Release 2 (8.1.6) for Windows NT
A73008-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i Administrator's Guide Release 2 (8.1.6) for Windows NT A73008-01 |
|
This appendix describes how to use Oracle SNMP Agent in Net8 for Windows NT.
Specific topics discussed are:
For a complete description of SNMP concepts and terms, detailed listings of management information contents, and suggestions on how to use SNMP effectively to develop management applications, see the Oracle SNMP Support Reference Guide.
Additional Information:
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a standard internet protocol enabling certain nodes in a network (the management stations or managing nodes) to query other network components or applications for information about their status and activities. Such a query is known as an SNMP poll. These items that can be polled are called managed elements.
The software used by a management station is called a management framework or management station. The management station uses the SNMP protocol to request information from subagents on the nodes being managed, and those agents send back the appropriate responses. The agents can also transmit messages called traps independently from the framework to well-known addresses in response to specific events. This enables quick and sometimes automatic reactions to the specific conditions indicated by the traps.
All requests sent to a given network node are handled by the same master agent. This agent redirects the requests to the appropriate managed elements on the node, in some cases using subagents. The information that SNMP can obtain is described in a structure called a Management Information Base (MIB), which is located on the node of the managed element.
Oracle SNMP support enables Oracle products such as Oracle8i for Windows NT to be located, identified, and monitored by a management station running at one or more centrally located nodes.
SNMP support allows a database to be remotely monitored by any SNMP-capable management software in a TCP/IP network. This feature enables key Oracle products running anywhere on an enterprise's network to be located, identified, and monitored by a management station running at a centrally located node. This is done in much the same way and using many of the same tools as have traditionally been used to monitor the activity of the network itself. Oracle SNMP thereby integrates the tasks of database administrators and network administrators, enabling both to use some of the same tools and to better integrate their tasks.
Oracle SNMP Agent allows you to configure an:
The OracleSNMPPeerMasterAgent is the process on a managed node that accepts queries from the management framework and communicates with the subagents to answer the query. It also can send SNMP traps independently in response to specific conditions. Only one master agent can exist on each managed node. Any node that does not have an agent will not be able to respond to SNMP requests.
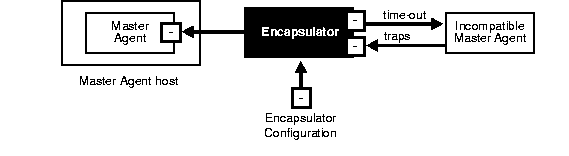
If you are currently using an incompatible agent, such as Microsoft SNMP, you must install the Encapsulator to encapsulate the Microsoft master agent such that all SNMP requests from a Network Management Station (NMS) are sent to OracleSNMPPeerMasterAgent, which then forwards the relevant requests to the encapsulated master agent through the encapsulator. If the encapsulator is not configured, Microsoft SNMP will not work.
This section briefly describes the major tasks that the network administrator must perform to enable the Oracle SNMP Agent.
Oracle SNMP Agent is installed with Oracle Universal Installer.
To configure Oracle SNMP support on a managed node:
The port is specified in the TRANSPORT section of the MASTER.CFG file located at ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\NETWORK\ADMIN.
For example, add the following section to the file:
TRANSPORT ordinary SNMP OVER UDP SOCKET AT PORT 161
COMMUNITY public ALLOW ALL OPERATIONS USE NO ENCRYPTION
The port is specified in the SERVICES file located at NT_HOME\SYSTEM32\DRIVERS\ETC.
For example, make sure you have the following line in the file:
snmp 1161/udp snmp
You must at least add an AGENT entry, including MIB subtrees manageable by NMS, for the encapsulated master agent.
For example, you should have a section like the following in the file:
AGENT AT PORT 1161 WITH COMMUNITY public SUBTREES 1.3.6.1.2.1.1, 1.3.6.1.2.1.2, 1.3.6.1.2.1.3, 1.3.6.1.2.1.4, 1.3.6.1.2.1.5, 1.3.6.1.2.1.6, 1.3.6.1.2.1.7, 1.3.6.1.2.1.8, 1.3.6.1.2.1.77 FORWARD ALL TRAPS;
You may start the master agent from the MS-DOS command prompt or from the Windows NT Control Panel's Services dialog box. Both ways are described below.
To start the master agent from the MS-DOS command prompt:
Invoke the master agent as follows:
C:\> CD ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\BIN C:\> AGENT CONFIGURATION_FILE TEMPORARY_FILE
where CONFIGURATION_FILE is the name of the master configuration file and TEMPORARY_FILE is a temporary file where storage information is to be stored. The master configuration file name is defaulted to MASTER.CFG.
To start the master agent:
The Services dialog box appears. Look for the OracleSNMPPeerMasterAgent service. A blank in Status column indicates that the service has stopped.
If the master is running, skip to Step 3. If the master is not running, continue to Step 2.
The master agent starts.
You may start the encapsulator from the MS-DOS command prompt or from the Windows NT Control Panel's Services dialog box. Both ways are described below.
|
Note: If the Encapsulator is to be used, the master agent must be started first. See "Starting the Master Agent" in this appendix. |
To start the encapsulator from the MS-DOS command prompt:
C:\> CD ORACLE_BASE|ORACLE_HOME\BIN C:\> ENCAPS [options]
There are six command line options as shown below. The options are:
To start the encapsulator from the Control Panel Window:
The Services dialog box appears. Look for the OracleSNMPPeerEncapsulator service. A blank in the Status column indicates that the service is stopped.
If the master is running, skip to Step 3. If the master is not running, continue to Step 2.
The encapsulator is started.
The MASTER.CFG file controls several aspects of the OracleSNMPPeerMaster Agent, including:
A sample MASTER.CFG file is shown in the figure below:
######################################################################### # Default Agent Configuration File # # This file allows MANAGERS to be specified. This is used to # specify which managers will be receiving which traps. # # Also, COMMUNITYs can be specified. This allows that agent to # be configured such that it will only except requests from # certain managers and with certain community strings. # # Syntax # TRANSPORT <name> SNMP # [OVER UDP SOCKET] # [AT <addr>] # COMMUNITY <communityName> # ALLOW <op> [,<op>]* [OPERATIONS] # [AS ENTITY <entityName>] # [MEMBERS <addrs> [,<addrs>] ] TRANSPORT ordinary SNMP OVER UDP SOCKET AT PORT 161 COMMUNITY public ALLOW ALL OPERATIONS USE NO ENCRYPTION
Below is a description of the TRANSPORT and COMMUNITY parameters.
The ENCAPS.CFG configuration file specifies which incompatible agents are to be encapsulated and what to make visible to the Network Management Station (NMS).
A sample ENCAPS.CFG configuration file is shown below:
########################################################################## # # THIS IS AN EXAMPLE OF AN ENCAPSULATOR CONFIGURATION FILE. # # USING THIS FILE, ENCAPSULATOR WILL ENCAPSULATE A NON-PEER # MIB2 AGENT ON THE SAME PROCESSOR, THAT'S LISTENING FOR SNMP # REQUESTS AT PORT 1161. # # IT ALLOWS THE NETWORK MANAGEMENT STATION TO VIEW THE 8 SUBTREES # MANAGED BY THAT AGENT, AND TO RECEIVE ALL THE TRAPS EMITTED BY # THAT AGENT. ALL THE REQUESTS AND TRAPS PASS THROUGH THE PEER # AGENT AND ENCAPSULATOR. AT THE SAME TIME THAT THE PEER AGENT # IS HANDLING ENCAPSULATOR, IT ALSO HANDLES ALL SUB-AGENTS THAT # WERE DEVELOPED WITH THE PEER TOOLKIT TO MANAGE OTHER MIBS. # Syntax: # [ # AGENT [ON HOST <ip>] [AT PORT <port>] [WITH COMMUNITY <community>] # SUBTREES <treelist> # [FORWARD <traplist> TRAPS] # ; # ]+ # AGENT AT PORT 1161 WITH COMMUNITY public SUBTREES 1.3.6.1.2.1.1, 1.3.6.1.2.1.2, 1.3.6.1.2.1.3, 1.3.6.1.2.1.4, 1.3.6.1.2.1.5, 1.3.6.1.2.1.6, 1.3.6.1.2.1.7, 1.3.6.1.2.1.8, 1.3.6.1.4.1.77 FORWARD ALL TRAPS;
Below is a description of the parameters.
Users of other network management systems, such as HP OpenView, may encounter interference with the encapsulator if they are installed on the same machine after installation of Oracle SNMP Agent. This results from an HP OpenView change to the SNMP port in the SERVICES file. The port specified for SNMP in the SERVICES file must match that specified in the ENCAPS.CFG file.
To resolve the problem, after installing HP Open View, change the SNMP port in either the SERVICES file or the ENCAPS.CFG, so that the two files agree.
|
|
 Copyright © 2000 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|