Release 1.0.2.2
A86635-02
Library |
Service |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Portal-to-Go Implementation Guide Release 1.0.2.2 A86635-02 |
|
This document describes how to create and manage Portal-to-Go services. Topics include:
Services enable end users to access the functionality of Portal-to-Go adapters. Services represent the link between the content source and the delivery target. They tie a specific adapter to the logical devices in the Portal-to-Go repository.
Services also define how users access the adapter. They can restrict or grant user access to the adapter's parameters. Services can set default values for a parameter, they can enable users to set a default, or they can hide the parameter from users altogether.
The following repository objects encapsulate and manage Portal-to-Go services:
Master services provide the actual implementation of the service. They specify the adapter used for the service and any service-specific parameters. An alias is a pointer to the service. Aliases are useful for distributing access to a master service among many users and groups. End users can access a master service only if the master service, or an alias to the master service, appears in a service tree they own or that a group they are a member of owns. Aliases can set parameter values that override values set at the master service.
You can manage service objects (master services, aliases, folders, and bookmarks) using the Service Designer. The Service Designer provides a tree view of the Portal-to-Go repository. The repository tree includes a Master Services folder and a Service Trees folder for managing services. You can create service objects in either folder. In most cases, however, you should place folders and master services in the Master Services root folder, and user- and group-owned folders and aliases in the Service Trees root folder.
By mapping an adapter to device transformers, master services link Portal-to-Go content sources to the delivery platforms. Each master service is based on one adapter. A master service creates its own instance of the adapter it uses. Therefore, several services can use the same type of adapter, and each can pass its own service-specific argument values.
Portal-to-Go end users typically invoke a master service by clicking on a menu item from their device. The information returned by the master service can be text, such as a movie review, or an application, such as an airline booking system. While a user request usually invokes a master service, a scheduled job can also invoke a master service.
You use the Create New Master Service form to create a master service in the Portal-to-Go repository. This form enables you to create a minimally configured master service object in the repository. After you complete the form, you must finish configuring the master service using its property panels.
This section describes the Create New Master Service form. "Modifying a Master Service" describes the additional parameters you must configure to create a master service.
To display the Create New Master Service form:
The Create New Master Service form appears.
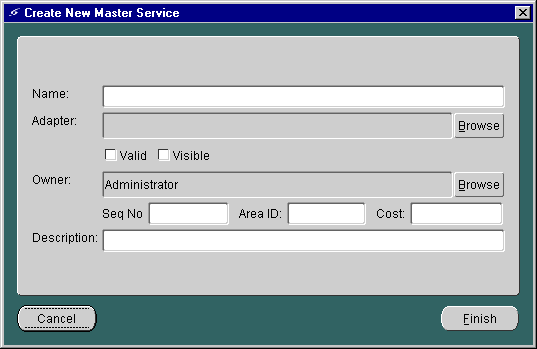
This form allows you to configure a new master service's general parameters. It takes the following parameters:
Click the Finish button to create the master service in the repository. Complete the configuration as follows:
The following section provides more information on the master service forms.
To modify a master service using the Service Designer, click the master service that you want to change. The object's property tabs appear in the right-hand panel of the Service Designer. You can enter new values directly in the parameter fields, then click Apply to save your changes.
Master services have the following property panels:
The General panel contains parameters that identify and describe the master service. It includes fields for the service name, the adapter on which the service is based, and the cost of the service. Typically, you set the properties in this panel using the Create New Master Service form when first creating the master service. For more information on the General properties, see "Creating a Master Service".
The Init Parameters panel shows the initialization parameters for the adapter. These parameters vary depending on the adapter implementation. The Service Designer generates the fields in this panel from the adapter definition for the master service. When Portal-to-Go first invokes the adapter, it passes the values you set in this panel to the adapter.
The following sections describe the initialization panels for master services based on the adapters provided by Portal-to-Go.
For a master service based on the Web Integration adapter, the Init Parameters panel appears as follows:
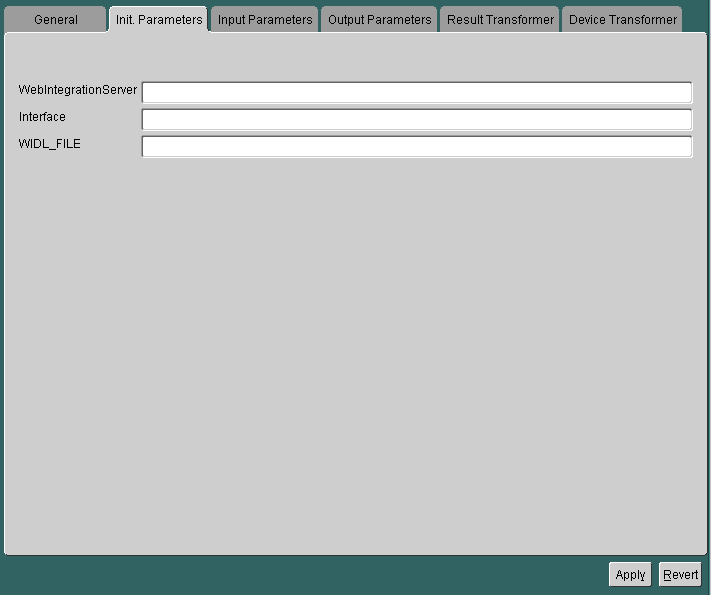
The Init Parameters panel contains the following parameters:
For a master service based on the SQL adapter, the Init Parameters panel appears as follows:
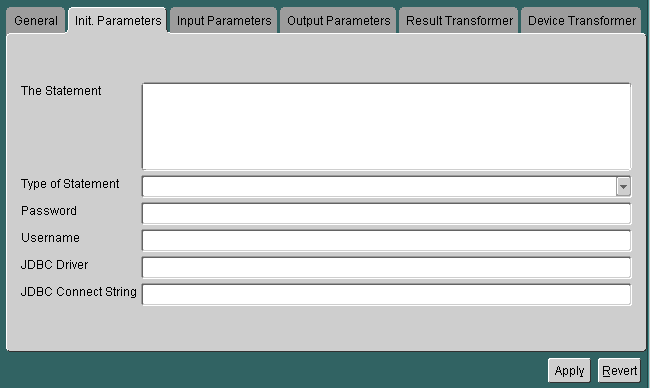
The panel includes the following parameters:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
|
The Statement |
The actual SQL statement that invokes the query, PL/SQL procedure, or stored procedure. Note: The SQL statement should be entered without a semicolon. You can use input variables in the SQL statement. You must indicate a variable in the statement by prefixing the variable with a colon. For example, you can specify an input variable in a PL/SQL statement as follows:
Where |
|
Type of Statement |
The type of SQL statement used by the master service. Allowable values: QUERY: for a select statement. This type of statement returns a Simple Result document. You can use output filtering with QUERY statements. For information on filtering output, see "Filtering Adapter Output" in Chapter 9, "Adapters". PLSQL: to use a PL/SQL procedure. This type of statement returns results to a database buffer. CALL: to run a stored procedure (SQL92 syntax only). This returns either a Simple Result or an Adapter Result element. |
|
Password |
The password of the database user. |
|
Username |
The name of the database user. |
|
JDBC Driver |
The type of JDBC driver used to access the SQL data source. |
|
JDBC Connect String |
The database connect string for the database to access. For example, to access an Oracle database using the thin driver, use the connect string: jdbc:oracle:thin:@domain:port:SID |
For a master service based on the stripper adapter, the Init Parameters panel appears as follows:
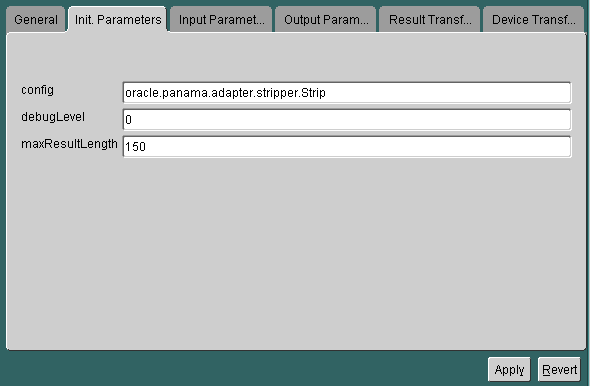
The panel contains the following parameters:
For more information on using the Stripper adapter, see "Extending the Stripper Adapter" in Chapter 9, "Adapters".
There are no Init parameters for this adapter.
For a master service based on the servlet adapter, the Init Parameters panel appears as follows:
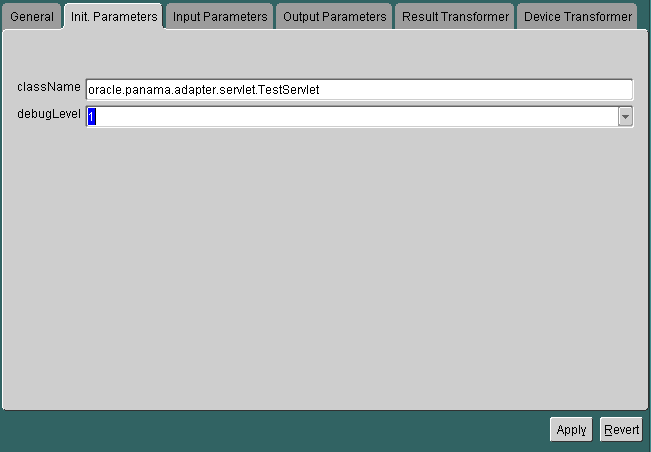
The panel contains the following parameters:
For more information on using the Servlet adapter, see "Creating a Service Using the Servlet Adapter" in this chapter.
The Input Parameters panel displays the input parameters for the adapter. The Service Designer queries the adapter definition to determine the parameters that appear in this panel. The master service passes the input parameter values to the adapter's invoke method every time the adapter executes.
Some parameters rely on user input for values. The values for other parameters, such as name of the WIDL service in the WIDL interface (PAsection), are set by the master service or master service alias. PAsection is an internal parameter, not exposed to the end user. In addition to PAsection, Portal-to-Go provides these input parameters:
You can configure your parameters in the Service Designer. Every Portal-to-Go parameter has the following attributes:
The following figure shows a sample Inputs panel for a Web service.
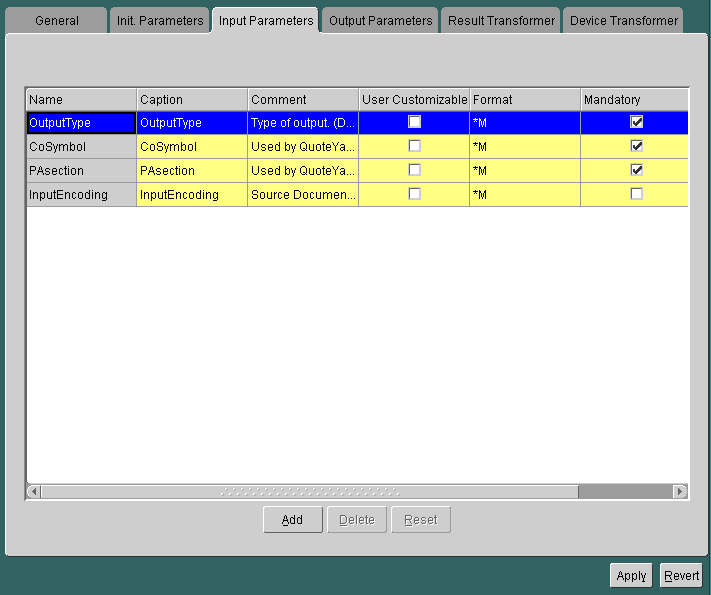
The master service determines the parameters to display in the panel by querying the adapter. Every input parameter defined in the WIDL interface appears in the Inputs panel, including parameters for other WIDL services within the WIDL interface.
In addition to the custom input parameters that you create, Web Integration services provide these parameters:
The OutputType specifies the type of XML output that the adapter should return. You can specify RawResult, to return content in Adapter Result format, or SimpleResult, to return content in Simple Result format. If returning raw result format, you must create a result transformer that converts the result into Simple Result for the device transformer. The result transformer should have the same name as the value you use for the PAsection parameter; that is, it should have the same name as the WIDL service. You use RawResult for chained services.
PAsection is the name of the WIDL service that you want the master service to invoke. A WIDL interface can include more than one WIDL service. Portal-to-Go lists the WIDL service names in a selection list in the value field.
InputEncoding specifies the encoding used to encode the source document. The source document is the URL that was used to create the WIDL file for this service. See Chapter 4, "Walkthroughs", for information on creating a Web service. The default value of this parameter is UTF-8. If the language of the source document is an Asian language, you can change the default encoding to the appropriate multi-byte encoding according to the IANA standards for the particular Asian language that is used in the source document. The InputEncoding parameter enables you to specify or change the encoding. It is part of the multi-byte character support. "National Language Support", in Chapter 7, "Rebranding the Personalization Portal", provides more information about multi-byte character support.
You can configure SQL input parameters just as you can Web service parameters. You specify input parameters in the SQL statement you use to implement the service. For information on creating parameterized SQL services, see "SQL Adapter Init Parameters".
For a master service based on the stripper adapter, the Inputs panel appears as follows:
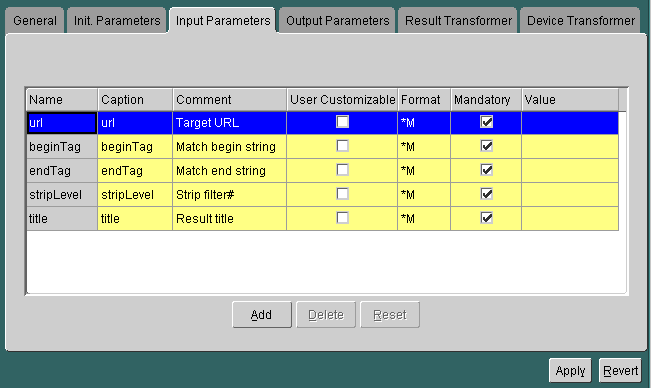
The panel contains the following parameters:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
|
url |
The URL of the source page. If you do not include the protocol in the URL, Portal-to-Go prepends this value with "http://". |
|
beginTag |
A string that matches the start point of the text retrieved from the URL target page. This value is optional. If not specified, the start point is the beginning of the page. |
|
endTag |
A string that matches the end point of the text retrieved from the URL target page. This value is optional. If not specified, the end point is the end of the page. |
|
stripLevel |
The strip level identifies the class used by the stripper adapter to filter the retrieved content. Portal-to-Go provides two levels: You can implement additional strip levels or filters. For more information, see "Extending the Stripper Adapter" in Chapter 9, "Adapters". |
|
title |
An optional title of the result. |
This adapter allows you to retrieve XML documents that are saved on the hard drive of your local machine and that conform to the SimpleResult DTD every time you want to bring up the service. You can also store static pages from the Web and retrieve them with this adapter from the hard drive of your local machine. For a service that is based on the URL adapter, the Input Parameters panel appears as follows:
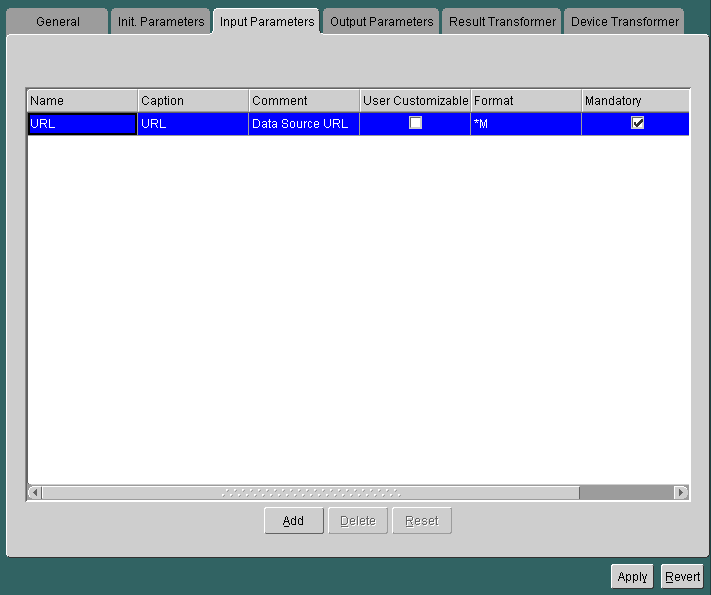
The panel contains the following parameter:
For a service that is based on the Servlet adapter, the Input Parameters panel appears as follows:
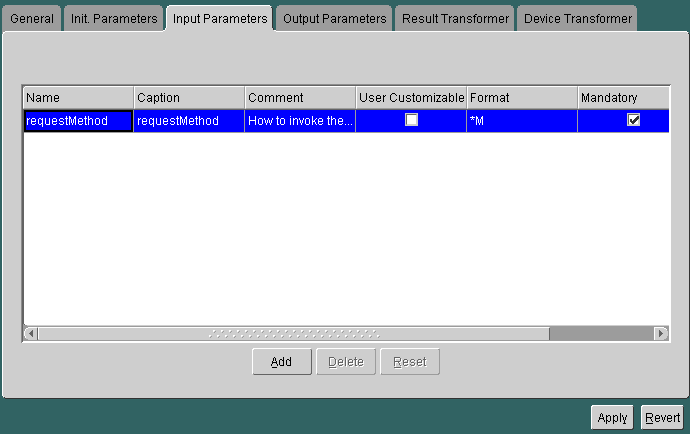
You can also define other input parameters and add them by clicking on the Add button. For more information, see "Creating a Service Using the Servlet Adapter".
The output parameters panel allows you to set captions for service output parameters.
You use the Result Transformer panel to specify a transformer for Portal-to-Go to use to convert Adapter Result content. Portal-to-Go provides two content formats, Adapter Result and Simple Result. Adapter Result is intended to be an intermediary format for passing raw data between services. Device transformers, which convert service content for the target format, cannot convert Adapter Result format. A result transformer must therefore convert the content to Simple Format before it can be processed by a device transformer.
To create a result transformer:
PAsection input parameter.
The Device Transformer panel lists the logical devices in the repository. You can specify a custom transformer to be used with the master service for a logical device. A custom transformer enables you to optimize the presentation of service content for a particular device. Since the transformer is specialized for a particular device and master service, you can associate a custom transformer with only one master service and one logical device.
You can delete a master service in the Service Designer as follows:
When you delete a master service, the Service Designer flags any aliases to the master service.
The Servlet adapter enables you to integrate other applications you might have which are already Java servlets. This provides a convenient way to call them as Portal-to-Go services and make them wirelessly available.
To create a Portal-to-Go service using the Servlet adapter:
Anything else you want to add is an exercise in building Java adapters.
Example:
Here is a Java file and a "make" file for a simple example.
--------------------------------------------------------------------- set JAVA_HOME=D:\Progra~1\jdk122 set CLASSPATH=.;%JAVA_ HOME%\jre\lib\rt.jar;d:\ptg102\Server\panama\server\classes;d:\ptg102\Server\pan ama\server\papz;d:\ptg102\Server\panama\lib\panama_ core.zip;d:\ptg102\Server\panama\lib\server.zip;d:\ptg102\Server\panama\lib\clie nt.zip;d:\ptg102\Server\panama\lib\xmlparserv2.jar;d:\ptg102\Server\panama\lib\c lasses111.zip;d:\ptg102\Server\panama\lib\jndi.jar;d:\ptg102\Server\panama\lib\s ervlet.jar;. %JAVA_HOME%\bin\javac TestServlet.java --------------------------------------------------------------------- package oracle.panama.adapter.servlet; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import javax.servlet.ServletConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import oracle.panama.core.admin.L; public class TestServlet extends HttpServlet { public void init(ServletConfig cfg) throws ServletException { L.n ("servlet initialized"); } public void doDelete (HttpServletRequest input, HttpServletResponse output) throws IOException, ServletException { L.n ("doDelete() invoked"); } public void doGet (HttpServletRequest input, HttpServletResponse output) throws IOException, ServletException { L.n ("doGet() invoked"); PrintWriter p = output.getWriter(); p.println ("<?xml version=\"1.0\">"); p.println ("<SimpleResult>"); p.println ("<SimpleText title=\"ServletAdapter Test\">"); p.println ("<SimpleTextItem title=\"Static text\">Hello World</SimpleTextItem>"); String p1 = input.getParameter ("param1"); String p2 = input.getParameter ("param2"); p.println ("<SimpleTextItem title=\"Parameters\">param1 = \"" + p1 + "\" and param2 = \"" + p2 + "\"</SimpleTextItem>"); p.println ("</SimpleText>"); p.println ("</SimpleResult>"); } public void doOptions (HttpServletRequest input, HttpServletResponse output) throws IOException, ServletException { L.n ("doOptions() invoked"); } public void doPost (HttpServletRequest input, HttpServletResponse output) throws IOException, ServletException { L.n ("doPost() invoked"); } public void doPut (HttpServletRequest input, HttpServletResponse output) throws IOException, ServletException { L.n ("doPut() invoked"); } public void doTrace (HttpServletRequest input, HttpServletResponse output) throws IOException, ServletException { L.n ("dotrace() invoked"); } }
A service tree is a folder you use to organize and distribute access to services. It can contain master services, service aliases, or other folders.
Folders make services accessible to users. When you create a new user, you also create a service tree for that user. Any service that you place in a user's service tree (or user's home), is accessible to the user.
Similarly, when you create a group, you specify the service trees that belong to the group. Any member of the group can access the services in that group's service trees. While a user can have only one private service tree, groups can have many service trees. Different groups can share the same service tree.
If you do not specify an owner when you create a service tree, the tree is public. If you specify an owner, the service tree is private. End users can access any public service tree, but they can only access their own private service trees. They have complete control of their service trees from the Personalization Portal; they can copy services between service trees, rename services, and create folders.
Portal-to-Go does not provide dependency tracking for a private service (a service in a private service tree). If the target service of the private service is no longer valid, an error occurs when a user attempts to submit a request for that service. Portal-to-Go then advises the user to delete the service from the private service tree.
You can create folders in either the Master Services folder or the Service Trees folder of the Portal-to-Go repository tree. To create a folder, you use the Create New Folder form.
To invoke the form:
The Create New Folder form appears as follows:
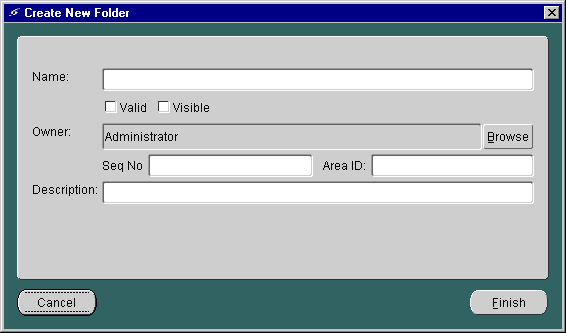
The panel includes the following parameters:
A service alias is a link to a master service, folder, or other alias. Service aliases help you to distribute service access to multiple users or groups. They also enable you to specialize master services, since default parameter values specified by an alias override values set at the master service. This characteristic provides several benefits. One benefit is that it enables you to localize services. For example, suppose you create a service that delivers restaurant information for a city. The adapter takes a single parameter, a location, and returns a list of restaurants in the area. While the master service can specify a more general location, such as the city, you can create aliases that provide a more specific parameter, such as a district within the city. You can then distribute the aliases, as appropriate, to user groups that you assemble based on the users' locations of residence.
To create a service alias:
The first form in the sequence appears as follows:
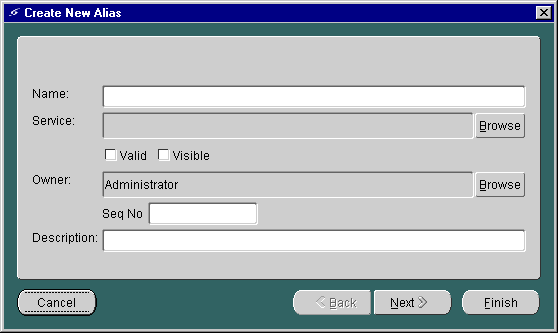
The panel includes the following parameters:
Complete the properties in the form and click Finish to create the alias in the repository. You do not need to complete the second form in the sequence. You can configure the runtime parameters for the alias by modifying the alias properties, just as you would for the master service on which the alias is based. For more information on specifying runtime parameters, see "Input Parameters Panel".
A bookmark is a Portal-to-Go service that points to an external resource. The external resource is typically a Web page that serves content in a format supported by the target device.
Portal-to-Go does not process the content of the bookmark target. As a result, bookmark services are not available to all targeted device, as are other Portal-to-Go services. In most cases, bookmarks are set in the personalization portal by the end user, not in the Service Designer.
To create a bookmark in the Service Designer, you use the Create New Bookmark form. To invoke the form:
The Create New Bookmark form appears:
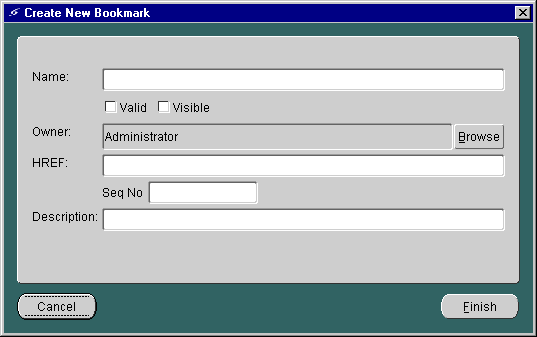
The panel includes the following parameters:
|
|
 Copyright © 2000 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|