You can connect to a virtual machine using its console. The console is the remote control system of Oracle VM, and enables you to work and interact with your virtual machines.
There are two types of virtual machine consoles in Oracle VM Manager: the console used to connect virtual machines in x86-based server pools, and the serial console used to connect to virtual machines in SPARC-based server pools. This section discusses both console types.
You can use the serial console to connect to a Linux guest virtual machine in an x86-based server pool, but the console is in read-only mode, and you cannot interact with the virtual machine.
Since the console applets included in Oracle VM Manager make use of Java, there are some requirements that you need to meet in order for the console applets to load properly within your browser. You may need to edit various browser settings in order to make use of these applets.
In order for the console applets to work properly, it is essential that a Java Runtime Environment is installed on the client system. Oracle recommends that you install the Oracle Java SE6 Update 35 for the most consistent and reliable behavior. For users accessing Oracle VM Manager from Mac OS X systems, Java SE7 Update 9 is recommended. You can download either of these Java Runtime Environments from http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html.
Some browsers allow you to disable Java applets and Javascript within the browser preferences. It is important that the use of these commonly used web features is permitted in order for the Oracle VM Manager and its console applets to function.
Some browsers include a built-in 'Popup Blocker'. When you first attempt to open a console, the browser may notify you that a popup window has been blocked. In order to allow the console to open successfully in future, you should add the IP address or URL of the Oracle VM Manager host to the allowed list in the popup blocker management dialog.
On Mac OS X systems using the Safari web browser, you are not provided with any notification that a popup window has been blocked. Ensure that you configure the browser to allow popups.
For users of Microsoft Internet Explorer versions 7 and up, it is important that you adjust your security settings to include the URL for your Oracle VM Manager instance within your Trusted Sites, and to ensure that the security level for Trusted Sites is set to Low. Some of Internet Explorer's default security settings prevent the application from opening the Java applet.
If you have VNC Viewer (from RealVNC), or TightVNC Viewer installed on your client computer, the Oracle VM Manager user interface finds the installation and uses it to create the connection with the virtual machine. Oracle recommends you install RealVNC on the client computer as it renders more quickly, has better keyboard support, and has less mouse control issues than Tight VNC.
If no client viewer is available, the Oracle VM Manager user interface looks for TightVNC on the Oracle VM Manager host computer and uses this to create the connection with the virtual machine. See the Oracle VM Installation and Upgrade Guide for information on installing TightVNC on the Oracle VM Manager host computer.
The key mapping for each VNC session is set when you create or edit a virtual machine, in the Keymap field. See Section 7.7, “Creating a Virtual Machine” and Section 7.10.2, “Editing a Virtual Machine” for information on creating and editing a virtual machine.
To connect to a virtual machine's console:
Click the Servers and VMs tab.
Select the server pool on which the virtual machine resides in the navigation tree.
Select Virtual Machines from the Perspective drop-down list. Select the virtual machine in the management pane, and click Launch Console
 in the management pane toolbar
in the management pane toolbar
A dialog box may be displayed requesting to start a Java proxy to connect to the virtual machine. Click OK.
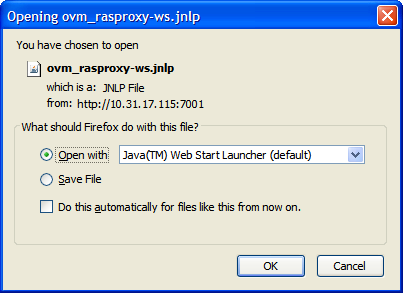
If a VNC viewer is found, it is started.
You can configure which VNC viewer to use with the Options > Configuration menu item of the Java RAS proxy window. Enter the path to the VNC client on the host computer; use quotes around the path if it contains spaces. You can additionaly specify the parameters
$andhost$if the VNC client requires these parameters in a different format than the defaultporthost:port-host=$. Click OK.host-port=$portTipIf the console does not start, check that your web browser allows pop-ups to be displayed. If you are using Microsoft Internet Explorer, add the base URL of Oracle VM Manager (for example,
http://example.com) to the list of trusted sites in the security settings. You may also need to downgrade the security level from medium to medium-low for the Trusted sites zone.If the virtual machine's console is in use by another user, a message is displayed asking if you want to take over the connection. If you take over the connection, the other user's session is disconnected and the VNC session is started on your client computer.
The virtual machine console is displayed. Log in and interact with the virtual machine as you would through any other VNC session. This example shows the initial installation screen for a virtual machine created with an Oracle Linux operating system ISO file.

If required, enter the user name and password of the guest operating system to log in to the operating system.
Depending on the method by which you created the virtual machine, you may need to continue with some further tasks before you can use the virtual machine.
If you created the virtual machine based on a template, you can directly use the guest operating system and applications installed in advance, without any further configuration.
If you created the virtual machine using the fully virtualized method, the installation of the guest operating system is triggered after your first login. Follow the installation wizard to install the guest operating system. For more information on creating virtual machines using the fully virtualized method, see Section 7.7, “Creating a Virtual Machine”.
NoteYou must install the guest operating system using a single ISO file. If your operating system installer consists of multiple ISO files, you cannot install it.
For information on the supported guest operating systems, see the Oracle VM Release Notes.
You cannot use the standard VNC-based console to connect to virtual machines on a SPARC-based server pool. Instead, use the Telnet-based serial console. The serial console behaves differently to the x86 console, and the console must be displayed using the Java Telnet Application (JTA2) package installed on the Oracle VM Manager host computer. See the Oracle VM Installation and Upgrade Guide for information on installing JTA2 on the Oracle VM Manager host computer.
The key mapping for each VNC session is set when you create or edit a virtual machine, in the Keymap field. See Section 7.7, “Creating a Virtual Machine” and Section 7.10.2, “Editing a Virtual Machine” for information on creating and editing a virtual machine.
To connect to a virtual machine's serial console:
Click the Servers and VMs tab.
Select the server pool on which the virtual machine resides in the navigation tree.
Select Virtual Machines from the Perspective drop-down list. Select the virtual machine in the management pane, and click Launch Serial Console
 in the management pane toolbar
in the management pane toolbar
A dialog box may be displayed requesting to start a Java proxy to connect to the virtual machine. Click OK.

The virtual machine console is displayed. Log in and interact with the virtual machine as you would through any other Telnet console session. If required, enter the user name and password of the guest operating system to log in to the operating system.