Release 2 (8.1.6)
A76989-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i SQL Reference Release 2 (8.1.6) A76989-01 |
|
SQL Statements (continued), 6 of 11
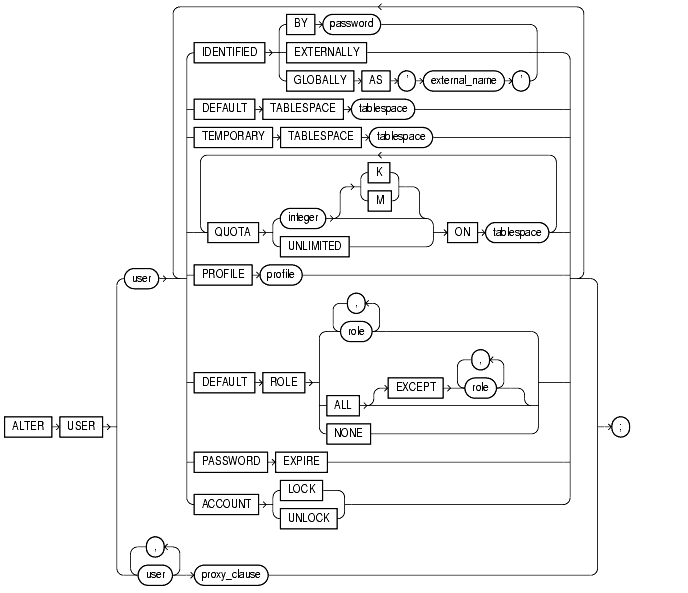
To change the authentication or database resource characteristics of a database user.
To permit a proxy server to connect as a client without authentication.
|
Note:
|
You must have the ALTER USER system privilege. However, you can change your own password without this privilege.
The keywords and parameters shown below are unique to ALTER USER or have different functionality than they have in CREATE USER. All the remaining keywords and parameters in the ALTER USER statement have the same meaning as in the CREATE USER statement. For information on these keywords and parameters, see "CREATE USER".
To assign limits on database resources to a user, see "CREATE PROFILE".
|
IDENTIFIED BY password |
Note: Oracle expects a different timestamp for each resetting of a particular password. If you reset one password multiple times within one second (for example, by cycling through a set of passwords using a script), Oracle may return an error message that the password cannot be reused. For this reason, Oracle Corporation recommends that you avoid using scripts to reset passwords. |
|
|
|
indicates that a user must be authenticated by way of an LDAP V3 compliant directory service such as Oracle Internet Directory. (See also "CREATE USER".)
You can change a user's access verification method to
You can change a user created as |
|
|
|
can contain only roles that have been granted directly to the user with a
Oracle enables default roles at logon without requiring the user to specify their passwords. See Also: "CREATE ROLE". |
|
|
proxy_clause |
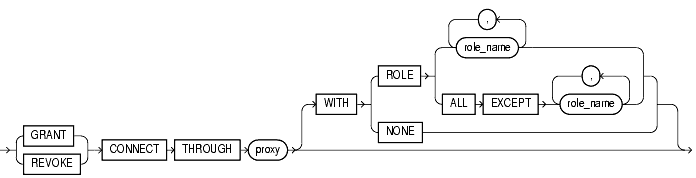
controls the ability of a proxy (an application or application server) to connect as the specified user and to activate all, some, or none of the user's roles. See Also: Oracle8i Concepts for more information on proxies and their use of the database. |
|
|
|
|
allows the connection. |
|
|
|
prohibits the connection. |
|
|
proxy |
identifies the proxy connecting to Oracle. |
|
|
|
specifies the roles that the application is permitted to activate after it connects as the user. If you do not include this clause, Oracle activates all roles granted to the specified user automatically. |
|
|
role_name |
permits the proxy to connect as the specified user and to activate only the roles that are specified by role_name. |
|
|
|
permits the proxy to connect as the specified user and to activate all roles associated with that user except those specified by role_name. |
|
|
|
permits the proxy to connect as the specified user, but prohibits the proxy from activating any of that user's roles after connecting. |
The following statement changes the user SCOTT's password to LION and default tablespace to the tablespace TSTEST:
ALTER USER scott IDENTIFIED BY lion DEFAULT TABLESPACE tstest;
The following statement assigns the CLERK profile to SCOTT:
ALTER USER scott PROFILE clerk;
In subsequent sessions, SCOTT is restricted by limits in the CLERK profile.
The following statement makes all roles granted directly to SCOTT default roles, except the AGENT role:
ALTER USER scott DEFAULT ROLE ALL EXCEPT agent;
At the beginning of SCOTT's next session, Oracle enables all roles granted directly to SCOTT except the AGENT role.
The following statement changes user TOM's authentication mechanism:
ALTER USER tom IDENTIFIED GLOBALLY AS 'CN=tom,O=oracle,C=US';
The following statement causes user FRED's password to expire:
ALTER USER fred PASSWORD EXPIRE;
If you cause a database user's password to expire with PASSWORD EXPIRE, the user (or the DBA) must change the password before attempting to log in to the database following the expiration. However, tools such as SQL*Plus allow you to change the password on the first attempted login following the expiration.
The following statement permits the proxy user APPSERVER1 to connect as the user JANE. It also allows APPSERVER1 to activate the role INVENTORY:
ALTER USER jane GRANT CONNECT THROUGH appserver1 WITH ROLE inventory;
The following statement takes away the right of proxy user APPSERVER1 to connect as the user JANE:
ALTER USER jane REVOKE CONNECT THROUGH appserver1;
|
|
 Copyright © 1999 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|