|
Oracle® Application Server 10g Concepts
10g (9.0.4) Part No. B10375-01 |
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle® Application Server 10g Concepts
10g (9.0.4) Part No. B10375-01 |
|
|
|
|
This chapter provides an overview of Oracle Application Server Wireless features and benefits. The topics include:
Up until now, traditional software applications have not accounted for the fact that employees are mobile. The time spent walking to and from meetings, warehouses, or customers is wasted time without access to key information. Oracle aims to solve this problem with Oracle Application Server Wireless by delivering the information that users want, on the mobile device they need it, thereby making them more productive and saving your enterprise money.
Oracle Application Server Wireless is a component of the Oracle Application Server that helps enterprises and service providers efficiently build, manage, and maintain wireless and voice applications. OracleAS Wireless makes Web and database applications, such as e-mail, news, and directory services accessible to mobile device users without having to rewrite content for every target platform. It transforms content and applications to any markup language supported by any device, such as HTML, WML, HDML, VoiceXML, VoxML, and SMS. Figure 4-1 shows the flow of information between a wireless client and a database application.
Oracle Application Server Wireless 10g (9.0.4) includes many new features and enhancements, improving the way enterprises and service providers conduct business.
Oracle Application Server Wireless can be split into five component groups:
Multi-Channel Server: The Multi-channel Server detects devices and transforms content and applications to the device.
Foundation Services: The Foundation Services are services to enhance applications and speed development. These are in the form of Java APIs or Web services.
Development Tools: The Development Tools help developers code, test, and debug wireless and voice applications.
Mobile Portal: The Mobile Portal is the end-user wireless portal to access the developed applications and content.
Mobile Applications: The Mobile Applications are out-of-the-box applications to get an enterprise mobile-enabled quickly.
Figure 4-2 shows these five groups with their subcomponents.
At the core of Oracle Application Server Wireless is the Multi-Channel Server, which enables application access through multiple delivery methods, such as SMS, voice access, WAP, and Pocket PCs. The Multi-Channel Server greatly simplifies and reduces the cost of development by acting as an intelligent wireless proxy for mobile applications. The magnitude of mobile devices and networks are relieved from developers’ concerns. Developers can now focus on creating mobile applications for any channel in one, future-proof open standards language. The new Multi-Channel Server extends the existing multi-channel capabilities of previous Oracle Application Server Wireless releases.
Applications written in XHTML are passed through the Multi-Channel Server and translated for any device and network. For example, an XHTML application passed through the Multi-Channel Server is translated to VoiceXML if a phone is accessing the application, and is translated to WML if a WAP phone is accessing the application. The stylesheets used to transcode are maintained and regularly updated by Oracle.
Also new to the Multi-Channel server are Multimedia Adaptation Services. Oracle Application Server Wireless Multimedia Adaptation Services provide device-specific adaptation of images, ringtones, voice grammars, and audio/video streams. Devices support different image formats and have different screen sizes and color depths. As part of the content adaptation performed by OracleAS Wireless in responding to a request, images are dynamically adapted to suit the device. Ringtone adaptation allows for conversion of ringtone data to formats supported by the most popular phones, such as RTTTL, iMelody, and MIDI. The flexible framework for ringtone adaptation allows developers to easily add support for new ringtone formats.
Java 2 Micro Edition (J2ME) provides a lightweight operating system for mobile devices, enabling client-side development using open standards. With the large number of J2ME-enabled phones on the market, vendors need a method for efficiently building, managing, and delivering J2ME applications to the right mobile users. Oracle Application Server Wireless 10g (9.0.4) includes complete, end-to-end support for building J2ME applications and delivering them to mobile devices. OracleAS Wireless J2ME support includes the J2ME Developer’s Kit and the J2ME Provisioning System.
There is a restriction on the complexity of J2ME applications because of the limited computing power of mobile devices. The more complicated the J2ME application is, the less usable the application will be on a mobile device. One way to create compelling J2ME applications is to use Web services. Applications are able to push some of the CPU-intensive logic to the Web services residing on the server side. However, even the call to Web services from J2ME devices is too CPU intensive. Oracle J2ME Developer’s Kit offers the ability to extend Web services to J2ME devices in an optimized manner for mobile devices. Using the J2ME Developer’s Kit, J2ME application (MIDlet) developers can make Web services calls through the Oracle Application Server J2ME proxy server using a client stub. Additionally, MIDlet developers can utilize built-in features optimizing communication, such as request and response caching, if the network is unavailable. The calls can automatically resume when the network connectivity resumes.
OracleAS Wireless streamlines the deployment, management, and delivery of J2ME applications with a provisioning system. The application management Web-based tool allows users to upload J2ME applications for management and secure storage. A byte-code inspector verifies the application for any malicious content. The OracleAS Wireless support for over-the-air (OTA) efficiently delivers applications to target users or devices. Digital rights management adds a digital layer around J2ME applications to support business logic that provides full control over the application. The digital wrapper supports billing strategies and application lifespan control.
Oracle Application Server Wireless 10g (9.0.4) further enhances intelligent messaging with functionality for actionable alerts, message adaptation, and failover delivery control. Also new are multi-media messaging (MMS) features that allow for richer messaging experiences. Existing messaging capabilities have been improved to include more flexible message templates, security to prevent message spoofing, support for message prioritization, and more flexibility in handling volume alerts.
OracleAS Wireless supports multi-media messaging (MMS) for rich mobile messages, including graphics, videos, and audio. MMS messages can be authored natively in SMIL or in open standards XHTML. Messages that are authored in XHTML are automatically adapted for wireless devices by OracleAS Wireless. The power of adaptation allows a message to be written once and automatically optimized for any target device.
Notifications are improved by allowing messages to be sent, and responded to, using the new actionable alerting capabilities, enabling further action from a sent alert. For example, a stock alert can prompt a user to take an action and sell when a target price is hit. Location can now also play a role in alerting. Location-based alerts generate and deliver alert messages based on a mobile user’s current location. For example, a field service coordinator receives an alert when a service engineer is within two miles of a customer with an urgent service request.
Asynchronous applications enable messaging devices, such as SMS and email devices, to access applications. A mobile user can maintain a session with an application via SMS or email. To invoke an application, the user sends a message with the message body containing the name of the application and any inputs. A separate message is sent back, by the application, with the results.
The Oracle Application Server Wireless Development Kit is a small footprint Oracle Application Server Wireless development environment for developing wireless and voice applications. This speeds the development process by giving extra flexibility to fit any development process using any IDE, development tool, Web service, and device simulator. The Wireless Development Kit can be used on any PC or laptop, connected or disconnected, to build and test wireless and voice applications. It is no longer necessary to have a full installation of Oracle Application Server to build and test wireless applications. The Wireless Development Kit supports development for voice, mobile browser, J2ME, and messaging applications.
Oracle offers a version of the Wireless Development Kit specifically for JDeveloper called the JDeveloper Wireless Extension. JDeveloper users can utilize the JDeveloper Wireless Extension for complete wireless development with code templates, wizards, code insight, and automatic deployment to Oracle Application Server.
The Wireless Web Clipping Server allows clipping and scraping of existing Web content to create wireless applications that reuse your existing PC browser-based applications. The Wireless Web Clipping Server is used to create many applications, each of which represents Web content that has been clipped and scraped from one or more Web sites scattered throughout a large organization.
To create a Wireless Web Clipping application, the user simply uses a Web browser to navigate to the Web page containing the desired content, then selects the portion of the page to clip and scrape. The user then sets some attributes, exposes input parameters if the Web clipping uses form-based submission, saves the application, and tests the application. The following are some of the features that the Wireless Web Clipping Server supports:
Navigation through various styles of login mechanisms, including form-based and JavaScript-based submission and HTTP Basic and Digest Authentication with cookie-based session management.
Fuzzy matching of clippings. If a Web clipping gets recorded within the source page or if its character font, size, or style changes, it will still be identified correctly by the Wireless Web Clipping Server and be delivered as the Wireless Web Clipping application content.
Reuse of a wide range of Web content, including basic support of pages written in HTML 4.0.1, JavaScript, applets, and plug-in enabled content, retrieved through HTTP GET and POST functions (form submission).
All Wireless Web Clipping application definitions are stored persistently in the Oracle Application Server infrastructure database. Any secure information, such as passwords, is stored in encrypted form, according to the Data Encryption Standard (DES), using Oracle encryption technology.
Oracle Application Server Wireless Location Services give access to the full Location Based Service (LBS) functionality, such as positioning, geocoding, mapping, driving directions, and business directory lookup in an open standards manner. Any application or generic client can use the included WSDLs to invoke the LBS Web services. In addition, OracleAS Wireless instances can use LBS features more conveniently by using the "Web service" provider proxy. This allows you to switch LBS providers without having to make modifications to the applications using LBS features.
For 10g (9.0.4), the LBS features have been made available through the Web-based tools in addition to being available through APIs. The LBS features allow mobile positioning, to provide the user’s current location, and privacy management, to control when and to whom a mobile user’s location is available. Both mobile positioning and the caching of the location information can be enabled or disabled by the system or by individual users. Users can grant mobile positioning access to other users or groups of users (communities) for a certain date range and for specified time windows.
This release also allows a mobile user/device to send the current location, which is usually provided by a GPS receiver, to OracleAS Wireless. The current location can be subsequently queried through the existing mobile positioning and privacy management framework. Users can also choose to position themselves manually using the location mark feature. A location mark can be either a point location specified by an address or a region specified by a city, state, or even a country.
In the previous release, users could configure multiple content providers for geocoding, mapping, driving directions, and business directory services. A provider was selected based on static ordering or its availability region. This release adds the ability to monitor the performance and reliability of providers and dynamically adjust the selection criteria. It also logs performance statistics that help administrators in managing their systems.
Enterprises can get up and running on wireless or voice applications quickly by deploying the mobile applications that are shipped with Oracle Application Server Wireless. The Mobile Office suite of applications provides wireless browser and voice access to email, calendars, address books, tasks, directories, and files. These applications are fully integrated, enabling the most convenient user experience through such features as directory-based or address book-based recipient selection while composing email messages.
All Mobile Office applications are based on standard protocols, allowing a simple integration into existing environments. Mobile Email gives access from any mobile device to any IMAP or POP3 server, including Microsoft Exchange and Lotus Domino. Mobile Directory connects to any LDAP directory server. And finally, Mobile Calendar integrates with Microsoft Exchange and Lotus Domino servers, and through published interfaces Oracle enables easy customization to support any calendar server.
In order to set up an Oracle Application Server Wireless environment, you must have the following:
An application to provide content
An application server
A Web site (URL)
A network provider (ISP or ASP)
Provisioning and security
A wireless server
A gateway (WAP, SMS)
A wireless network provider
Wireless devices
Wireless subscribers
When users request wireless service, the following steps occur:
The wireless device connects to the Gateway Provider.
The provider provides subscriber, device identification, and user preferences to the Device/Network Adapter.
The Device/Network Adapter invokes the XML Application Framework and HTTP Adapter.
The HTTP Adapter forwards the request to the application.
The HTTP Adapter retrieves the XML result from the application.
The result is forwarded to the client.
Figure 4-3 illustrates this flow in terms of the Oracle Application Server Wireless architecture.
Figure 4-3 Oracle Application Server Wireless Architecture
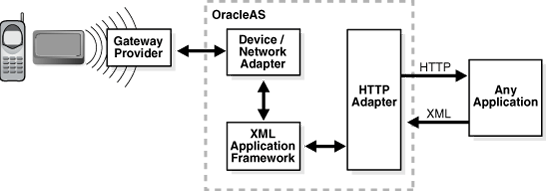
Oracle Application Server Wireless adapters pass application content to the core for processing. The adapter retrieves content from a wide variety of sources, including existing Web sites, databases, existing applications, and legacy systems, and converts the content into Mobile XML.
Each adapter can securely access content from any source, depending on the output of the source. For example, the HTTP Adapter can access content from any source that outputs XML. To render this content to a device, a developer points the HTTP Adapter to the application with a URL. The adapter converts the content to Mobile XML, the passes it to OracleAS Wireless transformers that processes the Mobile XML and deliver the result of the query to the wireless device.
Oracle Application Server Wireless transformers complete the conversion of application content from the original format to the target format. Result transformers convert the Mobile XML documents created by the adapters into Simple Result format. Device transformers then convert the Simple Result documents to the markup language appropriate for the requesting wireless device. Figure 4-4 illustrates this conversion process.
Figure 4-4 Oracle Application Server Wireless - Adapters and Transformers
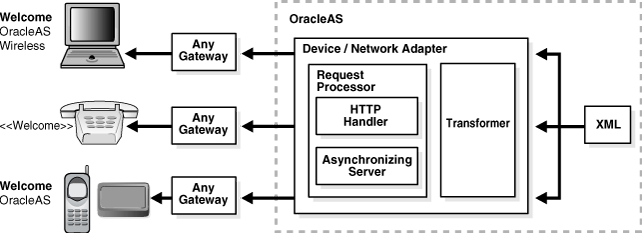
The Device/Network Adapter automatically transforms and optimizes the application content for any wireless device and network. It supports the following mobile technologies:
2-way pagers for asynchronous services (SMTP/SMS)
WAP devices
Voice for access through regular phone lines
PDA devices
OracleAS Wireless provides three types of transformers:
Generic service transformers: These are languages such as WML. Generic service transformers convert the Mobile XML to a generic WML format that works on any WAP-compliant wireless phone.
Device-specific transformers: These are optimized for a specific device. For example, instead of using the generic WML transformer, you can use a device-specific transformer that exploits the device characteristics of a specific phone. The Wireless initial repository includes transformers for several target formats, including CHTML, HDML, MML, VoiceXML, and VoxML.
Custom transformers: You can create custom transformers to target new device platforms and optimize content presentation for specific devices. Wireless publishes device transformation rule files so that anyone can create support for any type of device and markup language.