|
Siebel Field Service Guide > Scheduling and Dispatch > Optimization Engine >
Contract Scheduling
Contract Scheduling is a feature of the Optimizer that is designed for rapid scheduling of service appointments while maintaining the critical Optimizer requirements: enforcement of contractual deadlines and use of constraints when searching for solutions. Companies with the following needs may use Contract Scheduling:
- Same-day break/fix calls are a higher percentage of service calls.
- Service contracts specify penalties for failing to meet response times (for example, free labor or free parts).
- A large number of constraints must be respected.
Run Contract Scheduling from three locations in Field Service:
- Insert Activity button in the Dispatch Board screen > Unscheduled Activities view. This sends a request to either the ABS or the Optimizer to schedule an appointment or insert the selected activity into the optimized schedule, depending on times relative to the horizons.
- Contract Schedule button in the Activities screen > Schedule view. This sends a request for scheduling the selected activity.
- Load button in the Administration - Scheduling screen > Service Regions view > Activities subview. This is similar to the Insert Activity button in the Dispatch Board screen.
Insert Activity Button
The Insert Activity button obtains, for a selected activity, either a confirmed appointment from the ABS or it runs the Optimizer to schedule the activity. The Insert Activity button is similar to the Contract Schedule button in the Activities screen > Schedule view. For more information, see Contract Scheduling. Before using this button, make sure the following conditions are met:
- The service region is set in the Dispatch Board > Gantt Chart.
- The activity is not repeating.
- If the Lock Schedule flag is set (TRUE), then the Planned Start and Planned End values are not null.
- If the Lock Assignment flag is set (TRUE), then the activity assignee is not null.
The choice of sending the Insert Activity request to the ABS or Optimizer depends on the Earliest Start and the Latest Start values. These values determine whether the activity falls within the ABS or the Optimizer horizon:
- If the Latest Start value is null, sends the request to the ABS.
- If the Latest Start value is in the Glued period, does not insert the activity, but returns an error message.
- If the Latest Start value is less than the ABS start, sends the request to the Optimizer.
Contract Schedule Button
The Contract Schedule button has the same function as the Insert Activity button. Load Button
The Load button for activities is intended for synchronizing data in the cache if there have been manual changes to an activity. Before using the Load command, make sure the following conditions are met:
- The activity is not repeating.
- If Lock Schedule is set, then there are values for Planned Start and Planned End.
- If Lock Assignment is set, then there is an employee assigned to the activity.
The choice of sending the activity to the ABS or the Optimizer cache depends on these conditions:
- If Planned Start and Planned End are specified, then the choice of the ABS or Optimizer depends on matching these values to the dates for either the ABS or the Optimizer horizon.
- If Planned Start and Planned End are not specified, then the values for Earliest Start and Earliest End are used. If these values fall within the Optimizer horizon, then the activity goes to the Optimizer cache.
- If neither of these conditions succeeds, an error message is returned.
Cost Function
The cost function is the sum of factors that drive the optimization of a schedule. For each activity in the schedule, the Optimization Engine minimizes the value of the cost function while optimizing the schedule. The cost function indirectly calculates the monetary cost of carrying out a schedule. There is only one cost function for each service region. However, many service regions can use the same cost function. The cost function is the sum of the following factors, shown in Table 39:
Table 39. Factors in the Optimizer Cost Function
|
Calculation of the Factor |
Constraint Violation |
|
|
This is the sum of Rule Violation Costs for each soft constraint violated. A violation is proportional to the degree of the violation. The units for the amount of the violation are the same as defined for the constraint. Time units are in hours; all other cases use the activity. |
FSE Overtime |
Where, 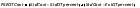 |
Tardiness |
|
Task Exclusion Penalty |
|
|
Task priority allows higher priority tasks to take precedence over low priority ones. This is important when there are not enough resources to schedule all activities. The Task Priority term uses the numeric value from the Order column in the Administration - Data screen > List of Values view (see Applications Administration Guide). This is the value that also appears in the Activities screen > More Info view, Priority field. Task Exclusion Penalty and Weight cannot be zero. If they are zero, no activities are scheduled. |
Travel Distance |
|
For all weights in the cost function, start with values of one (which approximate the real cost of scheduling an activity), then change these values as needed.
|