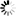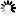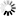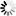Creating a Server Pool in Java is a straightforward operation. The WsDevClient class contains an example of this:
...
// Create a new server pool
ServerPool testPool = new ServerPool();
testPool.setName(testServerPoolName);
testPool.setVirtualIp(testServerPoolIp);
final Job serverPoolCreateJob = api.serverPoolCreate(testPool);
System.out.println("create server pool job id: " + serverPoolCreateJob.getId());
testPoolId = waitForJobComplete(api, serverPoolCreateJob, ServerPool.class);
In this example, we create a new ServerPool object using the
ServerPool model provided by the Oracle VM Manager Web Services Client
library included in the SDK. Using this model, we set various
parameters specific to the object. In this case, we only set
the required parameters which include the server pool name and
the server pool virtual IP address. In the example code, these
are set to the values defined for these variables in the
WsDevClient.properties file.
As described previously, a Job object is populated immediately in the return value provided by the serverPoolCreate method. This object is used by the waitForJobComplete method, which ensures that the server pool object is successfully created before continuing. We use the return value from the waitForJobComplete method to populate testPoolId value, which we use later to handle other server pool related activity for the newly created server pool.
The serverPoolCreate method is called from the OvmWsSoapClient class, where the following code is defined:
@Override
public Job serverPoolCreate(final ServerPool serverPool) throws WsException
{
try
{
return api.serverPoolCreate(serverPool);
}
catch (final WsException_Exception ex)
{
throw convertException(ex);
}
}As with most of the SOAP API calls, the methods defined in the OvmWsSoapClient class call equivalent methods directly from the API, as defined in the Oracle VM Manager Web Services Client library.