| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
System Administration Guide: Naming and Directory Services (NIS+) |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
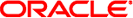
|
System Administration Guide: Naming and Directory Services (NIS+) |
Part I About Naming and Directory Services
Part II NIS+ Setup and Configuration
Solaris 1 Release and NIS-Compatibility Mode
NIS+ Setup and Configuration Preparation
Structure of the NIS+ Namespace
How NIS+ Servers Propagate Changes
NIS+ Cold-Start File and Directory Cache
An NIS+ Server Is Also a Client
NIS+ NIS_PATH Environment Variable
Preparing the Existing Namespace for NIS+
Two NIS+ Configuration Methods
4. Configuring NIS+ With Scripts
5. Setting Up the NIS+ Root Domain
8. Configuring an NIS+ Non-Root Domain
10. NIS+ Tables and Information
12. Administering NIS+ Credentials
14. Administering Enhanced NIS+ Security Credentials
15. Administering NIS+ Access Rights
16. Administering NIS+ Passwords
18. Administering NIS+ Directories
20. NIS+ Server Use Customization
23. Information in NIS+ Tables
Common NIS+ Namespace Error Messages
Objects in an NIS+ namespace can be identified with two types of names: partially-qualified and fully qualified. A partially qualified name, also called a simple name, is simply the name of the object or any portion of the fully qualified name. If during any administration operation you type the partially qualified name of an object or principal, NIS+ will attempt to expand the name into its fully qualified version. For details, see NIS+ Naming Conventions.
A fully qualified name is the complete name of the object, including all the information necessary to locate it in the namespace, such as its parent directory, if it has one, and its complete domain name, including a trailing dot.
This varies among different types of objects, so the conventions for each type, as well as for NIS+ principals, is described separately. This namespace will be used as an example:
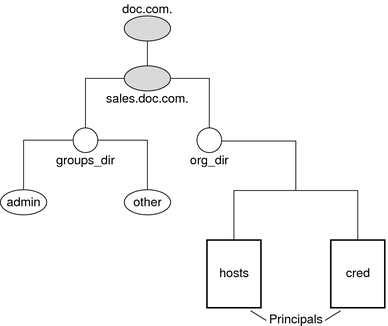
The fully qualified names for all the objects in this namespace, including NIS+ principals, are summarized below.
Figure 2-4 Fully-Qualified Names of NIS+ Namespace Components
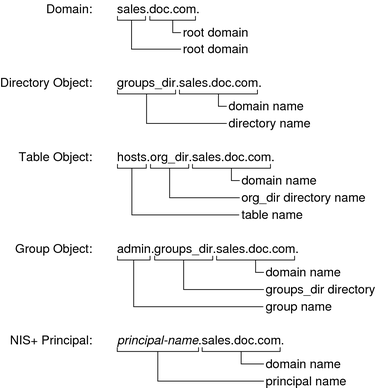
A fully qualified NIS+ domain name is formed from left to right, starting with the local domain and ending with the root domain:
doc.com. (root domain)
sales.doc.com. (subdomain)
intl.sales.doc.com. (a third level subdomain)
The first line above shows the name of the root domain. The root domain must always have at least two elements (labels) and must end in a dot. The last (right most) label may be anything you want, but in order to maintain Internet compatibility, the last element must be either an Internet organizational name (as shown below), or a two or three character geographic identifier such as .jp for Japan.
Table 2-4 Internet Organizational Domains
|
The second and third lines above show the names of lower-level domains.
A directory's simple name is simply the name of the directory object. Its fully qualified name consists of its simple name plus the fully qualified name of its domain (which always includes a trailing dot):
groups_dir (simple name)
groups_dir.manf.doc.com. (fully qualified name)
If you set up an unusual hierarchy in which several layers of directories do not form a domain, be sure to include the names of the intermediate directories. For example:
lowest_dir.lower_dir.low_dir.mydomain.com.
The simple name is normally used from within the same domain, and the fully qualified name is normally used from a remote domain. However, by specifying search paths in a domain's NIS_PATH environment variable, you can use the simple name from remote domains (see NIS+ NIS_PATH Environment Variable).
Fully qualified table and group names are formed by starting with the object name and appending the directory name, followed by the fully qualified domain name. Remember that all system table objects are stored in an org_dir directory and all group objects are stored in a groups_dir directory. (If you create your own NIS+ tables, you can store them anywhere you like.) Here are some examples of group and table names:
admin.groups_dir.doc.com. admin.groups_dir.doc.com. admin.groups_dir.sales.doc.com. admin.groups_dir.sales.doc.com. hosts.org_dir.doc.com. hosts.org_dir.doc.com. hosts.org_dir.sales.doc.com. hosts.org_dir.sales.doc.com.
To identify an entry in an NIS+ table, you need to identify the table object and the entry within it. This type of name is called an indexed name. It has the following syntax:
[column=value,column=value,...],tablename
Column is the name of the table column. Value is the actual value of that column. Tablename is the fully qualified name of the table object. Here are a few examples of entries in the hosts table:
[addr=129.44.2.1,name=pine],hosts.org_dir.sales.doc.com. [addr=129.44.2.2,name=elm],hosts.org_dir.sales.doc.com. [addr=129.44.2.3,name=oak],hosts.org_dir.sales.doc.com.
You can use as few column-value pairs inside the brackets as required to uniquely identify the table entry.
Some NIS+ administrative commands accept variations on this syntax. For details, see the nistbladm, nismatch, and nisgrep commands in Part 2.
Host names may contain up to 24 characters. Letters, numbers, the dash (-) and underscore (_) characters are allowed in host names. Host names are not case sensitive (that is, upper and lower case letters are treated as the same). The first character of a host name must be a letter of the alphabet. Blank spaces are not permitted in host names.
Note - Dots (.) are not permitted in host names. For example, a host name such as doc.2 is not permitted. Dots are not allowed in host names even if they are enclosed in quotes. For example, `doc.2' is not permitted. Dots are only used as part of a fully qualified host name to identify the domain components. For example, doc-2.sales.doc.com. is a correct fully qualified host name.
Domains and hosts should not have the same name. For example, if you have a sales domain you should not have a machine named sales. Similarly, if you have a machine named home, you do not want to create a domain named home. This caution also applies to subdomains. For example, if you have a machine named west you don't want to create a sales.west.doc.com subdomain.
NIS+ principal names are sometimes confused with Secure RPC netnames. However, one difference is worth pointing out now because it can cause confusion: NIS+ principal names always end in a dot and Secure RPC netnames never do. The following list provides examples.
olivia.sales.doc.com.
unix.olivia@sales.doc.com
Also, even though credentials for principals are stored in a cred table, neither the name of the cred table nor the name of the org_dir directory is included in the principal name.
You can form namespace names from any printable character in the ISO Latin 1 set. However, the names cannot start with these characters: @ < > + [ ] - / = . , : ;
To use a string, enclose it in double quotes. To use a quote sign in the name, quote the sign too (for example, to use o'henry, type o”'”henry). To include white space (as in John Smith), use double quotes within single quotes, like this:
`”John Smith”`
See NIS+ Host Names for restrictions that apply to host names.
Entering fully qualified names with your NIS+ commands can quickly become tedious. To ease the task, NIS+ provides a name-expansion facility. When you enter a partially qualified name, NIS+ attempts to find the object by looking for it under different directories. It starts by looking in the default domain. This is the home domain of the client from which you type the command. If it does not find the object in the default domain, NIS+ searches through each of the default domain's parent directories in ascending order until it finds the object. It stops after reaching a name with only two labels. Here are some examples (assume you are logged onto a client that belongs to the software.big.sales.doc.com. domain).