Overview of Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments
Oracle Solaris 11 uses ZFS file systems, where the swap and dump volumes are shared within the pool. For unshared file systems, ZFS is the only supported file system for boot environments on Oracle Solaris 11.
With the ZFS-based boot environment, the boot environments are clones of the existing ZFS partitions. This saves disk space and you do not need to reserve disk partitions for additional boot environments. The create and activate boot environment functionality is much faster than in previous versions.
Oracle Solaris 11 boot environments are managed through the beadm utility. A new boot environment is created whenever the kernel or system packages are installed or updated. This can result in high disk space utilization levels. By default, Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center monitors the disk (zpool) utilization of boot environments. If the utilization levels exceed defined thresholds, you can delete unwanted boot environments.
When a boot environment is created in the global zone, the following occurs:
-
A Boot Environment of the source boot environment is created (the boot environment from which it is cloned).
-
The currently active boot environment in all of the non-global zones is cloned and it is associated with the global zone boot environment that was just created.
When a global zone boot environment is activated, the active boot environment data set that is associated with that boot environment in each non-global zone is mounted and activated. Only one non-global zone boot environment that is associated with a global zone boot environment can be active.
When a global zone boot environment is deleted, all corresponding zone-specific boot environments are also deleted.
When a non-global zone is deleted, all corresponding boot environments are deleted. The boot environments for other zones are not deleted.
Displaying Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environment Details
The Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments tab provides you with a large amount of information about the boot environments that are associated with the selected physical or virtual Oracle Solaris 11 operating system.
This is particularly valuable since Oracle Solaris 11 boot environments are automatically created and they can quickly consume valuable resources. The following information is available:
-
Displaying Total ZPools Utilization for Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments
-
Displaying Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments
-
Displaying Snapshots for Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments
-
Displaying File Systems for Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments
-
Displaying Associated Zone Boot Environments
Displaying Total ZPools Utilization for Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments
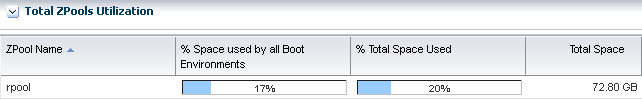
The first section in the Boot Environments tab is Total ZPools Utilization. It is compressed by default. Use the arrow to expand the table.
The amount of resources used by the zpool appears in this section, as shown in Figure 6-17.
Figure 6-17 Oracle Solaris 11 Total ZPools Utilization
Description of "Figure 6-17 Oracle Solaris 11 Total ZPools Utilization"
Displaying Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments
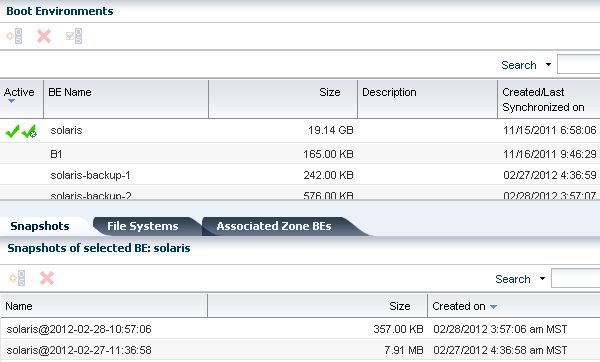
All boot environments that are associated with the physical or virtual operating system that is selected in the Assets tree appear in the Boot Environments table.
As shown in Figure 6-18, the active status, size, and when the boot environment was created appear in this section. A green check mark icon next to the boot environment name identifies the boot environment as active. A green check mark with a green circle and white x indicates that this is the boot environment that is active upon reboot. When two green check marks are visible in the Active column, the boot environment is active and is the active boot environment upon reboot.
Figure 6-18 Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments Tab
Description of "Figure 6-18 Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments Tab"
The lower section of the page has three tabs that provide details about the boot environment that you select in the Boot Environments table.
Displaying Snapshots for Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments
A snapshot is a point-in-time image of a Volume. It is a non-bootable copy of a boot environment that uses much less disk space than a boot environment. You can create a boot environment from a snapshot.
Non-bootable snapshots are available beginning with Oracle Solaris 11. Select a boot environment in the Boot Environments table to see all associated non-bootable snapshots in the Snapshots tab. You can select a snapshot in this tab and click the icon to create a boot environment from the snapshot.
Figure 6-19 Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environment Snapshots

Description of "Figure 6-19 Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environment Snapshots"
Displaying File Systems for Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments
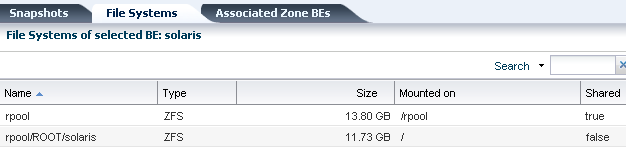
The File Systems tab provides file system details for the boot environment, or alternate boot environment, that you select in the Boot Environments tab.
As shown in Figure 6-20, the file system name, type, size and mount location appear in this table. You can also see if the file system is shared or not.
Figure 6-20 Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments File Systems
Description of "Figure 6-20 Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments File Systems"
Displaying Associated Zone Boot Environments
Associated Zone Boot Environments tab is populated with the boot environment details for a selected zone's boot environment. The zone might have multiple boot environments.
The table shows when the boot environment selected is active. As shown in Figure 6-21, you can see the boot environment name, the zone name, the size and when the boot environment was created. When you select an operating system that is not a zone, No Data appears in the table.
Figure 6-21 Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments Associated Zone BEs

Description of "Figure 6-21 Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environments Associated Zone BEs"
About Boot Environment Profiles and Plans for Oracle Solaris 11
A Boot Environments plan and profile for Oracle Solaris 11 operating systems identifies and defines how the boot environment is updated and activated. You can use an agent-managed or agentless-managed operating system.
Use the profile for Oracle Solaris 11 to perform the following tasks:
-
Create a Boot Environments profile that defines the creation policies
-
Create an OS update deployment plan, specifying a Boot Environments profile and an OS update profile
You can create profiles with different policy options. The following options are available for Oracle Solaris 11:
-
Create a new boot environment only when needed, such as when the OS update operation requires a reboot.
-
Always create a new boot environment.
-
Never create a new boot environment.
-
Activate and reboot.
Note:
Oracle Solaris 11 boot environments cannot have spaces in the name. When you name a boot environment, do not use spaces.
Create Boot Environments Profile for Oracle Solaris 11
Procedure to create boot environments profile for Oracle Solaris 11.
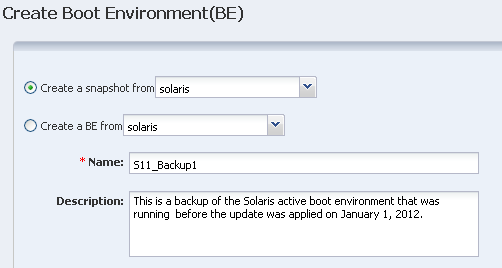
Creating an Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environment
You can create a bootable or non-bootable copy an existing boot environment. A non-bootable copy is call a snapshot. You can create a boot environment from a snapshot.
A new alternate boot environment is automatically created when you install or update the operating system's kernel or system packages.
Create an Oracle Solaris 11 Boot Environment
Procedure to create an Oracle Solaris 11 boot environment.
You can create a bootable or non-bootable (snapshot) copy of an Oracle Solaris 11 boot environment.
If you have a group that contains only Oracle Solaris 11 operating systems and you select the OS group as the target, a new boot environment is created for every active boot environment in the group. You can assign a common name for all of the boot environments. If you do not assign a common name, default names are assigned.