Release 8.0.6 for Windows NT
A69518-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8 Enterprise Edition Getting Started Release 8.0.6 for Windows NT A69518-01 |
|
This chapter describes the options available to you when you have existing databases on your computer and want to install the latest release of Oracle8 Enterprise Edition. In particular, it describes how to coexist different database releases in the same Oracle home or in multiple Oracle homes, and how to migrate an Oracle7 database or upgrade an earlier Oracle8 database release to the current release of Oracle8 Enterprise Edition. This chapter also includes information on migrating a Microsoft Access database to an Oracle8 database.
Specific topics discussed are:
Read this chapter if you have existing Oracle7 and/or Oracle8 databases on your computer and you want to install Oracle8 Enterprise Edition release 8.0.6. If you are installing Oracle8 Enterprise Edition on a computer that has no other Oracle database releases, you do not have to read this chapter.
|
Additional Information:
See Oracle8 Enterprise Edition Installation for Windows NT if you want to install Oracle8 Enterprise Edition on a computer containing no other databases. |
The generic Oracle8 Migration guide is the primary source of migration information in the Oracle documentation set. Read the first three chapters of that guide for information on how to prepare your existing databases for migration before performing a migration. Information on how to run the various migration and upgrade utilities is also provided in the generic guide, but the focus is on UNIX. This chapter provides information on using these utilities on Windows NT.
If you already have Oracle7, or Oracle7 and Oracle8 databases on your computer and want to install release 8.0.6, the following options are available to you.
If you are not sure what option is best for you, read the following overview sections:
Releases of Oracle for Windows NT and Windows 95 prior to release 8.0.4 only supported single Oracle homes, allowing you to install and run Oracle products in a single Oracle home. Different versions of Oracle products could be installed in the same Oracle home provided they had different second-digit release numbers. For example, you could install release 7.2 products and release 7.3 products in the same Oracle home (database coexistence). However, you could not install multiple third-digit releases of the same products. For example, you could not install release 7.3.2 and release 7.3.3 versions of the same Oracle products on the same computer; one installation would overwrite the other.
The multiple Oracle homes feature enables you to install one or more releases of Oracle products on the same computer in multiple Oracle homes. For example, with multiple Oracle homes, you can install release 8.0.6 products and 8.0.4 products in different Oracle homes on the same computer. You can still install different releases of Oracle products in the same Oracle home provided they have different second-digit release numbers. See Chapter 6, "Using Multiple Oracle Homes" for more information.
This section explains the difference between migrating, upgrading, and downgrading, and lists the Oracle database versions that can be migrated or upgraded.
Migrating is the process of transforming one database version to a later database version. For example, transforming an Oracle7 database to an Oracle8 database is migrating the database system. The term migrating is also used in this guide to refer to the transformation of a Microsoft Access database to an Oracle8 database.
Upgrading is the process of transforming one database release to another database release of the same database version. For example, transforming an Oracle8 database release 8.0.4 to release 8.0.6 is upgrading the database system.
Downgrading is the process of transforming an installed version of an Oracle database from a later release back into an earlier release. For example, transforming an Oracle database from release 8.0.6 back into release 8.0.3 is downgrading, and transforming an Oracle database from version 8 back into version 7 is downgrading.
You can easily migrate or upgrade databases across multiple Oracle homes. If you use the graphical user interface (GUI) Oracle Data Migration Assistant, all database instances on your system are displayed in a drop-down list. You select the Oracle database instance you want to migrate or upgrade and the assistant takes care of any multiple Oracle homes issues.
If you use the command line tools, MIG80 to migrate, or a U*.SQL script to upgrade, you need to copy files from one Oracle home directory to another. You must also ensure the PATH variable is set correctly so that any Oracle database tools you run are started from the correct Oracle home directory.
Check that your Oracle database release can be migrated or upgraded directly to Oracle8 Enterprise Edition. This table provides a list of the database releases you can migrate or upgrade and the tools you can use to perform these tasks:
An alternative method of migrating or upgrading is to:
The Export Utility puts all of the data in one large binary file that can require large amounts of disk space.
|
Additional Information:
See "Choose a Migration Method" in Chapter 2 "Preparing to Migrate" of Oracle8 Migration for information on when to use the Export/Import utilities for migrating a database. See "Export an Existing Database" and "Import a Database" for information on using these tools. |
Oracle7 and Oracle8 clients can communicate either with Oracle7 or Oracle8 databases. This functionality gives you maximum flexibility when designing your network and deciding when to:
Consider the following database coexistence issues before you decide which of the above options is most suitable for your requirements:
Can all my Oracle7 applications run on an Oracle8 database?
Most Oracle7 applications can run on an Oracle8 database. Some applications cannot run on an Oracle8 database unless you upgrade them to versions that support Oracle8 databases. If you have a combination of Oracle7 and Oracle8 applications, you may want to have an Oracle7 database and Oracle8 database exist on the same computer, until you have time to upgrade all your Oracle7 applications to Oracle8. Contact your application vendor to check if your third-party applications are supported with Oracle8 Enterprise Edition.
Check the following criteria to ensure successful Oracle7 client connections to an Oracle8 database. If the Oracle7 client and Oracle8 database are located in:
install both SQL*Net Client 2.3.x and Net8 Server in this home
install SQL*Net Client 2.3.x in the Oracle7 client home and Net8 Server in the Oracle8 home
install SQL*Net Client 2.3.x in the Oracle7 client home and Net8 Server in the Oracle8 home
If you are using these releases:
you can connect to the Oracle8 database without specifying a service name. Oracle7 client automatically uses the Bequeath Protocol Adapter when connecting to a local Oracle8 database.
you need to create a service name using SQL*Net Easy Configuration or Oracle Network Manager in the SQL*Net Client version 2.x TNSNAMES.ORA file. Ensure you specify this service name in the connect string when connecting to the Oracle8 database. The Bequeath Protocol Adapter is not supported when connecting from an Oracle7 client (release 7.3.3 or lower) to an Oracle8 database.
Check the following criteria to ensure successful Oracle8 client connections to an Oracle7 database. If the Oracle8 client and Oracle7 database are located in:
install both Net8 Client and SQL*Net Server 2.3.x in this home
install Net8 Client in the Oracle8 client home and SQL*Net Server 2.3.x in the Oracle7 home
install Net8 Client in the Oracle8 client home and SQL*Net Server 2.3.x in the Oracle7 home
Install Oracle7 and Oracle8 databases in the same Oracle home directory and have both Oracle7 and Net8 clients connecting to Oracle7 and Oracle8 databases. The figure below gives an example of this network configuration:
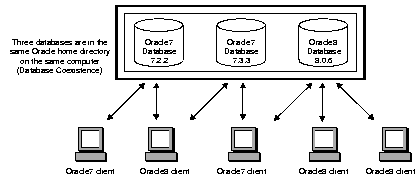
You can install different versions of Oracle databases in the same Oracle home provided they have different first or second-digit versions. For example, you can have release 7.2.x, 7.3.x, and 8.0.x databases in the same Oracle home.
You cannot install multiple third-digit releases of the same products. For example, you cannot install release 7.3.2 and release 7.3.3, or release 8.0.3 and release 8.0.4, in the same Oracle home; one installation overwrites the other.
Ensure that each database instance has a unique SID. In particular, be careful that you do not use the default SID ORCL for subsequent installations if you already have a starter database with the SID ORCL installed. If you do so, the services of the later installation overwrite the services of the earlier installation.
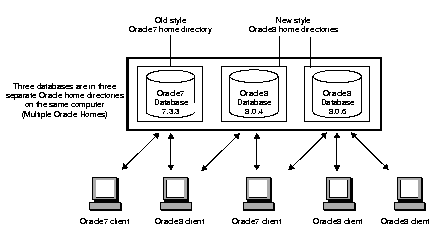
Install Oracle7 and Oracle8 databases in multiple (separate) Oracle homes and have both Oracle7 and Net8 clients connecting to Oracle7 and Oracle8 databases.
Multiple Oracle homes functionality only works with releases 8.0.4, 8.0.5, and 8.0.6. These are known as new style Oracle homes.
If you have, for example, release 7.3.3 products already installed, you cannot install any other release 7.x products in a separate Oracle home. Also, if you have release 8.0.3 or earlier 8.0.x products already installed, you cannot install any other of these products in a separate Oracle home. These are known as old style Oracle homes. The figure below gives an example of this network configuration:
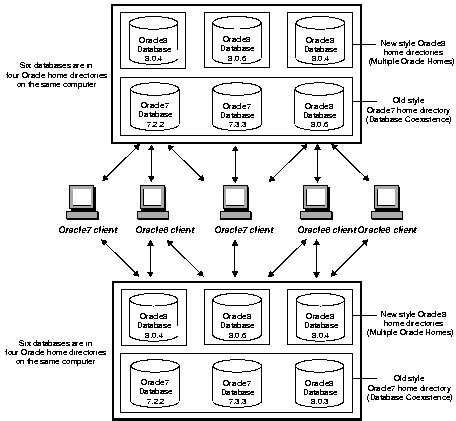
Install Oracle7 and Oracle8 databases on separate computers and have both Oracle7 and Net8 clients connecting to both databases. The figure below shows two computers and a number of Oracle7 and Oracle8 clients. On each computer you can have a mix of databases and products in both single and multiple Oracle homes.
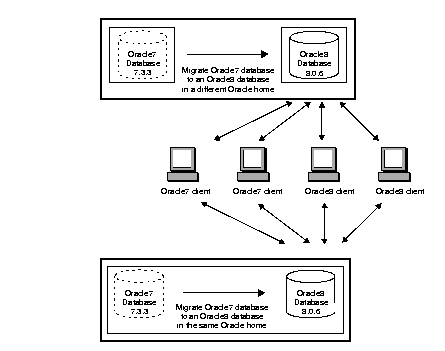
Migrate your Oracle7 database to an Oracle8 database and have both Oracle7 and Oracle8 clients connecting to the Oracle8 database. You can migrate your Oracle7 database to an Oracle8 database either in the same Oracle home or in a different Oracle home. See "Migrating an Oracle7 Database to Version 8" for instructions. The figure below illustrates this network configuration:
Upgrade your Oracle8 database, for example, release 8.0.4 to release 8.0.6 and have both Oracle7 and Oracle8 clients connecting to the release 8.0.6 Oracle8 database. You can upgrade databases either in the same Oracle home or across different Oracle homes. See "Upgrading an Oracle8 Database Release 8.0.x to 8.0.6" for instructions. The figure below illustrates this network configuration:
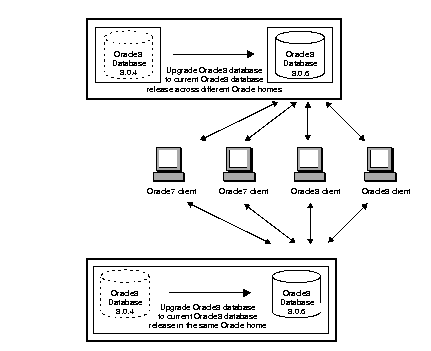
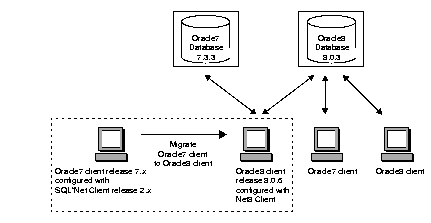
Migrate some or all of your Oracle7 clients to Oracle8 release 8.0.6 and migrate your Oracle7 database to an Oracle8 database or upgrade your Oracle8 database to the current Oracle8 release at a later date. See Net8 Getting Started for Windows NT and Windows 95/98 for instructions. The figure below illustrates this network configuration.
You can run different versions of Oracle databases on the same computer system at the same time. However, each version can only access a database that is consistent with its version. For example, if you have version 7 and version 8 of Oracle installed on the same computer system, the version 7 server can access version 7 databases, but not version 8 databases, and the version 8 server can access version 8 databases but not version 7 databases. The only way for a version 8 database to read version 7 database files is to perform a migration. You should be aware that after migration, the version 7 database will no longer be able to read the files.
In the following example, an Oracle7 release 7.3.3 starter database named ORACLE with a SID of ORCL is already installed in C:\ORANT. Now, create an Oracle release 8.0.6 database named PROD with a SID of PROD in C:\ORANT.
To install an Oracle8 database and Oracle7 database into the same Oracle home:
The Oracle Installation Settings dialog box appears.
The Select Installation Settings dialog box appears.
The Select Oracle8 Cartridge dialog box appears.
The Previous Version of Oracle Database Detected dialog box appears indicating that Oracle Installer has detected an earlier version of the database. You are asked if you want to migrate your Oracle7 database to release 8.0.6 using Oracle Data Migration Assistant.
The Select a Starter Database Configuration dialog box appears.
The following Oracle Database Assistant window appears:
When you get to the last window, click Finish to start the creation of the PROD database. More documentation is included with the assistant Help.
In the following example, an Oracle7 release 7.3.3 starter database called ORACLE with a SID of ORCL is already installed in C:\ORANT. Now, install the Oracle release 8.0.6 starter database ORCL in a separate Oracle home directory called C:\ORANTv8 with an Oracle home name of TESTv8.
To install an Oracle8 database and Oracle7 database in multiple (separate) Oracle homes:
The Oracle Installation Settings dialog box appears.
The Select Installation Settings dialog box appears.
The Select Oracle8 Cartridge dialog box appears.
The Select a Starter Database Configuration dialog box appears.
During installation of the release 8.0.6 database, Oracle Installer detects the listener of the previously installed release 7.3.3 database. To avoid conflicts of listening addresses (for example, the port number for TCP/IP), the new release 8.0.6 listener is not started and is set to Manual Startup mode. After installation is complete, modify the release 8.0.6 LISTENER.ORA file to resolve possible conflicts in listening addresses, and then start the listener. This is required to enable the release 8.0.6 database to accept connections from clients. See Net8 Getting Started for Windows NT and Windows 95/98 for information on how to modify the LISTENER.ORA file.
This section describes how to migrate an Oracle7 database to the current Oracle8 database release. You can choose either of the following tools to perform a migration:
Oracle Corporation recommends that new users use Oracle Data Migration Assistant to migrate databases because it is the easiest method to perform a migration. If you want to perform a migration manually using command line tools, use MIG80.
Before you start a migration using the assistant or MIG, read the following sections:
The following table lists and describes the ten issues you should be aware of that can affect Oracle7 to Oracle8 migration.
| Issues That Affect Migration | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The time it takes to migrate is not dependent on the size of the database, but on the number of objects in the data dictionary. For example, actual migration for a 3 1/2 GB database with 25,473 objects on a Sun E6000 with 20 CPUs, with datafiles stripped on the file system on 128 KB slices can take 1 1/2 hours. Remember to allow extra time for backing up and restoring database in case of problems. |
|
|
|
|
Make sure that all Oracle product versions, operating system versions, and third-party software versions are certified against Oracle8. See "Overview" for the list of supported Windows operating systems and versions. See "Oracle Products for Windows NT, Windows 95, and Windows 98" for a list of supported Oracle product versions for this release. |
|
|
Migration leaves all objects (packages, triggers, views, and so on) invalid except for tables. All other objects must be made valid again by recompilation. This can either be done manually (preferably by building a dependency tree before migration from dependency), otherwise this is done automatically as the objects are first accessed. The latter will of course slow down initial access. All estimated or calculated statistics are lost during migration. These need to be recalculated to ensure proper functionality of the Cost Based Optimizer. Some bitmapped indexes will get invalidated. Check all bitmapped indexes in the DBA_INDEXES table and recreate any that are marked as status unusable. |
|
|
If you edit the registry for any reason during the migration process, you need to reboot your computer. |
|
|
Oracle7 read-only tablespaces are readable by Oracle8 and do not require any conversion. But to prevent Oracle8 rowid conversions to take place every time a table is accessed, the tablespaces in read-only mode should be made read-write. Perform full table scans on all tables in the tablespace. After the full table scans are complete, you can put the tablespaces in read-only mode again. |
|
|
You can return the database to an Oracle7 version up until the ALTER DATABASE CONVERT command is run. If a failure occurs during ALTER DATABASE CONVERT (when it is converting the physical file headers of the datafiles), you must restore the database from backup and rerun the migration. Do not open the database between running the migration and executing the ALTER DATABASE CONVERT command. |
|
|
To avoid restoring the entire database due to any failures during the ALTER DATABASE CONVERT, put all tablespaces, except SYSTEM and ROLLBACK into read-only or offline normal mode. This causes the ALTER DATABASE CONVERT command to only convert the datafile headers for SYSTEM and ROLLBACK. If any errors occur, you need only restore the datafiles for the SYSTEM and ROLLBACK and rerun the migration. If the migration is successful, the headers for the rest of the datafiles will be converted when they are read-write or online. |
|
|
Most migration problems can be avoided if a test migration is performed first. Performing a test migration helps raise any problems that can occur as well as letting you see the amount of time it takes to migrate. See "Test the Migration Process" in Chapter 2, "Preparing to Migrate" in Oracle8 Migration. |
If you perform a migration, you may need to resolve the following networking issues:
Although Oracle7 clients using SQL*Net Client version 2.x can connect to Oracle8 databases, they should be migrated to Oracle8 clients configured with Net8 when their applications are upgraded to version 8. Note that SQL*Net version 2.x can coexist with Net8 in the same Oracle home directory.
To use the Net8 listener, you may need to change your network configuration on either the SQL*Net version 2.x or Net8 configurations to prevent a conflict. For example, you may need to change:
You may also need to start the Net8 listener and change the status of the service to Automatic Startup, depending upon your network needs. If you make changes to the listener, you must make changes to client configuration files to reflect those listener changes.
SQL*Net version 2.x uses configuration files from ORACLE_HOME\NETWORK\ADMIN, while Net8 uses files from ORACLE_HOME\NET80\ADMIN by default. If you want SQL*Net version 2.x and Net8 to use configuration files from the same directory, you can set the registry variable TNS_ADMIN.
|
Additional Information:
See Net8 Getting Started for Windows NT and Windows 95 for more information on setting TNS_ADMIN. |
When you migrate from an Oracle7 database in one Oracle home to an Oracle8 database release 8.0.6 in a different Oracle home, remove the SID from the Oracle7 Oracle home's LISTENER.ORA file and add it to the release 8.0.6 Oracle home's LISTENER.ORA file.
When you migrate from an Oracle7 database in one Oracle home to an Oracle8 database release 8.0.6 in a different Oracle home, the assistant does not remove the SID from the Oracle7 Oracle home's LISTENER.ORA file. To prevent a conflict when you start the Oracle7 listener, remove the SID entry from the Oracle7 Oracle home's LISTENER.ORA file.
When migrating from Oracle7 Server release 7.3.x to Oracle8 release 8.0.6, install the appropriate version of SQL*Net for the server before using Oracle Data Migration Assistant or MIG80. Migration will be unsuccessful if you do not install the appropriate versions of SQL*Net. You do not need to install a SQL*Net patch when migrating from Oracle7 release 7.3.4 to Oracle8 release 8.0.6.
| Migrating from... | Install... |
|---|---|
|
Oracle7 release 7.3.2.x and higher to Oracle8 |
SQL*Net release 2.3.2.1.4 and SQL*Net patch 2.3.2.1.12 Note: If you do not have SQL*Net release 2.3.2.1.4 on your system, you must install it before installing SQL*Net patch 2.3.2.1.12. SQL*Net release 2.3.2.1.4 is not available on the release 8.0.6 CD-ROM. You must install it from the release 7.3.2 CD-ROM. |
|
Oracle7 release 7.3.3.x and higher to Oracle8 |
SQL*Net release 2.3.3.0.3 |
|
|
To install SQL*Net patch 2.3.2.1.12 or 2.3.3.0.3:
|
Oracle Data Migration Assistant helps you migrate data from an Oracle7 database to an Oracle8 database. During installation of Oracle8 Enterprise Edition, you are prompted to migrate a database with this assistant if Oracle Installer detects that an earlier database release exists on your computer. If you do not want to migrate a database during the installation process, you can just install the assistant and use it later.
Complete the following steps before you use this assistant:
To migrate a database using Oracle Data Migration Assistant:
The Oracle Data Migration Assistant welcome window appears:
This section describes how to use MIG80 to migrate your Oracle7 database to an Oracle8 database.
|
Note: Information on how to run MIG80 (sometimes referred to as the Migration Utility) is provided in Oracle8 Migration, but the focus is on UNIX. This section provides information on using MIG80 on Windows NT. |
To migrate an Oracle7 database using MIG80:
Step 1: What To Do Before Using MIG80
Step 2: Prepare for Database Backup
Step 3: Shut Down the Oracle7 Database
Step 4: Back Up the Oracle7 Database
Step 5: Install MIG80 From Oracle8 Enterprise Edition CD-ROM
Step 7: Create Oracle8 Services and Database Files
Step 8: Remove Oracle7 Software (Optional)
Complete the following steps before you use MIG80:
When you are asked to enter commands at the SQL*DBA or Server Manager prompt, remember to use the appropriate version of the tool for the version of Oracle7 Server you are migrating:
| Use... | When Migrating From... |
|---|---|
|
SQLDBA71 |
Oracle7 release 7.1.x |
|
SQLDBA72 |
Oracle7 release 7.2.x |
|
SVRMGR23 |
Oracle7 release 7.3.x |
Check that your database release can be directly migrated to Oracle8 Enterprise Edition. MIG80 only migrates databases that are Oracle7, release 7.1.x or later. If the database is an earlier version (for example, version 6), migrate it to at least Oracle7 release 7.1.3.3.6 before migrating it to an Oracle8 database.
| Oracle7 Release... | Enter at the MS-DOS Command Prompt... |
|---|---|
|
7.1.x |
|
|
7.2.x |
|
|
7.3.x |
|
| Oracle7 Release... | Enter at the SQLDBA or SVRMGR Command Prompt... |
|---|---|
|
7.1.x |
|
|
7.2.x |
|
|
7.3.x |
|
The character set value is returned by the database. If the character sets are identical, then you can proceed to run MIG80.
If the character sets are different, before you run MIG80, you must set the NLS_LANG environment variable at the MS-DOS command prompt as follows:
AMERICAN_AMERICA.database character set
where database character set is substituted with the character set of your Oracle7 database. For example, if the character set of your Oracle7 database is JA16EUC, set the NLS_LANG environment variable as follows:
C:\> SET NLS_LANG=AMERICAN_AMERICA.JA16EUC
Messages output from MIG80 will now be in English. After MIG80 finishes, reset the NLS_LANG environment variable to its original value.
To obtain the list of database files you must back up:
| Oracle7 Release... | Enter at the SQLDBA or SVRMGR Command Prompt... |
|---|---|
|
7.1.x |
|
|
7.2.x |
|
|
7.3.x |
|
| Oracle7 Release... | Enter at the SQLDBA or SVRMGR Command Prompt... |
|---|---|
|
7.1.x |
|
|
7.2.x |
|
|
7.3.x |
|
Shut down the database. Do not use SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE or SHUTDOWN ABORT. If the database is not shut down before you start the migration, MIG80 stops and issues an error message. Also, if the database is not cleanly shutdown, any backup you make may be useless as it was taken while data was being written to the data files.
| Oracle7 Release... | Enter at the MS-DOS Command Prompt... |
|---|---|
|
7.1.x |
|
|
7.2.x |
|
|
7.3.x |
|
| Oracle7 Release... | Enter at the SQLDBA or SVRMGR Command Prompt... |
|---|---|
|
7.1.x1 |
|
|
7.2.x |
|
|
7.3.x |
|
|
1
For Oracle7 release 7.1 only, edit the INITSID.ORA file and set the REMOTE_LOGIN_PASSWORDFILE parameter to EXCLUSIVE or SHARED. |
The message Connected appears if you successfully connected to the database.
| Oracle7 Release... | Enter at the SQLDBA or SVRMGR Command Prompt... |
|---|---|
|
7.1.x |
|
|
7.2.x |
|
|
7.3.x |
|
|
Warning: If anything goes wrong with the Oracle7 database during migration, you will need to restore the database from the backup. Back up your database now as a precaution! |
Ensure the database was cleanly shut down before you back up. Ensure you back up the database files in the following list (and any other database files you may have created). Also, back up any scripts you may have created.
See Chapter 13, "Backing Up and Recovering Database Files", Oracle8 Concepts, Oracle8 Backup and Recovery, and Oracle8 Administrator's Guide for information on how to back up a database.
To stop services:
The operating system automatically detects your Oracle8 Enterprise Edition for Windows NT CD-ROM, and the Oracle8-Autorun dialog box appears.
Each time you insert your CD-ROM, the process described in Step 4 occurs. To restart Oracle Installer without removing and reinserting your CD-ROM, select the drive to which the CD-ROM is mapped, and double-click SETUP.EXE.
Attention:
The Oracle Installation Settings dialog box appears.
The Select Installation Options dialog box appears.
The Select Oracle8 Cartridge dialog box appears.
The Previous Version of Oracle Database dialog box appears indicating that Oracle Installer has detected an earlier version of the database. You are asked if you want to migrate your Oracle7 database to release 8.0.6 using Oracle Data Migration Assistant.
The Select a Starter Database Configuration dialog box appears.
MIG80 was installed as part of Oracle8 Utilities when you installed Oracle8 Enterprise Edition in "Step 5: Install MIG80 From Oracle8 Enterprise Edition CD-ROM".
C:\> NET START OracleServiceSID
C:\> SET ORACLE_SID=ORCL
This command creates the CONVERT.ORA file that is required in a later step to create Oracle8 Enterprise Edition control files.
The prompt Oracle7 Password appears.
MIG80 runs and displays the operations being performed. MIG80 can take considerable time to run. Please wait until it has finished running.
Check the results after running MIG80. If there are error messages see Appendix A, "Migration Utility Messages" of Oracle8 Migration for more information before going to Step 8.
C:\> NET STOP OracleServiceSID
| Oracle7 Release... | Enter at the MS-DOS Command Prompt... |
|---|---|
|
7.1.x |
|
|
7.2.x |
|
|
7.3.x |
|
MIG80 creates a convert file that contains the information of the version 7 control file. Later in the migration process, the convert file is used when you execute the ALTER DATABASE CONVERT command to create a new control file for version 8.
The default location of the convert file is ORACLE_HOME/RDBMS80 and the default filename in this directory is CONVERT.ORA.
After successfully running MIG80, perform a cold backup of the Oracle7 database. This backup serves the following purposes:
|
Additional Information:
See Chapter 13, "Backing Up and Recovering Database Files", Oracle8 Concepts, Oracle8 Backup and Recovery, and Oracle8 Administrator's Guide for information on how to back up a database. |
C:\> ORADIM80 -NEW -SID SID -INTPWD PASSWORD -MAXUSERS USERS -STARTMODE AUTO -PFILE ORACLE_HOME\DATABASE\INITSID.ORA
where:
If you use the default setting (8.0.0.0.0), you cannot use new features of release 8.0.4 and later such as Propagation in Advanced Queuing (AQ) and Improved SCN Generation. To use these new features, set the COMPATIBLE parameter to the following:
COMPATIBLE=8.0.4.0.0
See Appendix C "Version 8 INIT.ORA Changes" of Oracle8 Migration for more information on COMPATIBLE parameter values.
C:\> SVRMGR30
SVRMGR> CONNECT INTERNAL/PASSWORD
SVRMGR> STARTUP NOMOUNT
SVRMGR> ALTER DATABASE CONVERT;
This command uses the CONVERT.ORA file that was created earlier when you ran MIG80. All data files that are online are converted to Oracle8 Enterprise Edition format, and new control files are built. Control files are considerably larger in version 8 than in version 7. Control files in the tens of kilobytes size range in version 7 could be expanded into the range of tens of megabytes automatically during migration to version 8. This size increase could be important if a control file is on a raw device or if its available disk space is restricted.
SVRMGR> ALTER DATABASE OPEN RESETLOGS;
All rollback segments that are online when the Oracle8 database is opened are also opened and converted to the Oracle8 database format.
SVRMGR> SPOOL CATOUT.LOG
Oracle Corporation supplies other scripts with Oracle8 Enterprise Edition that create additional structures you can use in managing your database and creating database applications. These scripts are also located in ORACLE_HOME\RDBMS80\ADMIN. See the chapter "SQL*Scripts" in Oracle8 Reference for a complete list and descriptions of available scripts.
SVRMGR> SPOOL OFF
SVRMGR> SHUTDOWN
Performing a clean database shutdown flushes all caches, clears buffers, and performs other Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) housekeeping activities. These measures are an important final step to ensure the integrity and consistency of the newly migrated release 8.0.6 database.
The Oracle7 database has now been migrated to the Oracle8 database and is ready for use.
You can remove Oracle7 software if you have successfully migrated to Oracle8 Enterprise Edition and have a backup of the Oracle7 software. Oracle Installer warns you of any product dependencies that might cause problems if particular products are removed, and prompts you to confirm the deinstallation.
To remove Oracle7 software:
The Software Asset Manager window appears.
This section describes how to upgrade an Oracle8 database release 8.0.x to release 8.0.6. You can choose either of the following database tools to upgrade:
Oracle Corporation recommends that new users use Oracle Data Migration Assistant to upgrade databases because it is the easiest and quickest method to perform an upgrade. If you already have upgrade scripts from a previous Oracle database release, you can edit them to include the new upgrading scripts.
Oracle Data Migration Assistant helps you upgrade data from an Oracle8 database release 8.0.x to release 8.0.6. During installation of Oracle8 Enterprise Edition, you are prompted to upgrade a database with this assistant if Oracle Installer detects that a release 8.0.x database exists on your system. If you do not want to upgrade during the installation process, you can just install this assistant and use it later.
Before you use this assistant, ensure the Oracle8 database to be upgraded meets these requirements:
To upgrade a database using Oracle Data Migration Assistant:
The Oracle Data Migration Assistant welcome window appears:

You can run SQL scripts in Server Manager to upgrade an Oracle8 database release 8.0.x to release 8.0.6.
Review the following documents:
Upgrading consists of the following tasks:
Step 1: Shut Down the Release 8.0.x Database
Step 2: Back Up the Release 8.0.x Database
Step 3: Edit the COMPATIBLE Parameter in the 8.0.x INITSID.ORA File
Step 4: Install Oracle8 Enterprise Edition Release 8.0.6
C:\> SVRMGR30
SVRMGR> CONNECT INTERNAL/PASSWORD
The message Connected appears if you successfully connected to the database.
SVRMGR> SHUTDOWN
Perform a full offline backup of the database.
Ensure the database is cleanly shutdown before you back up. Ensure you back up the database files in the following list (and any other database files you may have created). Also, back up any scripts you may have created.
|
SYS1SID.ORA, USR1SID.ORA, RBS1SID.ORA, TMP1SID.ORA |
|
|
INITSID.ORA |
|
|
LOG1SID.ORA, LOG2SID.ORA |
|
|
CTL1SID.ORA |
To obtain the list of database files you must back up:
SVRMGR> SPOOL V8DBFILES.LOG
SVRMGR> SELECT MEMBER FROM V$LOGFILE;
SVRMGR> SELECT NAME FROM V$DATAFILE;
SVRMGR> SELECT VALUE FROM V$PARAMETER WHERE NAME = 'control_files';
SVRMGR> SPOOL OFF
See Chapter 13, "Backing Up and Recovering Database Files", Oracle8 Concepts, Oracle8 Backup and Recovery, and Oracle8 Administrator's Guide for information on how to back up a database.
Ensure the COMPATIBLE parameter is set to 8.0.0.0.0 or higher in the release 8.0.x INITSID.ORA file.
If you use the default setting (8.0.0.0.0) or higher, you cannot use new features of releases 8.0.4 and later such as Propagation in Advanced Queuing (AQ) and Improved SCN Generation. To use these new features, set the COMPATIBLE parameter to the following:
COMPATIBLE=8.0.4.0.0
See Appendix C "Version 8 INIT.ORA Changes" of Oracle8 Migration for more information on COMPATIBLE parameter values.
When the Oracle Installation Settings dialog box appears:
The Select Installation Options dialog box appears.
The Select Oracle8 Cartridge dialog box appears.
The Previous Version of Oracle Database dialog box appears indicating that Oracle Installer has detected an earlier version of the database. You are asked if you want to upgrade your Oracle8 database to release 8.0.6 using Oracle Data Migration Assistant.
The Select a Starter Database Configuration dialog box appears.
C:\> NET START ORACLESERVICEORCL
C:\> SET ORACLE_SID=ORCL
C:\> SVRMGR30
SVRMGR> CONNECT INTERNAL/PASSWORD
SVRMGR> STARTUP RESTRICT
SVRMGR> SPOOL UPGRADE.LOG
| To Upgrade... | Run Script1 | Enter at the Server Manager Prompt... |
|---|---|---|
|
8.0.1 |
Not supported |
|
|
8.0.2 to 8.0.6 |
Not supported |
|
|
8.0.3 to 8.0.6 |
U0800030.SQL |
where |
|
8.0.4 to 8.0.6 |
U0800040.SQL |
where |
|
8.0.4S |
Not supported |
|
|
8.0.5 to 8.0.6 |
U0800050.SQL |
where |
|
1
When you run any of these U*.SQL scripts, the CATALOG.SQL and CATPROC.SQL scripts, which create the system catalog views and all the necessary packages for using PL/SQL, are also run. |
Oracle Corporation supplies other scripts with Oracle8 Enterprise Edition that create additional structures you can use in managing your database and creating database applications. These scripts are also located in ORACLE_HOME\RDBMS80\ADMIN. See Oracle8 Reference for a complete list and descriptions of available scripts.
SVRMGR> @%ORACLE_HOME%\RDBMS80\ADMIN\UTLRP.SQL
SVRMGR> SPOOL OFF
Check the spool file UPGRADE.LOG you created in Step 6. and verify that every package and procedure compiled successfully. Correct any problems you find in the file. If you are upgrading from release 8.0.2, also check the UPGRADE2.LOG spool file.
SVRMGR> ALTER SYSTEM DISABLE RESTRICTED SESSION
SVRMGR> SPOOL UTLRESULT.LOGSVRMGR> @%ORACLE_HOME%\RDBMS80\ADMIN\UTLCONST.SQLSVRMGR> SPOOL OFF
A bad date constraint involves invalid date manipulation. An invalid date manipulation is one that implicitly assumes the century in the date, causing problems at the year 2000. The UTLCONST.SQL script runs through all of the check constraints in the database and sets constraints as bad if they include any invalid date manipulation. UTLCONST.SQL selects all the bad constraints at the end. After you run the script, the UTLRESULT.LOG file includes all the constraints that have invalid date constraints. UTLCONST.SQL does not correct bad date constraints, but it does disable them. Either drop the bad constraints or recreate them after you make the necessary changes.
SVRMGR> EXIT
Read the READMEMIG.DOC file located in the ORACLE_HOME\RDBMS80 directory for information on how to downgrade.
Oracle Migration Assistant for Microsoft Access helps you migrate data from a Microsoft Access database to an Oracle8 database. Specifically, Oracle Migration Assistant for Microsoft Access:
Oracle Migration Assistant for Microsoft Access can migrate several types of Microsoft Access databases, including:
Oracle Migration Assistant for Microsoft Access can be used to migrate both 16-bit Access 2.0 databases and 32-bit Microsoft Access 7.0 databases.
To prepare a Microsoft Access database for migration:
To migrate a database using Oracle Migration Assistant for Microsoft Access:
The Oracle Migration Assistant for Microsoft Access welcome window appears:

This section lists known issues and restrictions with Oracle Migration Assistant for Microsoft Access.
|
|
Copyright © 1999 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|