Release 8.0.4 for Windows NT
A55925-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Parallel Server Getting Started Release 8.0.4 for Windows NT A55925-01 |
|
This chapter describes how instances are managed through initialization files and Oracle Parallel Server Manager (OPSM).
Specific topics covered in this chapter are:
An initialization parameter file is an ASCII text file containing a list of parameters. Each node consists of an initialization parameter file named INITSID.ORA with parameters unique for an instance and an initialization parameter file named INIT_COM.ORA with common parameters shared from node-to-node.
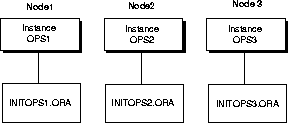
The INITSID.ORA initialization parameter files point to INIT_COM.ORA file for common parameters and define the:
INIT_COM.ORA is called by the individual parameter files through the IFILE parameter.
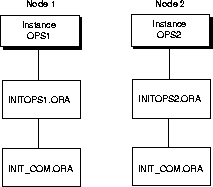
In a parallel server, some initialization parameters must have the same values for every instance, whether individual or common parameter files are used. By referencing the common parameter file using the IFILE parameter within the individual parameter files, instances that have individual parameter files can use the correct parameter values for those that must be identical. This also allows individual parameter files with different values.
Figure 7-3 shows the contents of INITOPS1.ORA:
instance_number=1 thread=1 rollback_segments=(RB1, RB2, RB3, RB4, RB5, RB6, RB7, RB8) ifile=c:\orant\ops\init_com.ora
Figure 7-4 shows the contents of INITOPS2.ORA:
instance_number=2 thread=2 rollback_segments=(RB9, RB10, RB11, RB12, RB13, RB14, RB15, RB16) ifile=c:\ORANT\ops\init_com.ora
Figure 7-5 shows a sample INIT_COM.ORA file:
db_name=ops db_files = 1024 control_files = `\\.\OPS_cntr01' db_file_multiblock_read_count = 8 db_block_buffers = 200 shared_pool_size = 10000000 log_checkpoint_interval = 10000 processes = 59 parallel_max_servers = 5 log_buffer = 8192 sequence_cache_entries = 10 sequence_cache_hash_buckets = 10 max_dump_file_size = 10240 background_dump_dest=%RDBMS80%\trace user_dump_dest=%RDBMS80%\trace db_block_size = 2048 remote_login_passwordfile = shared text_enable = TRUE job_queue_processes = 2 job_queue_interval = 10 job_queue_keep_connections = false distributed_lock_timeout = 300 distributed_transactions = 5 open_links = 4 parallel_server = true
This section describes the following:
Initialization parameters with the prefix GC (Global Constant) are relevant only for an Oracle Parallel Server. These parameters are specified in the INIT_COM.ORA file.
Global constant parameter settings determine the size of the collection of global locks that protect the database buffers on all instances. The settings you choose affect the use of certain operating system resources.
Of the instances (OPS1, OPS2, and so on), the first instance to start up in shared mode determines the values of the global constant parameters for the other instances. The control file records the values of the GC_* parameters when the first instance starts up.
When another instance attempts to start up in shared mode, the Oracle Server compares the values of the global constant parameters in its parameter file with those already in use and issues a message if any values are incompatible. The instance cannot mount the database unless it has the correct values for its global constant parameters.
The global constant parameters for an Oracle Parallel Server are:
Multiple instance issues concerning initialization parameters \are summarized in the following table.
Certain initialization parameters are critical at database creation or affect certain database operations. These parameters must have the same value for every instance in an Oracle Parallel Server specified in each INIT_COM.ORA file for each instance. For example, the values of DB_BLOCK_SIZE and CONTROL_FILES must be identical for every instance. Other parameters can have different values for different instances; for example, INIT_SQL_FILES can have any value because it is ignored except when the database is created.
The following initialization parameters must have identical values for every instance in a parallel server:
Chapter 18, "Administering Multiple Instances", of the Oracle8 Parallel Server Concepts & Administration includes descriptions of the initialization parameters:
The database for which the instance is started must have access to the appropriate initialization parameter files. Oracle Parallel Server uses the initialization parameter files located in ORACLE_HOME\DATABASE, unless you specify a different initialization file with the PFILE option at startup.
To customize Oracle8 Enterprise Edition for Windows NT databases functions, you need to edit the initialization parameter files. Use any ASCII text editor to modify the file.
Although instances can be started and stopped individually from each node using Server Manager, it is not always the most efficient way. OPSM allows you to manager, start and stop one or more instances from one node or from an Oracle Enterprise Manager Console, thus centralizing the management of instances.
|
Additional Information:
See Chapter 6, "Installing and Configuring Oracle Parallel Server Manager", for OPSM requirements and setup. |
After the repository is built, the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console appears with access to the Oracle Parallel Servers in the Navigator tree. An instance or multiple instances are started or stopped by:
|
Additional Information:
See Chapter 2, "Oracle Parallel Server Management Operations", in the Oracle Parallel Server Management User's Guide and the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide for further information about managing Oracle Parallel Servers and parallel server instances from Oracle Enterprise Manager. |
If you configured the Oracle Performance Manager, you can display a variety of tabular and graphic performance statistics for parallel server.
|
Additional Information:
See the Oracle Parallel Server Management User's Guide for further information about using the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console and Oracle Performance Manager. |
The OPSCTL.EXE utility allows you to manage all Oracle Parallel Server instances from each node. You can choose to start or stop all instances on an individual node.
|
Note: The following requirements are met if you followed all the steps in Chapter 5, "Configuring Oracle Parallel Server" and Chapter 6, "Installing and Configuring Oracle Parallel Server Manager". |
OPSCTL requires the following:
OPSCTL.EXE uses this user to start services on remote machines, so this user must have the equivalent of administrator access on each of the nodes. You can either use the default Oracle Enterprise Manager Console credential to access your Oracle Parallel Server or supply a different account name/password combination when creating a startup/shutdown job. In either case, the account used must have DBA privileges on an instance of Oracle Parallel Server in order to start or stop that instance.
OPSCTL START Command Line Usage
OPSCTL START -CCONNECT_STRING -NDATABASE_NAME [-ISID, SID] [-F] [-T] [-U] [-M]
[-Y|-E] [-v] [-h]
where:
To start all instances:
C:\> CD ORACLE_HOME\BIN C:\ORACLE_HOME\BIN> OPSCTL START -CINTERNAL/PASSWORD -NDATABASE_NAME
To start an individual instance:
C:\> CD ORACLE_HOME\BIN C:\ORACLE_HOME\BIN> OPSCTL START -ISID -CINTERNAL/PASSWORD -NDATABASE_NAME
OPSCTL STOP Command Line Usage
OPSCTL STOP -CCONNECT_STRING -NDATABASE_NAME [-ISID, SID] [-F] [-T] [-U] [-M]
[-v] [-h]
where:
To stop all instances:
C:\> CD ORACLE_HOME\BIN C:\ORACLE_HOME\BIN> OPSCTL STOP -CINTERNAL/PASSWORD -NDATABASE_NAME
To stop an individual instance:
C:\> CD ORACLE_HOME\BIN C:\ORACLE_HOME\BIN> OPSCTL STOP -ISID -CINTERNAL/PASSWORD -NDATABASE_NAME