Identifying Your Organization's Revenue Classes
You need to create a revenue class in Oracle Sales Compensation for every discrete type of revenue your company receives. You define a new revenue class when:
- Only a subset of your salespeople get compensation for a given type of revenue.
For example, Figure 3 - 4 shows how Global Computers compensates both direct salespeople and sales consultants for the PC, Peripherals, Consulting and Maintenance revenue classes. However, Global compensates only direct salespeople for the Support, Education, and Documentation revenue classes. Thus, the company must define discrete revenue classes for these types of revenue.
- Compensation varies by type of revenue.
For example, Figure 3 - 4 shows how Global uses different compensation practices for its two main PC models, the Sentinel and the Envoy. The Sentinel has a higher quota, or revenue goal, but has no incentives associated with that type of revenue; the Envoy has a lower quota but, because the company is currently trying to increase sales of the new Envoy model, this type of revenue has an incentive associated with it.
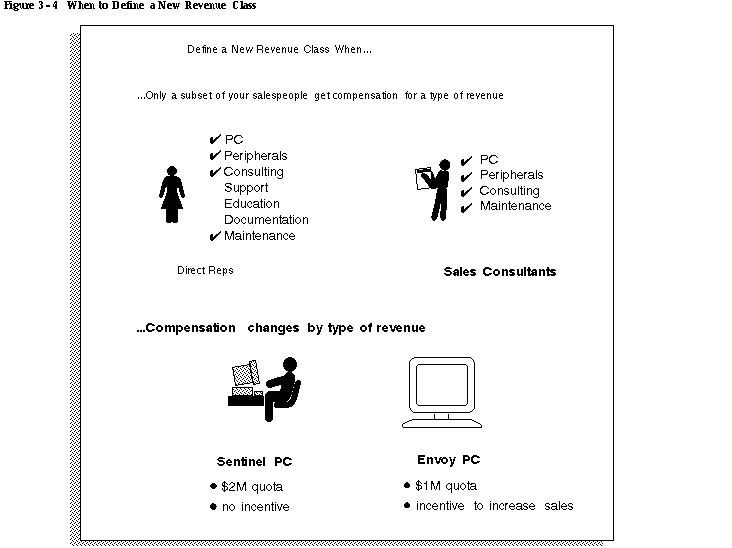
As you determine which revenue classes you need, keep in mind the hierarchy of broader revenue classes and their subclasses. For example, as shown in Figure 3 - 4, Global Computers compensates its two types of PC revenue differently. Thus, Global must define two separate subclasses for the broader PC revenue class.
After identifying your revenue classes, you need to group them into a hierarchical structure which lets you create compensation plans that use both very granular revenue classes or broad revenue classes. See Arranging Revenue Classes into a Hierarchy.
