date.
- Partial Period
-
Enter a code from UDC table 15/PP that specifies how the system generates fees and interest when an invoice has been paid during a generation period (see AAPF). Values are:
Blank: The system does not generate fees or interest for a generation period during which the invoice is paid.
1: The system generates fees and interest as if the invoice were open during the entire generation period.
2: The system pro-rates fees and interest according to the number of days the invoice was open during the generation period versus the total number of days in the Generation Period.
- BCd/AdjR (billing receipt code)
-
Enter the G/L offset (billing/receipt) code that the system uses to retrieve estimated charges. For example, suppose you enter a control record for billing the expense participation class related to common area maintenance. If the tenant has been billed a recurring estimated charge for this class through the recurring billing process, the estimated charges must be subtracted from the calculated actual charge and only the difference billed to the tenant.
- Amount
-
Enter the amount that the system uses as fee or interest amount.
Note:
You can enter either an amount or a rate, but you cannot enter both. - Rate
-
Enter the percentage that the system uses to assess the fee or interest. Enter the percentage as a decimal value. For example, enter .05 to specify 5 percent.
Note:
You can enter either an amount or a rate, but you cannot enter both. - Rate Scope
-
Enter a code from UDC table 15/FC that specifies the time period in which to apply the rate.
- Rate Indc (rate indicator code)
-
Enter a code from UDC table 15/RA that specifies the rate the system uses to calculate the fee or interest amount. Values are:
Blank: Flat rate.
%: Rate from Fee and Interest table.
1: First variable rate.
2: Second variable rate.
3: Third variable rate.
4: Fourth variable rate.
- Open Amnt (open amount code)
-
Enter a code from UDC table 15/OA that specifies the amount associated with an invoice which is used to generate the fee or interest amount. Values are:
Blank: Original: The gross billing amount of the invoice.
1 or A: Average. The average open amount during a generation period.
2 or L: Last. The open amount at the end of a generation period.
- Comp Flag (compounded flag)
-
Enter a code from UDC table 15/CP that specifies to the A/R Fee and Interest Generation program whether the rate is compounded. Compounded fee or interest amounts are created as adjustments to the affected invoice. There may be only one compounding entry for any fee and interest table. Values are:
Blank: Non-compounded.
1:Compounded.
- Seq (auto generation sequence number)
-
Enter the sequence number. The sequence number is used to control the order in which AR Fee and Interest entries are processed and displayed.
- Grace Periods
-
Enter the number of grace periods. This value, along with the Grace Period Type, determines the amount of time that the grace period, if any, is in effect. The grace period is measured from the Start Date (see FISD). For example, if the start date for an invoice is October 1, 2008, the number of grace periods is 10, and the Grace Period Type is 1 day, then no fee or interest would be generated for the invoice until the generation date was past October 11, 2008.
- Grace Period Type
-
Enter the amount of time that the grace period covers. For example, if the number of grace periods is eight, then the total grace period could be eight days, eight months, or eight years. Values are:
D: Days.
M: Months.
Y: Years.
- Maximum Periods
-
Enter the maximum periods. The system uses this value, along with the Maximum Period Type, to determine the amount of time that an individual entry can be applied to an invoice. For example, if the entry is a one-time flat fee, then the Maximum Periods would be 1 and the Maximum Period Type would match whatever the Fee Frequency indicated. If the entry is a monthly rate which is not to be applied more than 12 times, then the Maximum Periods could be 12 and the Maximum Period Type 2 (months) or the Maximum Periods could be 1 and the Maximum Period Type 3 (years). The maximum periods are measured from the start date. If there is a grace period of 10 days, but a maximum of 1 day, the system never bills the fee.
The grace period must be less than the maximum period. The system processes any generation period (see AAPF) that starts before the maximum periods are finished.
For example, if the entry is a monthly fee and if the Maximum Periods are 90 and the Maximum Period Type is 1 (days), then the system processes the first three months, even if the end of the third month falls outside of the 90 days.
- Maximum Period Type
-
Enter a value that specifies the maximum period type. This value, along with the maximum periods, is used to determine the amount of time that an individual entry can be applied to an invoice. Values are:
D: Days
M: Months
Y: Years
- Payment Terms
-
Enter a value that specifies the terms of payment, including the percentage of discount available if the invoice is paid by the discount due date. Use a blank code to indicate the most frequently-used payment term. You define each type of payment term on the Payment Terms Revisions form. Examples of payment terms include:
Blank: Net 15.
001: 1/10 net 30.
002: 2/10 net 30.
003: Due on the 10th day of every month.
006: Due upon receipt.
This code prints on customer invoices.
- Billing Control ID
-
Displays the Billing Control ID, which is used to keep track of all the periods that have been generated and posted. For billing generation type 5, the Billing Control ID is stored with the invoice information in the Lease Billings History table (F1511HB) rather than in the Billings Generation Control Master table (F15011B).
19.3 Generating Fees and Interest
This section provides an overview of the fee and interest generation process and discusses how to:
-
Run the Fee & Interest Generation program.
-
Set processing options for Fee & Interest Generation (R15160).
19.3.1 Understanding the Fee and Interest Generation Process
Use the Fee & Interest Generation program (R15160) to generate a batch of invoices for fees and interest against accounts receivable invoices and adjustments for interest on security deposits. The program is based on the Customer Ledger table and controlled by the fee tables in the Fees and Interest table (F1525B).
You can calculate interest earned on security deposits. You must first set up the revenue bill code, such as INTR (interest) in a security group. After you calculate the interest earned, you can then generate the accounts payable voucher using the Security Deposit Refund Generation program (R15655) to refund the interest, the security deposit, or both.
|
Important: You can generate fees and interest for a tenant more than once in the same period until a batch is posted. If you inadvertently generate a batch of fees and interest, and have not yet posted it, you can delete the batch. The system deletes the batch header, the batch transactions, and the corresponding records in the Lease Billings History table (F1511HB). After you post a batch, you cannot delete it. |
This table lists the tasks that you might perform after you generate fee and interest billing records to complete the billing generation process:
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Generate the billing edit register (Required) | After you generate fee and interest records, you must run the XJDE0005 version of the Billing Edit/Register program (R15300) to validate the transactions in the batch and to change the batch status. |
| Review the invoice journal | You can review the batch of invoice fee records before you post them, and revise or delete transactions as necessary. |
| Review the receipts journal | You can review the batch of receipt (adjustment) records before you post them, and revise or delete transactions as necessary.
See Processing Options for Receipts Journal Report (R03B311). |
| Post invoices (Required) | After you generate the billing edit register, you must post the billing transactions to generate the invoice records. |
| Post receipts (Required) | After you generate the receipt (adjustment) transactions, you must post them to update the general ledger.
See Posting Receipts. |
| Print invoices | After you post invoices, you can print and send them to the tenants.
See Printing Invoices. |
| Print statements | After you post invoices, you can print statements and send them to the tenants.
See Printing Statements. |
| Review billings transactions | You can review billing transactions in detail using the Billings Transaction Inquiry program (P15211). |
| Review invoices | You can review the invoices generated from billing transactions using the Tenant Ledger Inquiry program (P15222). |
| Review vouchers | You can review the vouchers generated from billing transactions using the Supplier Ledger Inquiry program (P0411). |
19.3.2 Running the Fee & Interest Generation Program
Select Fee & Interest (G1527), Fee & Interest Generation.
19.3.3 Setting Processing Options for Fee and Interest Generation (R15160)
Processing options enable you to specify the default processing for programs and reports.
19.3.3.1 Select
- 1. Fee Type
-
Specify a code from UDC table 15/FY that specifies the type of fee to process.
- 2. Generation Date
-
Specify the date to use to select the invoice records for which you want to generate fees or interest. The system selects only those invoice records with an open amount that have a due date that is on or before the date that you enter. If you leave this processing option blank, the system uses the current date.
- 3. G/L Date For Invoices
-
Specify the general ledger date to assign to the fee or interest invoice records that the system generates.
- 4. Invoice Date
-
Specify the date to assign to the fee or interest records that the system generates. If you leave this processing option blank, the system assigns the current date as the invoice date.
19.3.3.2 Process
- 1. File Update
-
Specify whether the program runs in proof or final mode. Values are:
Blank: Proof mode. The system generates only a report.
1: Final mode. The system generates the fee or interest record, updates the appropriate tables, and generates a report.
- 2. File Update Method
-
Specify whether the system generates one fee record for each invoice or one fee record for each unique bill code that appears on the invoice. Regardless of the value that you specify, the report includes one line for each late fee amount by bill code. Values are:
Blank: Generate one fee record for each unique bill code that is entered on the invoice. The system summarizes the fee amount by the bill code if the invoice has multiple pay items for the same bill code.
1: Generate one late fee for the invoice, regardless of the number of pay items or the bill codes.
- 3. Late Fee Processing
-
Specify whether the system verifies that the Subject to Late Fees option (LTFE) is selected in the Bill Codes / Adjustment Reasons program (P1512) for the bill code for which the late fee is processed. Values are:
Blank: Verify that the option is selected. The system does not generate late fees for bill codes that do not have the Subject to Late Fees option selected.
1: Do not verify that the option is selected. The system generates late fees for all of the bill codes specified, regardless of the setting of the Subject to Late Fees option.
- 4. Security Deposit Write-Off Reason Code
-
Specify the reason code that the system uses to retrieve the offset account for the Receipts Detail record (F03B14) that the system generates for the compounded interest on security deposits. The system retrieves the account from the AAI item RAxx, where xx is the reason code.
The system uses this processing option only when you specify to generate compounded interest on security deposits. If the Compound Flag field (COPF) is set to blank, the system ignores this processing option.
- 5. Late Fee Write-Off Reason Code
-
Specify the reason code that the system uses to retrieve the offset account for the Receipts Detail record (F03B14) that the system generates for the interest on fees. The system retrieves the account from the AAI item RAxx, where xx is the reason code.
The system uses this processing option only when you specify to generate fees that are compounded. If the Compound Flag field (COPF) on the Fees and Interests record (F1525B) is set to blank, the system ignores this processing option.
- 6. Variable Fee Or Interest Rates
-
Specify the rate that the system uses to calculate the fee or interest when the value in the Rate Indicator Code field (RAIF) in the Fee and Interest table (F1525B) equals 1, 2, 3, or 4. The system uses the rate from this processing option that corresponds to the value entered in the Rate Indicator field. If the value of the Rate Indicator field is a percent, the system ignores this processing option.
Enter the rate in decimal format. For example, enter .05 to specify 5 percent.
19.3.3.3 Currency
- 1. Exchange Rate Retrieval Date
-
Specify the date that the system uses to retrieve the exchange rate from the Currency Exchange Rates table (F0015) when the system generates the fee in a currency that is different from the currency code assigned to the company. Values are:
Blank: General ledger date.
1: Invoice date.